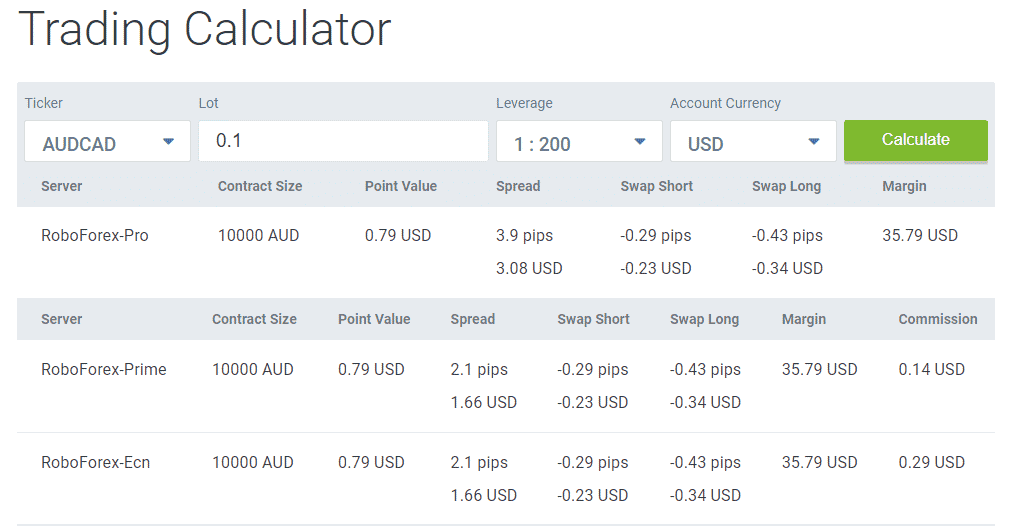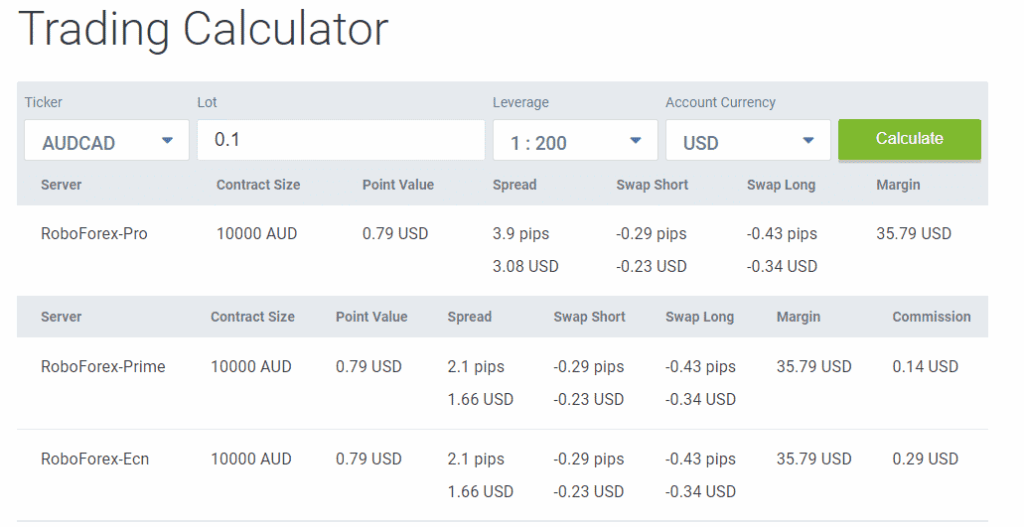
Leverage Calculator: Understanding and Utilizing Financial Leverage
In the world of finance, leverage is a powerful tool that can amplify both profits and losses. Understanding how to calculate and effectively utilize leverage is crucial for investors, traders, and businesses alike. A leverage calculator is an essential instrument for assessing the potential impact of leverage on your investments and financial decisions. This article provides a comprehensive overview of leverage, its calculation, and how a leverage calculator can be used to make informed choices.
What is Leverage?
Leverage refers to the use of borrowed capital to increase the potential return of an investment. It’s essentially using someone else’s money to amplify your gains. While this can lead to significant profits, it also magnifies the potential for losses. Common forms of leverage include margin trading, loans, and debt financing.
For instance, in margin trading, an investor borrows funds from a broker to increase the size of their trading position. In corporate finance, a company might use debt to finance expansion projects, hoping that the returns from the project exceed the cost of the debt.
Why Use a Leverage Calculator?
A leverage calculator is a tool that helps you determine the financial impact of using leverage. It allows you to input different scenarios and see how leverage affects your potential profits and losses. This is particularly useful for:
- Risk Management: Understanding the potential downside of leverage is crucial for managing risk. A leverage calculator helps you assess how much you could lose if your investment doesn’t perform as expected.
- Decision Making: By comparing different leverage scenarios, you can make more informed decisions about how much leverage to use.
- Financial Planning: Businesses can use a leverage calculator to evaluate the impact of debt financing on their financial statements and overall profitability.
How a Leverage Calculator Works
A typical leverage calculator requires several inputs to provide an accurate assessment. These inputs usually include:
- Investment Amount: The total amount you plan to invest.
- Leverage Ratio: The ratio of borrowed funds to your own capital. For example, a leverage ratio of 2:1 means you are borrowing twice the amount of your own investment.
