CFD vs. Spread Betting: Unveiling the Key Differences
For those navigating the world of financial trading, the terms CFD (Contract for Difference) and spread betting often arise. Both offer ways to speculate on the price movements of various assets without owning the underlying asset itself. However, understanding the difference between CFD and spread betting is crucial for making informed decisions aligned with your individual trading goals and risk tolerance. This article provides a comprehensive overview of these two popular trading methods, highlighting their distinctions and similarities.
What is CFD Trading?
A Contract for Difference (CFD) is an agreement between two parties to exchange the difference in the value of an asset between the time the contract is opened and when it is closed. CFDs allow traders to speculate on the price movements of a wide range of assets, including stocks, indices, commodities, and currencies. When you trade CFDs, you don’t actually own the underlying asset; instead, you’re trading a contract based on its price fluctuations.
CFDs are leveraged products, meaning you only need to deposit a small percentage of the total trade value (known as margin) to open a position. This leverage can amplify both profits and losses. It’s important to carefully consider the risks associated with leverage before engaging in CFD trading. [See also: Understanding Leverage in Trading]
Key Features of CFD Trading:
- Leverage: Allows traders to control larger positions with a smaller initial investment.
- Wide Range of Markets: Access to various asset classes, including stocks, indices, commodities, and currencies.
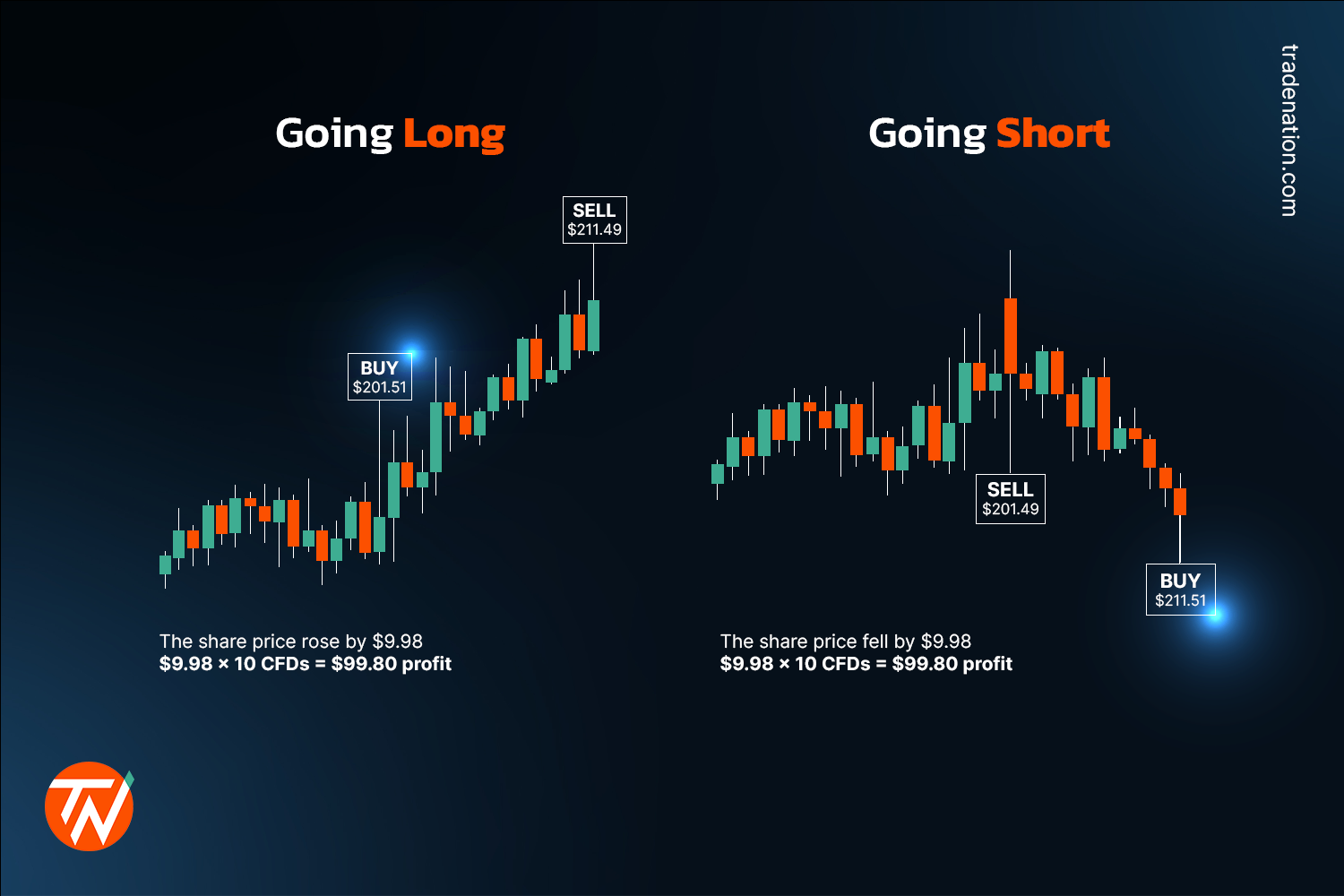
- Trading in Both Directions: Ability to profit from both rising (going long) and falling (going short) markets.
