CFD vs Spread Betting: Unveiling the Key Differences
In the dynamic world of financial trading, Contracts for Difference (CFDs) and spread betting stand out as popular derivatives, offering traders exposure to various markets without directly owning the underlying assets. While both instruments share similarities, understanding the nuances between CFD trading and spread betting is crucial for making informed decisions. This article delves into the core differences, exploring aspects like taxation, market access, risk management, and regulatory oversight to help you determine which option aligns best with your trading goals and risk tolerance.
What are CFDs?
CFD, or Contract for Difference, is an agreement between two parties to exchange the difference in the value of an asset from the time the contract is opened until it’s closed. Traders speculate on whether the price of an asset will rise or fall. If the prediction is correct, the trader profits; if incorrect, they incur a loss. CFDs cover a wide range of assets, including stocks, indices, commodities, and currencies.
CFDs are leveraged products, meaning traders can control a large position with a relatively small amount of capital. This leverage can amplify both profits and losses, making risk management essential. [See also: Managing Risk in CFD Trading]
What is Spread Betting?
Spread betting involves speculating on the movement of financial markets, but instead of buying or selling an asset, you bet on whether the price will go up or down. The broker provides a ‘spread,’ which is the difference between the buying and selling price. Your profit or loss depends on the accuracy of your prediction and the size of your stake per point of movement.
Like CFDs, spread betting is a leveraged product, offering the potential for significant gains but also carrying substantial risk. A key difference lies in how profits are taxed, particularly in certain jurisdictions like the UK.
Key Differences Between CFD and Spread Betting
While both CFD trading and spread betting allow you to speculate on price movements, several key differences distinguish them:
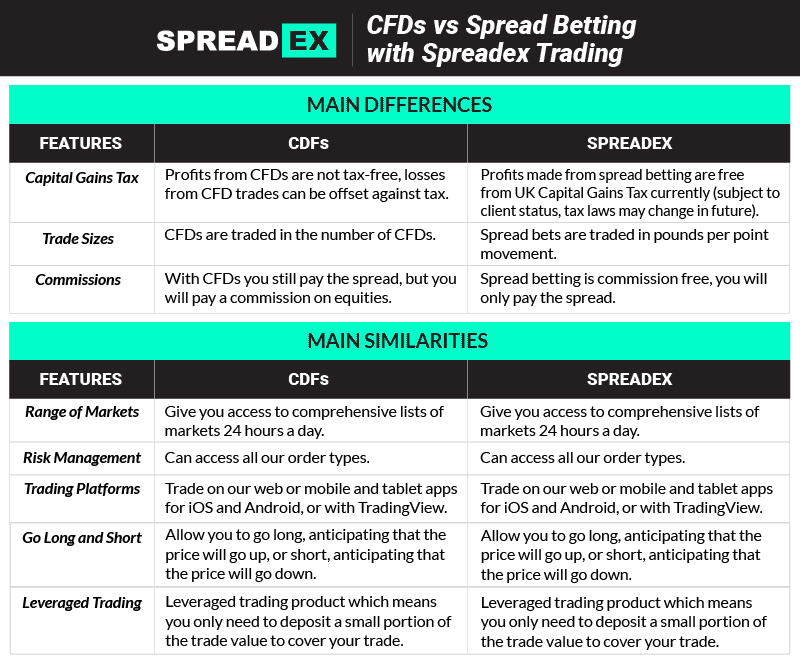
Taxation
Taxation is a significant differentiator. In the UK and Ireland, profits from spread betting are generally exempt from Capital Gains Tax (CGT) and Stamp Duty. This is because spread betting is legally classified as gambling. Conversely, profits from CFD trading are typically subject to CGT. This tax advantage often makes spread betting more attractive to traders in these regions. Always consult with a tax professional for personalized advice.
Market Access
Both CFDs and spread betting offer access to a wide range of markets, including stocks, indices, commodities, forex, and even cryptocurrencies. However, the specific markets available may vary depending on the broker. Generally, the range of available markets is quite similar across both platforms.
