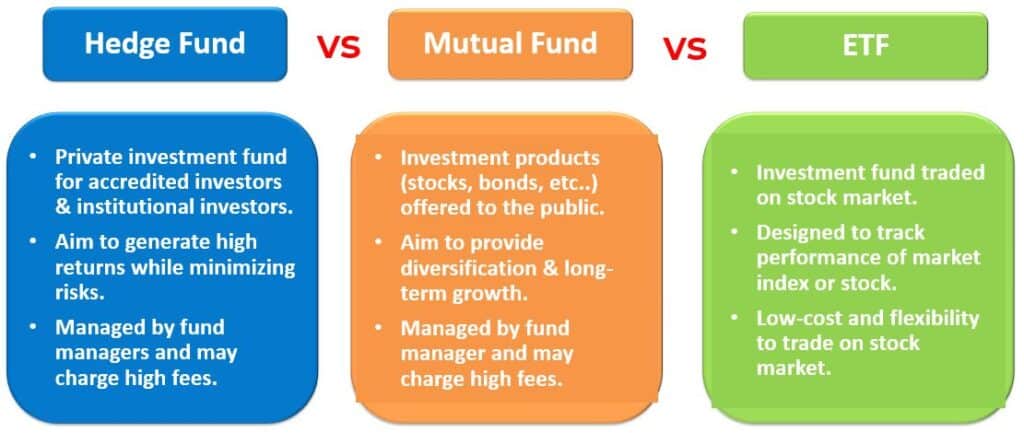
Hedge Funds vs. Mutual Funds: Understanding the Key Differences
Navigating the world of investments can often feel like traversing a complex maze. Among the various investment vehicles available, hedge funds and mutual funds stand out as two popular options. However, despite their shared goal of generating returns for investors, significant differences between hedge funds and mutual funds exist. This article will delve into these distinctions, providing a comprehensive understanding of each, their target investors, investment strategies, regulatory oversight, and associated risks. Understanding the differences between hedge funds and mutual funds is critical for investors looking to allocate capital effectively.
What are Mutual Funds?
Mutual funds are investment vehicles that pool money from numerous investors to purchase a diversified portfolio of assets, such as stocks, bonds, or other securities. These funds are managed by professional fund managers who make investment decisions based on the fund’s stated objectives. Mutual funds are highly regulated and transparent, making them accessible to a wide range of investors, including individuals with relatively small amounts to invest.
Key Characteristics of Mutual Funds
- Diversification: Mutual funds offer instant diversification, spreading investment across various securities to mitigate risk.
- Liquidity: Investors can typically buy or sell shares of a mutual fund on any business day.
- Regulation: Mutual funds are heavily regulated by entities like the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) in the United States.
- Transparency: Mutual funds are required to disclose their holdings and performance regularly.
- Accessibility: Mutual funds are generally available to all investors, regardless of their net worth or income.
What are Hedge Funds?
Hedge funds, on the other hand, are investment partnerships that employ a wider range of investment strategies and often target higher returns. These funds are typically less regulated than mutual funds and are generally available only to accredited investors—those with high net worth or income. The differences between hedge funds and mutual funds extend to their investment approach and regulatory environment.
Key Characteristics of Hedge Funds
- Sophisticated Strategies: Hedge funds may utilize strategies such as short selling, leverage, and derivatives to generate returns.
- Limited Regulation: Hedge funds are subject to less regulatory oversight compared to mutual funds.
- Accredited Investors Only: Hedge funds are typically only accessible to accredited investors who meet specific financial criteria.
- Higher Fees: Hedge funds often charge higher fees, including performance-based fees (e.g., the “2 and 20” model).
- Less Transparency: Hedge funds are not required to disclose their holdings as frequently as mutual funds.
Detailed Comparison: Hedge Funds vs. Mutual Funds
To fully grasp the differences between hedge funds and mutual funds, let’s examine them across several key dimensions:
Investor Eligibility
One of the most significant differences between hedge funds and mutual funds lies in investor eligibility. Mutual funds are open to virtually anyone, while hedge funds restrict access to accredited investors. This restriction is in place because hedge funds are considered riskier investments, and regulators want to ensure that only those with the financial means to absorb potential losses can participate. The high minimum investment required for hedge funds often acts as a barrier for smaller investors. Understanding these restrictions is crucial when considering the differences between hedge funds and mutual funds.
