Decoding the Bollinger Squeeze: A Comprehensive Guide for Traders
In the dynamic world of financial markets, identifying potential breakout opportunities is crucial for successful trading. One popular technique used by traders to spot these opportunities is the Bollinger Squeeze. This article will delve into the intricacies of the Bollinger Squeeze, exploring its mechanics, interpretation, and application in various trading strategies. Understanding the Bollinger Squeeze can significantly enhance a trader’s ability to anticipate market movements and make informed decisions. This guide aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of the Bollinger Squeeze, enabling traders to effectively incorporate it into their trading toolkit.
What is the Bollinger Squeeze?
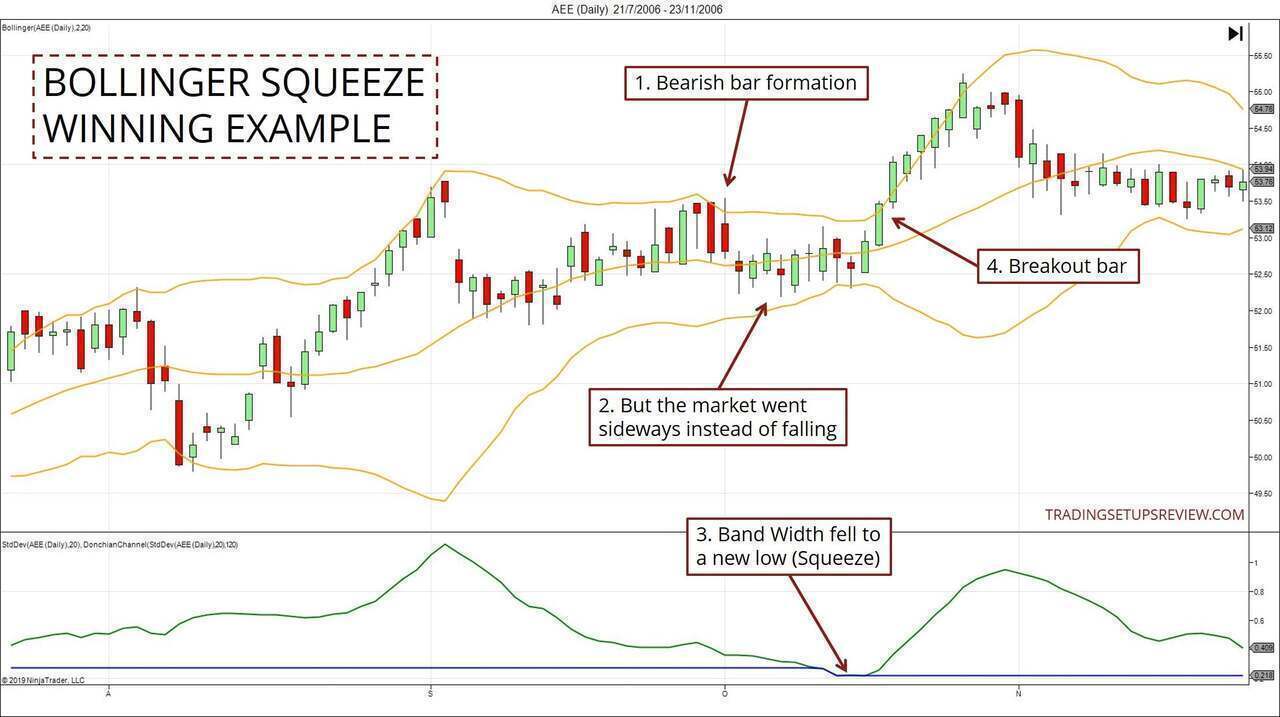
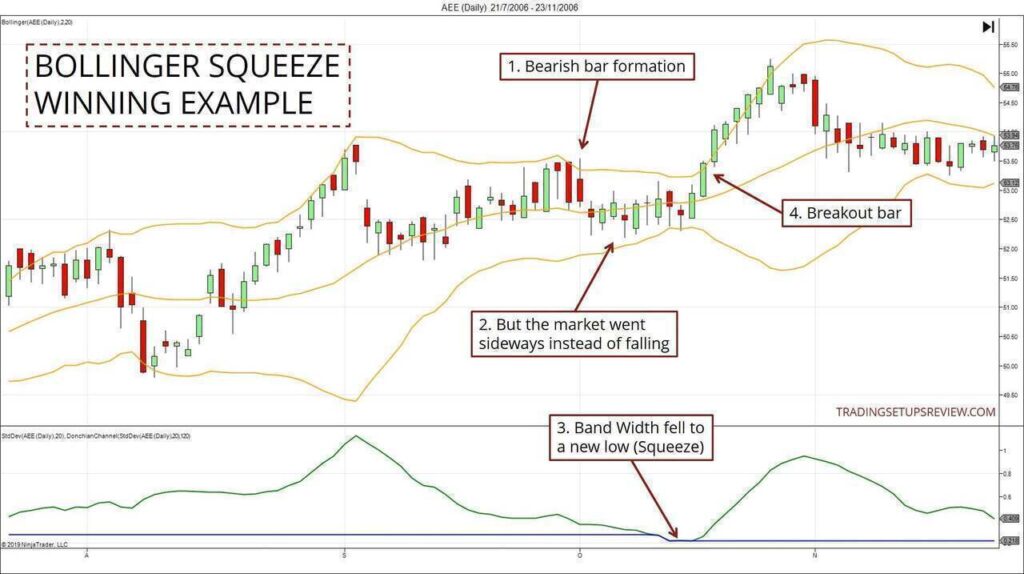
The Bollinger Squeeze is a technical analysis tool developed by John Bollinger in the 1980s. It is based on the concept that periods of low volatility are often followed by periods of high volatility. The squeeze occurs when the Bollinger Bands, which are volatility bands placed above and below a moving average, narrow significantly. This narrowing suggests that volatility is unusually low and that a significant price move is imminent.
Bollinger Bands consist of three lines: a middle band, which is typically a 20-day simple moving average (SMA), an upper band, which is the SMA plus two standard deviations, and a lower band, which is the SMA minus two standard deviations. The standard deviation is a measure of how much the price deviates from the average. When the bands squeeze together, it indicates that the price is trading within a narrow range, suggesting low volatility.
How the Bollinger Squeeze Works
The underlying principle of the Bollinger Squeeze is that volatility tends to revert to the mean. When volatility is low, it is likely to increase, and when volatility is high, it is likely to decrease. The Bollinger Squeeze identifies periods of low volatility, suggesting that an increase in volatility is likely to occur soon. The squeeze itself does not indicate the direction of the breakout; it only signals that a breakout is likely to happen. Traders then need to use other technical indicators and analysis techniques to determine the likely direction of the price move. [See also: Understanding Volatility in Trading]