- Interest Rate: The interest rate on the borrowed funds.
- Expected Return: The anticipated return on your investment.
Based on these inputs, the calculator will provide outputs such as:
- Total Investment Value: The total value of your investment, including the borrowed funds.
- Interest Paid: The total interest paid on the borrowed funds.
- Net Return: The return on your investment after deducting interest payments.
- Return on Equity: The return on your own capital, taking into account the leverage used.
Example of Using a Leverage Calculator
Let’s say you want to invest $10,000 in a stock, and you’re considering using leverage with a ratio of 2:1. The interest rate on the borrowed funds is 5%, and you expect a return of 10% on your investment.
Here’s how you would use a leverage calculator:
- Investment Amount: $10,000
- Leverage Ratio: 2:1
- Interest Rate: 5%
- Expected Return: 10%
The leverage calculator would then provide the following results:
- Total Investment Value: $30,000 (Your $10,000 + $20,000 borrowed)
- Interest Paid: $1,000 (5% of $20,000)
- Gross Return: $3,000 (10% of $30,000)
- Net Return: $2,000 ($3,000 – $1,000)
- Return on Equity: 20% ($2,000 / $10,000)
In this scenario, using leverage has significantly increased your return on equity from 10% (without leverage) to 20%. However, it’s important to remember that if the investment loses value, your losses would also be amplified.
Benefits of Using Financial Leverage
When used wisely, financial leverage can offer several benefits:
- Increased Returns: As demonstrated in the example, leverage can amplify your returns on investment.
- Access to Larger Investments: Leverage allows you to control a larger asset base with a smaller amount of capital.
- Tax Benefits: In some cases, interest payments on borrowed funds may be tax-deductible, reducing the overall cost of leverage.
Risks of Using Financial Leverage
Despite its potential benefits, leverage also carries significant risks:
- Magnified Losses: Just as leverage can amplify gains, it can also magnify losses. If your investment performs poorly, you could lose more than your initial investment.
- Interest Costs: Borrowed funds come with interest costs, which can eat into your profits and increase your overall risk.
- Margin Calls: In margin trading, if your account value falls below a certain level, your broker may issue a margin call, requiring you to deposit additional funds to cover your losses.
- Increased Financial Stress: Managing leveraged positions can be stressful, especially during periods of market volatility.
Types of Leverage
Leverage can take many forms, depending on the context:
- Margin Trading: Borrowing funds from a broker to trade stocks, options, or other securities.
- Real Estate: Using a mortgage to finance the purchase of a property.
- Corporate Debt: Companies borrowing money to finance operations, expansions, or acquisitions.
- Derivatives: Using financial instruments like options and futures to gain leveraged exposure to an underlying asset.
Leverage Ratios in Corporate Finance
In corporate finance, leverage ratios are used to assess a company’s level of debt relative to its equity or assets. Common leverage ratios include:
- Debt-to-Equity Ratio: Measures the amount of debt a company uses to finance its assets relative to the value of shareholders’ equity.
- Debt-to-Asset Ratio: Measures the proportion of a company’s assets that are financed by debt.
- Interest Coverage Ratio: Measures a company’s ability to pay interest expenses from its operating income.
These ratios provide insights into a company’s financial risk and its ability to meet its debt obligations. A high leverage ratio may indicate that a company is highly indebted and faces a greater risk of financial distress.
Tips for Using Leverage Wisely
If you decide to use leverage, it’s important to do so responsibly and with a clear understanding of the risks involved. Here are some tips for using leverage wisely:
- Understand the Risks: Before using leverage, make sure you fully understand the potential downsides and how much you could lose.
- Start Small: Begin with a small amount of leverage and gradually increase it as you become more comfortable.
- Use Stop-Loss Orders: Place stop-loss orders to limit your potential losses if your investment performs poorly.
- Monitor Your Positions: Regularly monitor your leveraged positions and be prepared to take action if the market moves against you.
- Diversify Your Portfolio: Don’t put all your eggs in one basket. Diversify your portfolio to reduce your overall risk.
- Use a Leverage Calculator: Use a leverage calculator to analyze different scenarios and understand the potential impact of leverage on your investments.
Leverage in Different Markets
The availability and regulations surrounding leverage vary across different markets. For example:
- Forex Market: The foreign exchange (forex) market typically offers high leverage ratios, sometimes as high as 50:1 or even 100:1. This allows traders to control large positions with relatively small amounts of capital.
- Stock Market: Leverage in the stock market is generally more limited, with margin requirements typically around 50%.
- Real Estate Market: The real estate market relies heavily on leverage in the form of mortgages, which allow buyers to purchase properties with a relatively small down payment.
Understanding the leverage options and regulations in different markets is crucial for making informed investment decisions. [See also: Margin Trading Strategies]
The Future of Leverage
As financial markets evolve, the use of leverage is likely to continue to play a significant role. Technological advancements and regulatory changes will shape the future of leverage, creating new opportunities and challenges for investors and businesses. It’s essential to stay informed about these developments and adapt your strategies accordingly.
Conclusion
Leverage can be a powerful tool for increasing returns, but it also carries significant risks. A leverage calculator is an invaluable resource for understanding and managing these risks. By using a leverage calculator to analyze different scenarios, you can make more informed decisions about how much leverage to use and ultimately improve your financial outcomes. Remember to always use leverage responsibly and with a clear understanding of the potential downsides.