Demystifying the Swap Calculator: A Comprehensive Guide for Informed Decisions
In today’s complex financial landscape, understanding the intricacies of swaps is crucial for both individuals and institutions. A swap calculator is an indispensable tool for navigating these complexities, offering clarity and precision in evaluating the potential benefits and risks associated with swap agreements. This article provides a comprehensive overview of swap calculators, their functionalities, applications, and limitations, empowering you to make more informed decisions. We’ll explore various types of swaps, how swap calculators work, and provide practical examples to illustrate their use.
What is a Swap and Why Use a Swap Calculator?
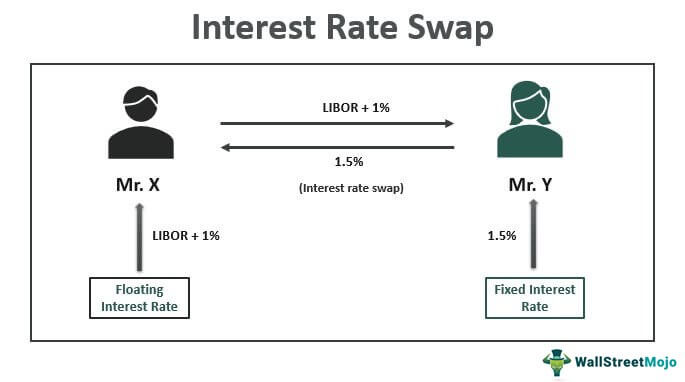
A swap is a derivative contract through which two parties exchange financial instruments. These instruments can be almost anything, but most swaps involve cash flows based on a notional principal amount, which is not actually exchanged. The most common types of swaps are interest rate swaps, currency swaps, and credit default swaps. [See also: Understanding Interest Rate Swaps for Beginners]
The primary reason to use a swap calculator is to accurately determine the fair value of a swap and analyze its potential cash flows. Without a swap calculator, estimating these values can be extremely complex and time-consuming, requiring advanced mathematical and financial knowledge. A swap calculator streamlines the process, providing quick and reliable results. It allows users to:
- Evaluate Swap Opportunities: Determine if a swap aligns with their financial goals.
- Manage Risk: Understand the potential risks and rewards associated with a swap.
- Negotiate Terms: Secure favorable terms when entering into a swap agreement.
- Monitor Performance: Track the performance of existing swaps and make adjustments as needed.
Types of Swaps and Their Respective Calculators
Different types of swaps require specialized swap calculators due to their unique characteristics. Here are some of the most common types:
Interest Rate Swaps
An interest rate swap involves exchanging a fixed interest rate for a floating interest rate, or vice versa, on a notional principal amount. A swap calculator for interest rate swaps typically considers factors such as the fixed rate, the floating rate index (e.g., LIBOR, SOFR), the term of the swap, and the discount rate. These calculators help determine the present value of the cash flows and the overall value of the swap.
Currency Swaps
A currency swap involves exchanging principal and interest payments in one currency for principal and interest payments in another currency. A swap calculator for currency swaps takes into account the exchange rates, interest rates in both currencies, and the term of the swap. These calculators are used to hedge against currency risk and to access financing in different currencies. [See also: Hedging Currency Risk: Strategies and Tools]
Credit Default Swaps (CDS)
A credit default swap (CDS) is a financial contract where a buyer pays a premium to a seller for protection against a specific credit event, such as a default by a borrower. A swap calculator for CDS involves complex calculations related to probabilities of default, recovery rates, and the credit spread. These calculators are used to assess the risk and pricing of credit protection.
Equity Swaps
An equity swap involves exchanging cash flows based on the return of an equity index or a basket of stocks for a fixed or floating interest rate. These swaps allow investors to gain exposure to equity markets without directly owning the underlying assets. A swap calculator for equity swaps will factor in expected equity returns, dividend yields, and interest rates.
How a Swap Calculator Works: The Underlying Mechanics
While the specific calculations vary depending on the type of swap, the fundamental principles behind a swap calculator remain the same. Here’s a general overview of the process:
- Input Data: The user inputs the relevant parameters, such as the notional principal, interest rates, term of the swap, and any other specific details required for the type of swap being analyzed.
