Forecasting Stocks: A Comprehensive Guide to Predicting Market Trends
In the dynamic world of finance, the ability to accurately forecast stocks is a highly sought-after skill. Whether you’re an individual investor or a seasoned portfolio manager, understanding the methods and techniques used to predict future stock prices can significantly impact your investment decisions. This article provides a comprehensive overview of stock forecasting, exploring various approaches, their strengths and weaknesses, and the factors that influence their accuracy.
Understanding the Basics of Stock Forecasting
Forecasting stocks involves analyzing historical data, current market conditions, and various economic indicators to predict future stock prices. It’s not an exact science, and no method guarantees perfect accuracy due to the inherent volatility and complexity of the stock market. However, by understanding the underlying principles and employing appropriate techniques, investors can make more informed decisions and manage risk effectively.
Key Concepts in Stock Forecasting
- Technical Analysis: This approach focuses on analyzing historical price and volume data to identify patterns and trends that may indicate future price movements.
- Fundamental Analysis: This method involves evaluating a company’s financial health, industry position, and overall economic environment to determine its intrinsic value.
- Quantitative Analysis: This approach uses mathematical and statistical models to identify investment opportunities and predict stock prices.
- Sentiment Analysis: This involves gauging market sentiment and investor psychology to predict short-term price fluctuations.
Technical Analysis: Charting the Course of Stocks
Technical analysis is a popular method for forecasting stocks, particularly among short-term traders. It relies on the premise that historical price and volume data can provide valuable insights into future price movements. Technical analysts use a variety of charts, indicators, and patterns to identify potential buying and selling opportunities.
Common Technical Indicators
- Moving Averages: These smooth out price data over a specific period to identify trends.
- Relative Strength Index (RSI): This measures the magnitude of recent price changes to evaluate overbought or oversold conditions.
- Moving Average Convergence Divergence (MACD): This identifies potential trend changes by comparing two moving averages.
- Fibonacci Retracements: These use Fibonacci ratios to identify potential support and resistance levels.
Limitations of Technical Analysis
While technical analysis can be a useful tool for forecasting stocks, it’s important to recognize its limitations. It is subjective and relies heavily on interpretation, which can lead to different conclusions among analysts. Additionally, technical analysis may not be effective in predicting long-term price movements or when significant fundamental changes occur.
Fundamental Analysis: Evaluating Intrinsic Value
Fundamental analysis is a method for forecasting stocks that focuses on evaluating a company’s intrinsic value. This involves analyzing its financial statements, industry position, competitive landscape, and overall economic environment. The goal is to determine whether a stock is undervalued or overvalued relative to its true worth.
Key Financial Metrics
- Earnings Per Share (EPS): This measures a company’s profitability on a per-share basis.
- Price-to-Earnings Ratio (P/E Ratio): This compares a company’s stock price to its earnings per share.
- Debt-to-Equity Ratio: This measures a company’s leverage and financial risk.
- Return on Equity (ROE): This measures a company’s profitability relative to its shareholders’ equity.
The Importance of Economic Factors
In addition to company-specific factors, fundamental analysis also considers the broader economic environment. Factors such as interest rates, inflation, and economic growth can significantly impact a company’s performance and stock price. Analyzing these macroeconomic trends is crucial for accurate stock forecasting.
Limitations of Fundamental Analysis
Fundamental analysis can be time-consuming and requires a deep understanding of financial statements and economic principles. It also relies on assumptions and estimates, which can be subject to error. Furthermore, fundamental analysis may not be effective in predicting short-term price movements, as market sentiment and other factors can influence stock prices in the short run.
Quantitative Analysis: Leveraging Statistical Models
Quantitative analysis uses mathematical and statistical models to identify investment opportunities and forecast stocks. This approach is often used by hedge funds and institutional investors who have access to sophisticated data and analytical tools. Quantitative analysts develop algorithms that can analyze vast amounts of data and identify patterns that may not be apparent to human analysts.