Identifying the Squeeze
The primary indicator of a Bollinger Squeeze is the narrowing of the Bollinger Bands. Traders typically look for periods when the upper and lower bands come closer together than they have been in recent history. There is no hard-and-fast rule for how narrow the bands must be to qualify as a squeeze, but a visual inspection of the chart can often reveal potential squeeze situations. Some traders use a ratio of the band width to the middle band to quantify the squeeze.
Confirming the Breakout
Once a Bollinger Squeeze is identified, traders need to confirm the breakout before entering a trade. A breakout occurs when the price moves decisively above the upper band or below the lower band. This breakout signals the start of a new trend. Traders often use other technical indicators, such as volume, momentum oscillators, and chart patterns, to confirm the breakout. High volume during the breakout is a particularly strong confirmation signal.
Using the Bollinger Squeeze in Trading Strategies
The Bollinger Squeeze can be incorporated into various trading strategies, including trend following, breakout trading, and mean reversion. Here are some common strategies:
- Breakout Trading: This strategy involves waiting for the price to break out above the upper band or below the lower band and then entering a trade in the direction of the breakout. Traders often use stop-loss orders to limit their risk.
- Trend Following: This strategy involves using the Bollinger Squeeze to identify potential trend reversals. When the price breaks out above the upper band, it may signal the start of an uptrend, and when the price breaks out below the lower band, it may signal the start of a downtrend.
- Mean Reversion: This strategy involves betting that the price will eventually return to its average value. After a Bollinger Squeeze, the price may move sharply in one direction, but it is likely to eventually revert to the mean. Traders can use this strategy to profit from short-term price fluctuations.