- Commission: Typically charged on each trade, although some brokers offer commission-free CFD trading with wider spreads.
- Taxation: Tax treatment of CFD trading varies by jurisdiction. In some regions, profits may be subject to capital gains tax.
What is Spread Betting?
Spread betting involves speculating on the price movement of financial instruments. Instead of buying or selling an asset, you bet on whether its price will rise or fall. The spread is the difference between the buying and selling price quoted by the broker. Your profit or loss is determined by the accuracy of your prediction and the size of your stake per point of movement in the asset’s price. Like CFDs, spread betting is also a leveraged product.
Spread betting is particularly popular in the UK and Ireland due to its potential tax advantages. In many cases, profits from spread betting are exempt from capital gains tax. This is a significant difference between CFD and spread betting, making it an attractive option for some traders. Consult with a tax advisor to understand the specific tax implications in your jurisdiction. [See also: Tax Implications of Trading]
Key Features of Spread Betting:
- Leverage: Similar to CFDs, spread betting offers leveraged trading, amplifying potential gains and losses.
- Tax Advantages: In some jurisdictions, profits may be tax-free.
- Spread: The difference between the buying and selling price quoted by the broker.
- Stake per Point: You determine the amount you’re willing to risk per point of movement in the asset’s price.
- Limited Markets: While a wide range is available, the market selection can sometimes be more limited compared to CFDs.
The Core Difference Between CFD and Spread Betting
The most significant difference between CFD and spread betting lies in their tax treatment. As mentioned earlier, spread betting profits are often tax-free in certain jurisdictions, while CFD profits are typically subject to capital gains tax. This is a major consideration for many traders when choosing between the two. However, this is jurisdiction dependent and should be verified.
Another subtle difference between CFD and spread betting is the way profits and losses are calculated. With CFDs, your profit or loss is the difference between the opening and closing price of the asset, multiplied by the number of contracts you hold. With spread betting, your profit or loss is determined by the number of points the asset moves in your favor or against you, multiplied by your stake per point. While the end result is similar, the mechanics of calculation are slightly different.
While both offer leverage, the specific margin requirements and leverage ratios can vary between CFD brokers and spread betting providers. Always compare the terms and conditions offered by different providers before making a decision. Understanding these nuances is crucial when weighing the difference between CFD and spread betting.
Detailed Comparison: CFD vs. Spread Betting
Let’s examine a more detailed comparison to further illuminate the difference between CFD and spread betting:
- Taxation: Spread betting often offers tax advantages (e.g., tax-free profits) in certain regions, while CFD profits are usually subject to capital gains tax.
- Markets: Both offer access to a wide range of markets, but CFDs may offer a slightly broader selection in some cases.
- Regulation: Both are regulated financial products, but the specific regulatory frameworks may vary depending on the jurisdiction.
- Pricing: CFDs typically involve a commission per trade, while spread betting profits are built into the spread.
- Calculation of Profit/Loss: CFDs calculate profit/loss based on the price difference multiplied by the number of contracts. Spread betting calculates it based on the number of points moved multiplied by the stake per point.
Advantages and Disadvantages
CFD Trading Advantages:
- Flexibility: Ability to trade a wide range of assets.
- Leverage: Amplifies potential profits.
- Short Selling: Easy to profit from falling markets.
CFD Trading Disadvantages:
- Leverage: Amplifies potential losses.
- Taxation: Profits are typically subject to capital gains tax.
- Complexity: Can be complex for novice traders.
Spread Betting Advantages:
- Tax Advantages: Potential tax-free profits in some jurisdictions.
- Simplicity: Relatively straightforward to understand.
- Leverage: Amplifies potential profits.
Spread Betting Disadvantages:
- Leverage: Amplifies potential losses.
- Spread: The spread reduces potential profits.
- Limited Markets: Market selection may be more limited compared to CFDs.
Choosing Between CFD and Spread Betting
The best choice between CFD trading and spread betting depends on your individual circumstances, trading goals, and risk tolerance. Consider the following factors:
- Tax Implications: If you are in a jurisdiction where spread betting profits are tax-free, this can be a significant advantage.
- Trading Style: Consider your preferred trading style and the types of assets you want to trade.
- Risk Tolerance: Both CFD trading and spread betting involve leverage, which can amplify both profits and losses. Assess your risk tolerance carefully.
- Broker Fees and Spreads: Compare the fees and spreads offered by different brokers and providers.
Ultimately, understanding the difference between CFD and spread betting is key to making an informed decision. Do your research, compare the options, and choose the trading method that best suits your needs. [See also: Choosing the Right Trading Platform]
Conclusion
Both CFDs and spread betting offer opportunities to profit from the price movements of financial assets without owning them directly. The key difference between CFD and spread betting primarily lies in their tax treatment, with spread betting often offering tax advantages in certain jurisdictions. Before engaging in either type of trading, it is crucial to understand the risks involved, especially those associated with leverage. Conduct thorough research, compare different brokers, and consider seeking professional advice before making any investment decisions. By understanding the nuances of each, you can make a more informed choice that aligns with your financial goals and risk appetite. Always remember that trading involves risk, and you could lose more than your initial investment.