Pricing and Spreads
The pricing structures for CFDs and spread betting are similar, with brokers typically making their money through the spread (the difference between the buying and selling price) and sometimes through commissions. It’s important to compare the spreads offered by different brokers, as they can significantly impact your profitability. Some brokers might offer tighter spreads on CFDs, while others may have more competitive spreads on spread betting.
Regulation
Both CFDs and spread betting are regulated by financial authorities, but the specific regulatory framework can differ depending on the jurisdiction. In the UK, both are regulated by the Financial Conduct Authority (FCA). This regulation provides a level of protection for traders, ensuring that brokers adhere to certain standards of conduct and financial stability. [See also: Understanding Financial Regulations for Traders]
Leverage
Both CFDs and spread betting are leveraged products, allowing traders to control a larger position with a smaller initial investment. The level of leverage offered can vary depending on the asset and the broker. While leverage can amplify profits, it also magnifies losses, making it crucial to use risk management tools like stop-loss orders. The FCA and other regulatory bodies have imposed restrictions on leverage levels to protect retail traders.
Contract Size and Flexibility
CFDs typically offer more flexibility in terms of contract size. You can often trade in smaller increments, allowing for more precise position sizing. Spread betting, on the other hand, usually involves betting a fixed amount per point of movement. This can be less flexible for traders with smaller accounts or those who prefer to fine-tune their position sizes.
Transparency
The transparency of pricing and execution can vary between CFD and spread betting brokers. It’s essential to choose a reputable broker that provides clear and transparent pricing information. Look for brokers that offer direct market access (DMA) or similar execution models, as these can provide greater transparency.
Advantages and Disadvantages
CFDs
Advantages:
- Access to a wide range of markets.
- Flexibility in contract size.
- Can be used for hedging existing positions.
Disadvantages:
- Profits are typically subject to Capital Gains Tax (CGT).
- Leverage can magnify losses.
- Overnight financing charges may apply.
Spread Betting
Advantages:
- Profits are generally exempt from Capital Gains Tax (CGT) in certain jurisdictions (e.g., UK and Ireland).
- Leverage can amplify profits.
- No commission charges (typically).
Disadvantages:
- Less flexibility in contract size.
- Leverage can magnify losses.
- Can be perceived as gambling.
Choosing Between CFD and Spread Betting
The best choice between CFD trading and spread betting depends on your individual circumstances, trading style, and risk tolerance. Consider the following factors:
- Tax Implications: If you are based in a country where spread betting profits are tax-free, this can be a significant advantage.
- Trading Style: If you prefer more flexibility in contract size, CFDs may be a better option.
- Risk Tolerance: Both CFDs and spread betting are leveraged products, so it’s crucial to have a solid risk management strategy in place.
- Market Access: Ensure that the broker offers access to the markets you want to trade.
- Regulations: Choose a broker that is regulated by a reputable financial authority.
Risk Management
Both CFD trading and spread betting involve significant risk due to leverage. It is crucial to implement robust risk management strategies, including:
- Stop-Loss Orders: To limit potential losses on a trade.
- Take-Profit Orders: To automatically close a trade when a desired profit level is reached.
- Position Sizing: To control the amount of capital at risk on each trade.
- Risk-Reward Ratio: To assess the potential profit relative to the potential loss on a trade.
Never trade with money you cannot afford to lose. [See also: Advanced Risk Management Techniques for Traders]
Conclusion
CFD trading and spread betting both offer opportunities to profit from the movement of financial markets. Understanding the differences in taxation, contract size, and other factors is essential for making an informed decision. Whether you choose CFDs or spread betting, always prioritize risk management and choose a reputable broker. Both CFD and spread betting, when approached responsibly, can be valuable tools in a trader’s arsenal. Remember to conduct thorough research and seek professional advice before engaging in any form of trading. The key to success lies in understanding the intricacies of each instrument and tailoring your strategy to your individual circumstances. This comprehensive comparison of CFD vs spread betting should provide a solid foundation for your trading journey. Consider your personal financial situation, trading goals, and risk appetite before making any decisions.