- Cash Flow Calculation: The swap calculator projects the expected cash flows based on the input data. This involves calculating the interest payments, principal exchanges (if applicable), and any other relevant cash flows.
- Discounting: The future cash flows are discounted back to their present value using an appropriate discount rate. The discount rate reflects the time value of money and the risk associated with the cash flows.
- Valuation: The present values of all the cash flows are summed to determine the fair value of the swap. This value represents the theoretical price at which the swap should trade.
- Sensitivity Analysis: Many swap calculators also offer sensitivity analysis, which allows users to see how the value of the swap changes under different scenarios. This can be useful for understanding the potential risks and rewards associated with the swap.
Practical Examples of Using a Swap Calculator
Let’s illustrate the use of a swap calculator with a couple of practical examples:
Example 1: Interest Rate Swap
A company wants to hedge against rising interest rates. They enter into an interest rate swap where they pay a fixed rate of 3% and receive a floating rate based on SOFR on a notional principal of $10 million for a term of 5 years. Using a swap calculator, they can determine the expected cash flows and the fair value of the swap. The swap calculator would project the SOFR rate over the next 5 years based on market expectations and then calculate the net cash flows the company would receive or pay each period. By discounting these cash flows, the swap calculator provides an estimate of the swap’s current value. If the calculated value is positive, it suggests the swap is currently favorable to the company.
Example 2: Currency Swap
A US-based company needs to make payments in Euros. They enter into a currency swap where they exchange US dollars for Euros at the current exchange rate, with an agreement to re-exchange the currencies at a future date. The swap calculator would factor in the interest rates in both the US and the Eurozone, as well as the exchange rate fluctuations. The swap calculator helps determine the cost of the swap compared to borrowing directly in Euros and hedging the currency risk separately.
Choosing the Right Swap Calculator
With numerous swap calculators available online and in software packages, selecting the right one is crucial. Consider the following factors:
- Accuracy: Ensure the swap calculator uses accurate and up-to-date market data and employs sound financial models. Look for calculators from reputable financial institutions or software providers.
- User-Friendliness: Choose a swap calculator that is easy to use and understand. The interface should be intuitive, and the results should be clearly presented.
- Features: Consider the features offered by the swap calculator. Does it offer sensitivity analysis? Can it handle different types of swaps? Does it provide detailed reports?
- Cost: Some swap calculators are free, while others require a subscription or one-time purchase. Consider your budget and the value you expect to receive from the swap calculator.
Limitations of Swap Calculators
While swap calculators are powerful tools, it’s important to recognize their limitations:
- Assumptions: Swap calculators rely on assumptions about future interest rates, exchange rates, and other market variables. These assumptions may not always be accurate, and the actual results may differ significantly from the calculated results.
- Complexity: Swaps can be complex financial instruments, and swap calculators may not capture all of the nuances and risks involved. It’s important to consult with a financial professional before entering into a swap agreement.
- Data Quality: The accuracy of a swap calculator depends on the quality of the input data. If the data is inaccurate or incomplete, the results will be unreliable.
The Future of Swap Calculators
The future of swap calculators is likely to be driven by advancements in technology and increasing demand for more sophisticated risk management tools. We can expect to see:
- Integration with AI and Machine Learning: AI and machine learning algorithms can be used to improve the accuracy of swap valuations and to identify potential risks and opportunities.
- Real-Time Data Integration: Swap calculators will be increasingly integrated with real-time market data feeds, providing users with up-to-the-minute information.
- Cloud-Based Solutions: Cloud-based swap calculators will become more prevalent, offering users access to powerful tools from anywhere in the world.
- More User-Friendly Interfaces: Swap calculators will become even easier to use, with more intuitive interfaces and interactive visualizations.
Conclusion
A swap calculator is an essential tool for anyone involved in swap transactions, from corporate treasurers to individual investors. By understanding how these calculators work and their limitations, you can make more informed decisions and better manage the risks associated with swaps. Remember to choose a swap calculator that is accurate, user-friendly, and meets your specific needs. As technology continues to evolve, swap calculators will become even more powerful and accessible, further empowering users to navigate the complex world of swaps.