Investment Strategies
Another crucial difference between hedge funds and mutual funds is the range of investment strategies employed. Mutual funds typically adhere to more conservative strategies, focusing on long-term growth and diversification. They are often restricted in their use of leverage, short selling, and derivatives. Hedge funds, in contrast, have far greater flexibility. They can employ complex strategies to profit from market inefficiencies, using leverage to amplify returns and short selling to profit from declining asset prices. This flexibility also introduces higher risk. The strategies used highlight the differences between hedge funds and mutual funds in their approaches to risk and return.
Regulation
The regulatory environment is a key differentiator. Mutual funds are subject to stringent regulations under the Investment Company Act of 1940, which mandates transparency, disclosure, and investor protection. Hedge funds, operating under exemptions from these regulations, face fewer constraints. This lack of stringent oversight allows hedge funds greater operational freedom but also exposes investors to potentially higher risks. The level of regulation is a fundamental difference between hedge funds and mutual funds.
Fees and Expenses
The fee structure also highlights the differences between hedge funds and mutual funds. Mutual funds typically charge management fees, which are a percentage of the assets under management (AUM). These fees are generally lower than those charged by hedge funds. Hedge funds often employ a “2 and 20” fee structure, charging a 2% management fee and a 20% performance fee (a share of the profits). This performance-based fee incentivizes fund managers to generate high returns but can also result in higher overall costs for investors. [See also: Understanding Investment Fees]
Transparency
Mutual funds are required to disclose their holdings and performance regularly, providing investors with transparency into their investment strategy and results. Hedge funds operate with considerably less transparency. They are not required to disclose their holdings as frequently and may keep their strategies confidential. This lack of transparency can make it difficult for investors to assess the risks associated with a hedge fund. The degree of transparency is a significant difference between hedge funds and mutual funds.
Liquidity
Mutual funds typically offer daily liquidity, allowing investors to buy or sell shares on any business day. Hedge funds often have lock-up periods, restricting investors from withdrawing their money for a specified period. This illiquidity is a trade-off for the potential of higher returns and the specialized strategies employed by hedge funds. This liquidity difference between hedge funds and mutual funds is a critical consideration for investors.
Risk and Return Profiles
Considering the differences between hedge funds and mutual funds, their risk and return profiles vary significantly. Mutual funds aim for steady, long-term growth with moderate risk. Hedge funds, with their aggressive strategies, seek higher returns but also carry greater risk. The potential for substantial gains is balanced by the potential for significant losses. Investors must carefully assess their risk tolerance and investment goals before choosing between these options. The risk-return relationship is a key difference between hedge funds and mutual funds.
Choosing Between Hedge Funds and Mutual Funds
Selecting between hedge funds and mutual funds depends on several factors, including your investment goals, risk tolerance, financial resources, and investment knowledge. If you are a retail investor seeking diversification, liquidity, and transparency with a moderate risk appetite, mutual funds are likely a better fit. If you are an accredited investor comfortable with illiquidity, less transparency, and higher risk in pursuit of potentially higher returns, a hedge fund might be an option. Understanding the differences between hedge funds and mutual funds is crucial in making an informed decision. [See also: Investing for Beginners]
Factors to Consider
- Investment Goals: What are you hoping to achieve with your investment?
- Risk Tolerance: How much risk are you willing to take?
- Financial Resources: Do you meet the eligibility requirements for hedge funds?
- Investment Knowledge: Do you understand the complexities of hedge fund strategies?
The Future of Hedge Funds and Mutual Funds
Both hedge funds and mutual funds continue to evolve in response to market changes and investor demands. The mutual fund industry has seen the rise of exchange-traded funds (ETFs), offering similar diversification benefits with lower fees and greater trading flexibility. The hedge fund industry is facing increased scrutiny and pressure to improve transparency and reduce fees. Despite these changes, both investment vehicles will likely remain integral parts of the financial landscape. Staying informed about the differences between hedge funds and mutual funds will be crucial for investors navigating the future of investment.
Conclusion
The differences between hedge funds and mutual funds are significant and impact every aspect of the investment experience, from investor eligibility to investment strategies, regulation, fees, transparency, liquidity, and risk-return profiles. Mutual funds provide a regulated, transparent, and accessible avenue for diversified investing, while hedge funds offer sophisticated strategies and the potential for higher returns, albeit with higher risk and less regulation. Understanding these key differences between hedge funds and mutual funds is essential for making informed investment decisions that align with your individual financial goals and risk tolerance. By carefully considering these factors, investors can navigate the investment landscape with greater confidence and achieve their financial objectives. The critical difference between hedge funds and mutual funds boils down to risk tolerance, investment knowledge, and access to capital.