Combining with Other Indicators
The Bollinger Squeeze is often used in conjunction with other technical indicators to improve its accuracy. Some common indicators used with the Bollinger Squeeze include:
- Volume: High volume during a breakout can confirm the validity of the breakout.
- Momentum Oscillators: Indicators like the Relative Strength Index (RSI) and the Moving Average Convergence Divergence (MACD) can help identify overbought or oversold conditions and confirm the direction of the breakout.
- Chart Patterns: Chart patterns, such as triangles, flags, and head and shoulders patterns, can provide additional confirmation of the breakout direction.
Advantages and Disadvantages of the Bollinger Squeeze
Like any technical analysis tool, the Bollinger Squeeze has its advantages and disadvantages. Understanding these pros and cons can help traders use the tool more effectively.
Advantages
- Identifies Potential Breakouts: The Bollinger Squeeze is effective at identifying periods of low volatility that are likely to be followed by periods of high volatility.
- Versatile: The Bollinger Squeeze can be used in various trading strategies and can be combined with other technical indicators.
- Easy to Understand: The Bollinger Squeeze is relatively easy to understand and implement, even for novice traders.
Disadvantages
- False Signals: The Bollinger Squeeze can generate false signals, especially in choppy or sideways markets.
- No Directional Bias: The Bollinger Squeeze does not indicate the direction of the breakout, requiring traders to use other tools to determine the likely direction of the price move.
- Lagging Indicator: The Bollinger Squeeze is a lagging indicator, meaning that it is based on past price data and may not accurately predict future price movements.
Real-World Examples of Bollinger Squeeze
To illustrate how the Bollinger Squeeze works in practice, let’s consider a few real-world examples:
- Stock A: A stock that has been trading in a narrow range for several weeks. The Bollinger Bands have narrowed significantly, indicating a Bollinger Squeeze. Traders anticipate a breakout and watch for confirmation signals.
- Currency Pair B: A currency pair that has been experiencing low volatility. The Bollinger Bands are tight, suggesting a potential Bollinger Squeeze. Traders use volume and momentum indicators to confirm the direction of the breakout.
- Commodity C: A commodity that has been consolidating for several days. The Bollinger Bands are squeezing together, indicating a potential breakout. Traders use chart patterns to identify the likely direction of the price move.
Tips for Using the Bollinger Squeeze
Here are some tips for using the Bollinger Squeeze effectively:
- Use Confirmation Signals: Always use confirmation signals, such as volume, momentum oscillators, and chart patterns, to confirm the breakout before entering a trade.
- Set Stop-Loss Orders: Always set stop-loss orders to limit your risk.
- Adjust Parameters: Experiment with different parameters for the Bollinger Bands to find the settings that work best for your trading style and the specific market you are trading.
- Consider Market Conditions: The Bollinger Squeeze works best in trending markets. Avoid using it in choppy or sideways markets.
- Practice: Practice using the Bollinger Squeeze in a demo account before trading with real money.
The Bollinger Squeeze and Algorithmic Trading
The Bollinger Squeeze is also used in algorithmic trading strategies. Algorithmic trading involves using computer programs to automatically execute trades based on predefined rules. The Bollinger Squeeze can be programmed into an algorithm to identify potential breakout opportunities and automatically enter trades. Algorithmic trading can help traders execute trades more efficiently and consistently. [See also: Algorithmic Trading Strategies]
Conclusion
The Bollinger Squeeze is a valuable technical analysis tool that can help traders identify potential breakout opportunities. By understanding the mechanics of the Bollinger Squeeze and using it in conjunction with other technical indicators and analysis techniques, traders can significantly enhance their ability to anticipate market movements and make informed trading decisions. While the Bollinger Squeeze has its limitations, it remains a popular and widely used tool among traders of all levels. Remember to always use confirmation signals and set stop-loss orders to manage your risk effectively. With practice and experience, the Bollinger Squeeze can become a powerful addition to your trading toolkit. Mastering the Bollinger Squeeze is a journey that requires dedication and continuous learning. By staying informed and adapting to changing market conditions, you can maximize the benefits of this versatile tool and achieve your trading goals.