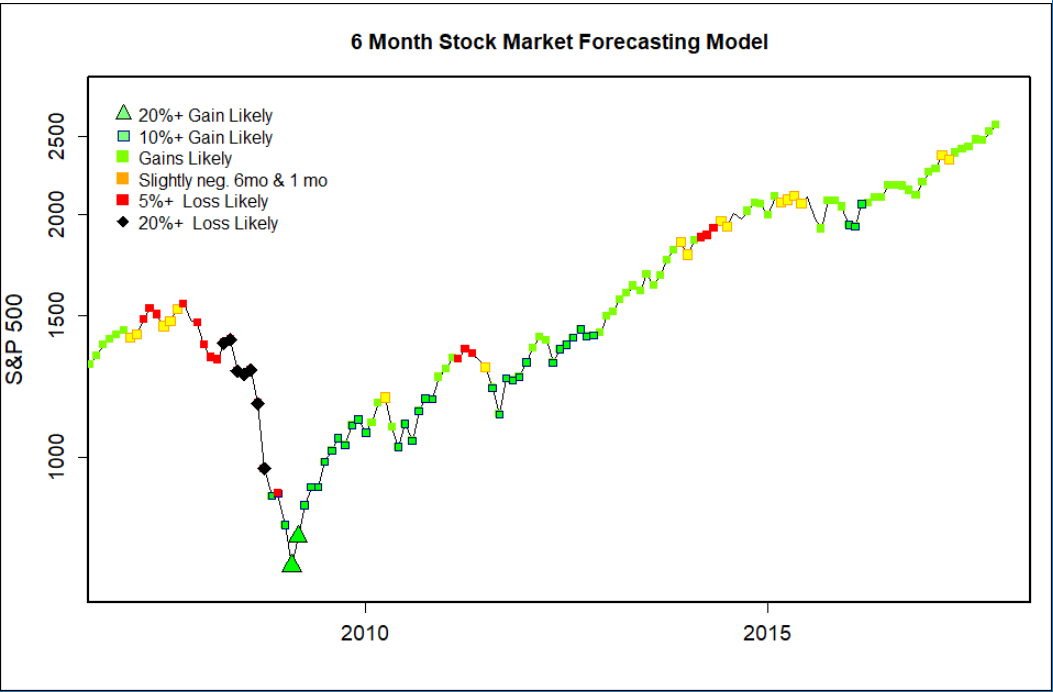
Forecasting Stocks: Navigating the Volatile World of Stock Market Predictions
The allure of predicting the future, particularly in the realm of finance, is undeniable. Forecasting stocks, with the promise of substantial returns, has captivated investors for generations. But what does it really mean to forecast stocks, and how reliable are these predictions? This article delves into the complexities of stock market forecasting, exploring the methodologies, challenges, and the inherent uncertainties involved.
Understanding Stock Market Forecasting
Forecasting stocks involves using various analytical techniques to predict the future price movements of stocks or a stock market index. These techniques can range from fundamental analysis, which focuses on a company’s financial health and industry trends, to technical analysis, which examines historical price and volume data to identify patterns and potential trading opportunities. Quantitative analysis, employing mathematical and statistical models, also plays a significant role.
Fundamental Analysis
Fundamental analysis is rooted in the belief that a stock’s intrinsic value can be determined by examining a company’s financial statements, industry position, and overall economic outlook. Analysts scrutinize factors such as revenue growth, profitability, debt levels, and management effectiveness to assess whether a stock is undervalued or overvalued. Forecasting stocks using this approach often involves projecting future earnings and cash flows to estimate the company’s fair value.
Technical Analysis
Technical analysts, on the other hand, believe that all relevant information is already reflected in a stock’s price and trading volume. They use charts and indicators to identify trends, patterns, and potential turning points in the market. Common technical indicators include moving averages, relative strength index (RSI), and Fibonacci retracements. While fundamental analysis focuses on the ‘why’ behind price movements, technical analysis is more concerned with the ‘when’ and ‘how’. Forecasting stocks through technical analysis is about identifying opportunities based on historical data and patterns.
Quantitative Analysis
Quantitative analysis employs mathematical and statistical models to identify investment opportunities and forecast stocks. These models can range from simple regression analysis to complex algorithms that incorporate various economic and financial variables. Quantitative analysts often use computers to process large amounts of data and identify patterns that might be missed by human analysts. This approach relies heavily on data and statistical rigor to generate predictions.