Common Quantitative Models
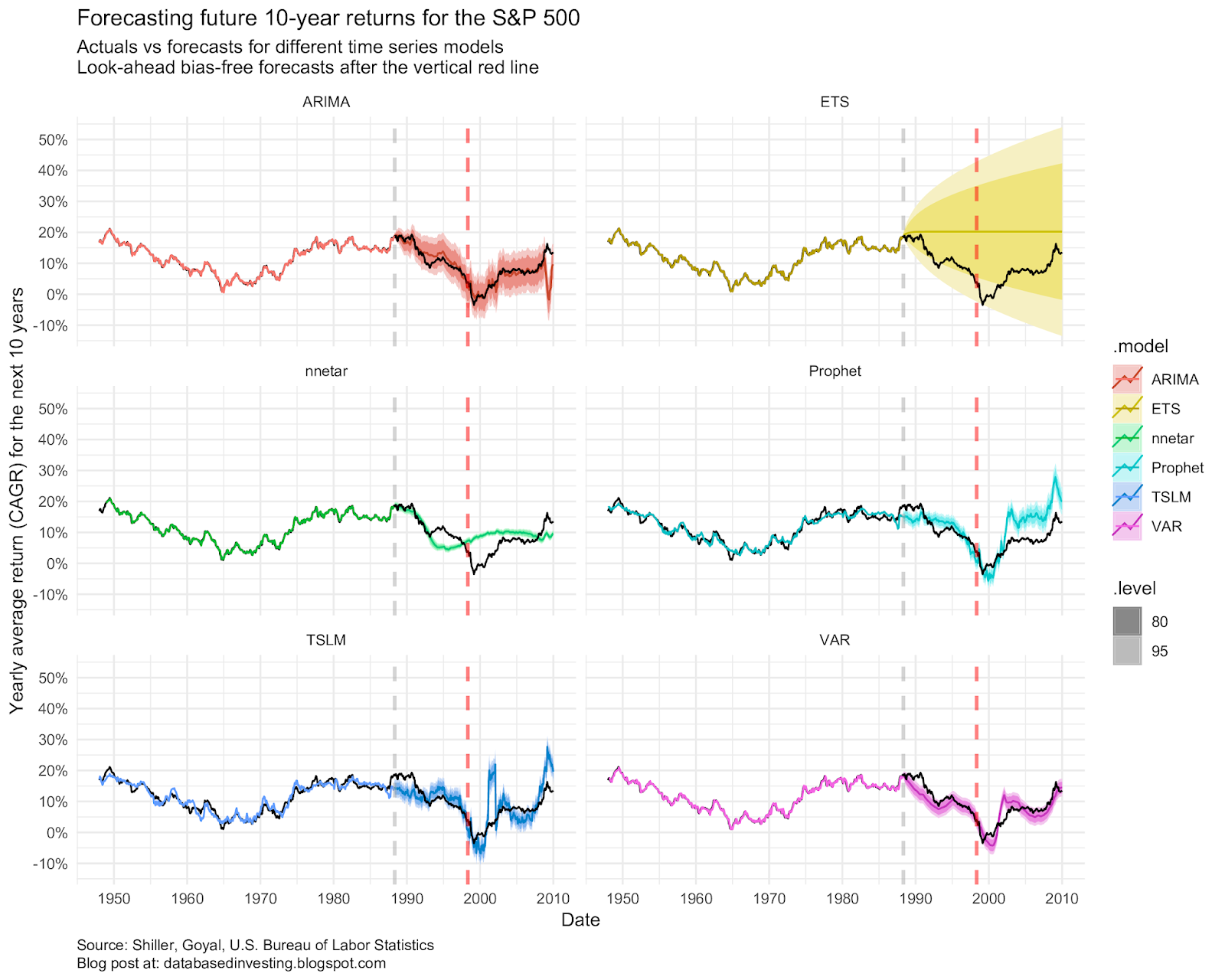
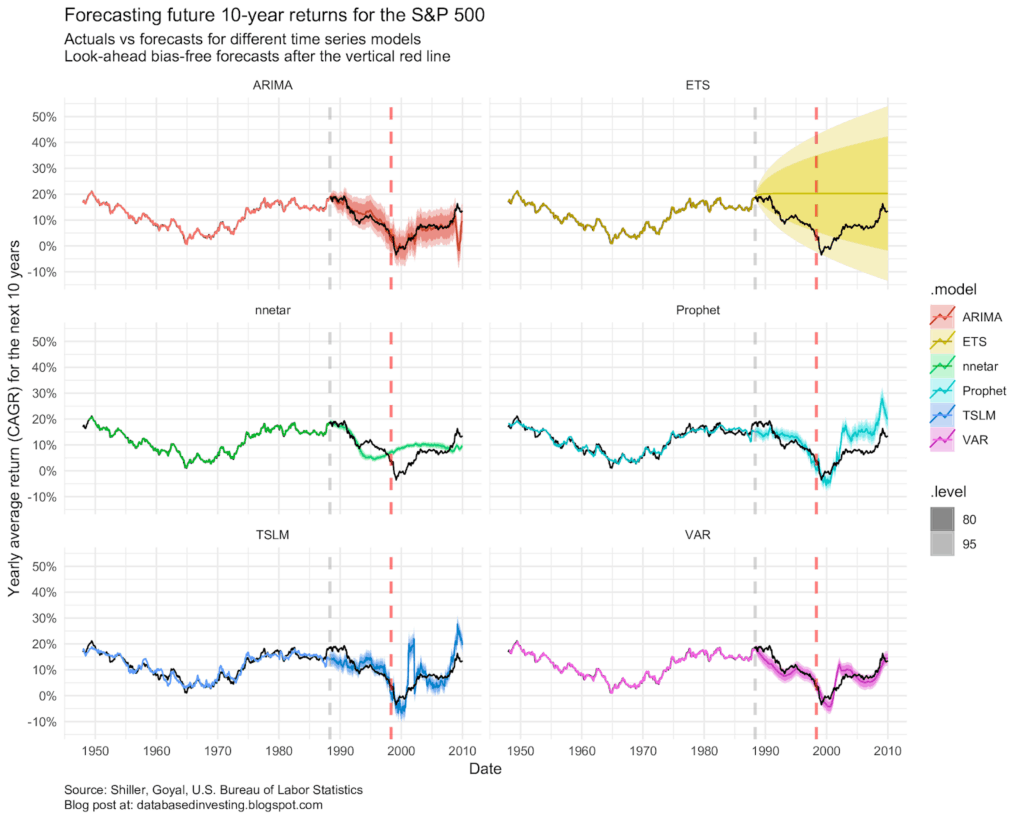
- Time Series Analysis: This uses historical data to identify patterns and trends that can be used to predict future values.
- Regression Analysis: This examines the relationship between a dependent variable (e.g., stock price) and one or more independent variables (e.g., economic indicators).
- Machine Learning: This uses algorithms that can learn from data and improve their predictive accuracy over time.
The Role of Data in Quantitative Analysis
Data is the lifeblood of quantitative analysis. Quantitative analysts rely on a wide range of data sources, including financial statements, market data, economic indicators, and alternative data sources such as social media sentiment. The quality and accuracy of the data are critical for the success of quantitative models.
Limitations of Quantitative Analysis
Quantitative analysis can be complex and requires specialized skills in mathematics, statistics, and computer programming. It also relies on historical data, which may not be representative of future conditions. Additionally, quantitative models can be over-optimized to fit historical data, leading to poor performance in real-world trading.
Sentiment Analysis: Gauging Market Psychology
Sentiment analysis involves gauging market sentiment and investor psychology to predict short-term price fluctuations. This approach recognizes that stock prices are influenced not only by fundamental and technical factors but also by the emotions and biases of investors. Sentiment analysts use a variety of tools and techniques to measure market sentiment, including news articles, social media posts, and investor surveys.
Sources of Sentiment Data
- News Articles: Analyzing the tone and content of news articles can provide insights into market sentiment.