The Challenges of Forecasting Stocks
Despite the sophisticated tools and techniques available, forecasting stocks remains a notoriously difficult endeavor. The stock market is influenced by a multitude of factors, many of which are unpredictable. Economic events, geopolitical tensions, investor sentiment, and even unforeseen events like natural disasters can all significantly impact stock prices. The inherent complexity and randomness of the market make accurate forecasting a constant challenge.
Market Efficiency
The efficient market hypothesis (EMH) posits that stock prices fully reflect all available information. If the EMH holds true, it would be impossible to consistently outperform the market through forecasting stocks, as any new information would be immediately incorporated into prices. While the EMH has been debated and challenged, it highlights the difficulty of gaining an informational edge in the market.
Behavioral Finance
Behavioral finance recognizes that human psychology plays a significant role in investment decisions. Investors are often driven by emotions such as fear and greed, which can lead to irrational behavior and market inefficiencies. These behavioral biases can make it difficult to predict how investors will react to certain events, further complicating the process of forecasting stocks. [See also: Understanding Market Sentiment]
Data Limitations
Even with access to vast amounts of data, analysts are limited by the quality and completeness of the information available. Financial statements can be subject to accounting manipulations, and economic data may be revised or inaccurate. Furthermore, historical data may not be a reliable predictor of future performance, especially in rapidly changing industries. The limitations of data can significantly impact the accuracy of forecasts stocks.
The Role of Technology in Stock Forecasting
Technology has revolutionized the field of stock forecasting, providing analysts with powerful tools for data analysis, modeling, and prediction. Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) are increasingly being used to identify patterns and relationships in vast datasets that would be impossible for humans to detect. These technologies can also be used to automate trading strategies and manage risk.
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
AI and ML algorithms can analyze vast amounts of financial data, news articles, and social media sentiment to identify potential trading opportunities and forecast stocks. These algorithms can learn from past data and adapt to changing market conditions, making them potentially more accurate than traditional forecasting methods. However, it’s important to note that AI and ML models are only as good as the data they are trained on, and they can still be susceptible to biases and errors. [See also: AI-Powered Stock Trading]
Algorithmic Trading
Algorithmic trading involves using computer programs to execute trades based on predefined rules and parameters. These algorithms can be used to automate trading strategies, manage risk, and take advantage of short-term market inefficiencies. Algorithmic trading has become increasingly prevalent in the stock market, accounting for a significant portion of trading volume. While algorithmic trading can be efficient and cost-effective, it can also contribute to market volatility and flash crashes.
Using Stock Forecasts Wisely
While forecasting stocks can be a valuable tool for investors, it’s important to use forecasts wisely and understand their limitations. No forecasting method is perfect, and all forecasts are subject to error. Investors should consider multiple sources of information and develop their own independent analysis before making investment decisions.
Diversification
Diversification is a key risk management strategy that involves spreading investments across a variety of asset classes, industries, and geographic regions. By diversifying their portfolios, investors can reduce their exposure to any single investment and mitigate the impact of unexpected events. Diversification is particularly important when relying on forecasts stocks, as it can help to cushion the impact of inaccurate predictions.
Due Diligence
Before investing in any stock, it’s crucial to conduct thorough due diligence. This involves researching the company’s financial performance, industry position, and management team. Investors should also consider the risks associated with the investment and understand the potential downside. Due diligence can help investors make informed decisions and avoid costly mistakes. [See also: How to Research Stocks Effectively]
Long-Term Perspective
Investing in the stock market should be viewed as a long-term endeavor. Trying to time the market based on short-term forecasts is often a losing game. Investors should focus on building a diversified portfolio of high-quality stocks and holding them for the long term. A long-term perspective can help investors weather market volatility and achieve their financial goals. Forecasting stocks can inform long term strategies, but should not be the sole driver.
Conclusion: The Art and Science of Forecasting Stocks
Forecasting stocks is a complex and challenging undertaking that combines elements of both art and science. While various analytical techniques can be used to predict future price movements, the stock market is inherently unpredictable. Investors should use forecasts wisely, understand their limitations, and conduct their own independent analysis before making investment decisions. The key to successful investing is not to rely solely on forecasts, but to develop a well-rounded investment strategy that incorporates diversification, due diligence, and a long-term perspective. Ultimately, the ability to accurately forecast stocks remains an elusive goal, but a deeper understanding of the market and its dynamics can improve investment outcomes.