- Social Media: Monitoring social media platforms for mentions of companies and stocks can reveal investor sentiment.
- Investor Surveys: Surveys of investors can provide a direct measure of their sentiment and expectations.
Interpreting Sentiment Data
Interpreting sentiment data can be challenging, as it is often noisy and contradictory. Sentiment analysts use a variety of techniques to filter out the noise and identify meaningful signals. They may also combine sentiment data with other types of data, such as technical and fundamental data, to improve their stock forecasting accuracy.
Limitations of Sentiment Analysis
Sentiment analysis is inherently subjective and can be influenced by biases and emotions. It is also difficult to quantify and may not be reliable in predicting long-term price movements. However, sentiment analysis can be a valuable tool for short-term traders who are looking to capitalize on market fluctuations.
Factors Affecting Stock Forecasting Accuracy
The accuracy of stock forecasting depends on a variety of factors, including the method used, the quality of the data, and the overall market conditions. No method guarantees perfect accuracy, and investors should be aware of the limitations of each approach.
Market Volatility
Market volatility can significantly impact the accuracy of stock forecasting. In highly volatile markets, stock prices can fluctuate rapidly and unpredictably, making it difficult to identify trends and patterns. During periods of high volatility, investors should be cautious and avoid making hasty decisions.
Economic Events
Economic events, such as interest rate changes, inflation reports, and geopolitical events, can also impact stock prices. These events can create uncertainty and volatility in the market, making it difficult to predict future price movements. Investors should stay informed about economic events and their potential impact on their investments.
Company-Specific News
Company-specific news, such as earnings announcements, product launches, and management changes, can also affect stock prices. Positive news can boost investor confidence and drive up stock prices, while negative news can have the opposite effect. Investors should carefully monitor company-specific news and its potential impact on their investments.
Best Practices for Stock Forecasting
While there is no foolproof method for forecasting stocks, there are several best practices that can improve your chances of success.
- Diversify your approach: Don’t rely on a single method for forecasting stocks. Use a combination of technical, fundamental, quantitative, and sentiment analysis to get a more comprehensive view of the market.
- Stay informed: Keep up-to-date on market news, economic events, and company-specific developments.
- Manage risk: Don’t invest more than you can afford to lose. Use stop-loss orders to limit your potential losses.
- Be patient: Investing is a long-term game. Don’t expect to get rich quick.
- Continuously learn: The stock market is constantly evolving. Stay up-to-date on the latest trends and techniques.
Conclusion: Navigating the Complex World of Stock Forecasting
Forecasting stocks is a complex and challenging endeavor, but it can be a rewarding one for those who are willing to put in the time and effort. By understanding the various methods and techniques used to predict future stock prices, investors can make more informed decisions and manage risk effectively. Remember that no method guarantees perfect accuracy, and it’s important to stay informed, manage risk, and continuously learn to navigate the ever-changing world of the stock market. [See also: Stock Market Analysis Techniques] Understanding the nuances of forecasting stocks can lead to better investment outcomes. Always remember that forecasting stocks is not about predicting the future with certainty, but about making informed decisions based on the available data and analysis. The ability to forecast stocks, even with a degree of uncertainty, is a valuable asset in the financial world. The process of forecasting stocks requires diligence, continuous learning, and a healthy dose of skepticism. Many investors seek to forecast stocks to improve their portfolio performance. Ultimately, the goal of forecasting stocks is to increase the probability of making profitable investment decisions. The key to successfully forecast stocks lies in understanding the strengths and weaknesses of different forecasting methods. Investors often use various tools to forecast stocks and manage their investments. Effective forecasting stocks combines both art and science, requiring both analytical skills and market intuition. To effectively forecast stocks, it’s crucial to stay updated with the latest market trends and economic indicators. Successful investors often rely on multiple strategies to forecast stocks and mitigate risk. The ability to forecast stocks accurately can significantly enhance investment returns and financial security. Understanding the dynamics of forecasting stocks is essential for anyone looking to succeed in the stock market.