Do Bearer Bonds Still Exist? Understanding Their History and Modern Relevance
The question, “Do bearer bonds still exist?” often arises in discussions about financial history, regulatory changes, and even crime dramas. These instruments, once a common fixture in the financial landscape, have largely faded from prominence due to concerns about tax evasion and money laundering. However, understanding their history and current status is crucial for a comprehensive grasp of financial markets.
What are Bearer Bonds?
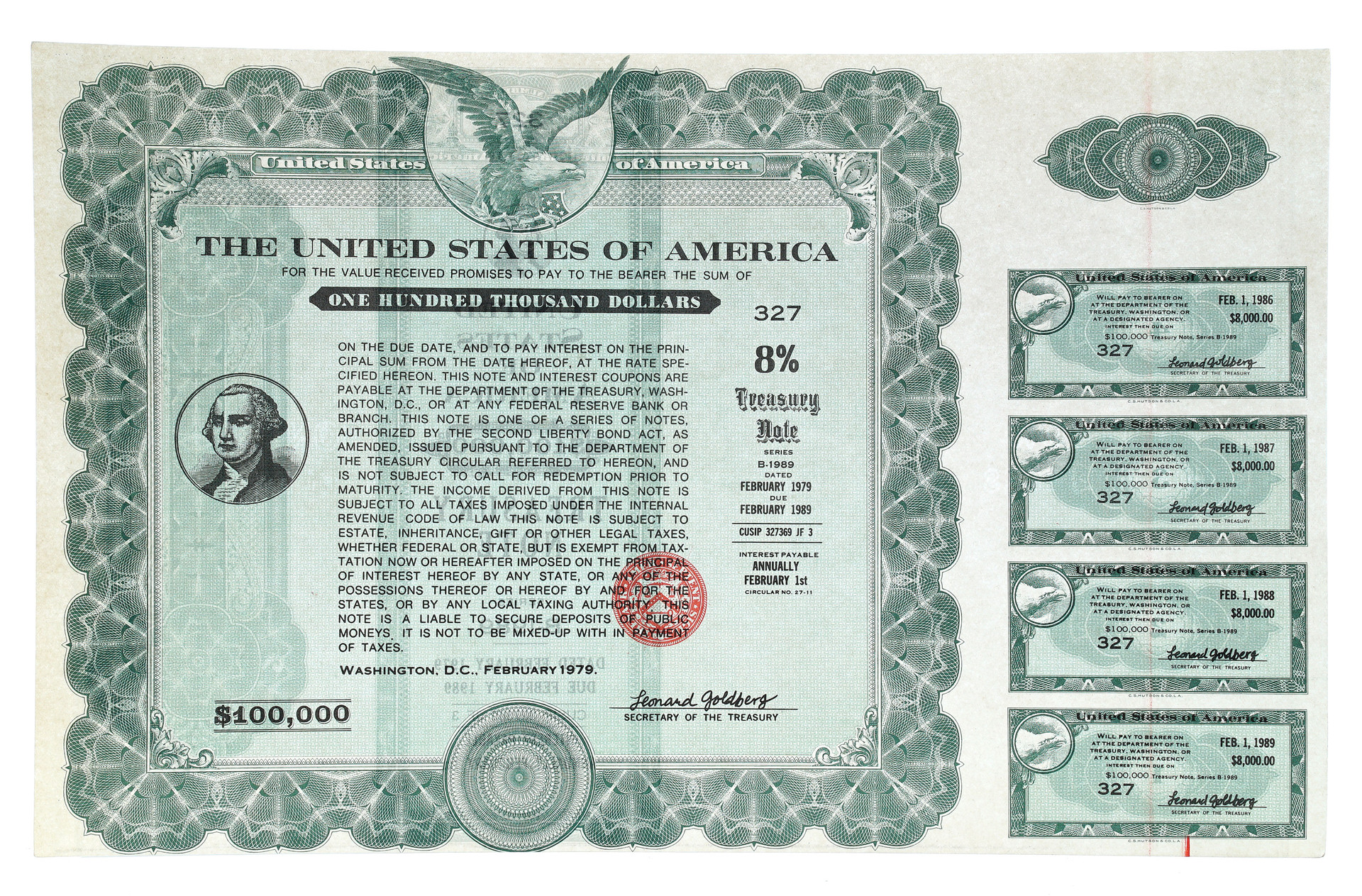
To answer the question “Do bearer bonds still exist?”, it’s important to first understand what they are. A bearer bond is a debt security that is unregistered – no record of the owner is kept by the issuer. Ownership is determined solely by possession of the physical bond certificate. Whoever holds the bond is presumed to be the owner and is entitled to receive interest payments and the principal upon maturity. This characteristic made them highly attractive for those seeking anonymity.
Historical Context
Bearer bonds were widely used throughout the 19th and 20th centuries. They facilitated international trade and finance, allowing capital to flow across borders with relative ease. Governments and corporations alike issued bearer bonds to raise funds for various projects, from infrastructure development to wartime financing. Their anonymity made them appealing to investors who valued privacy or wished to avoid taxation in their home countries. The ease of transfer also contributed to their popularity. They were essentially cash in paper form.
The Rise and Fall of Bearer Bonds
While bearer bonds offered convenience and privacy, these very features also made them susceptible to abuse. By the late 20th century, concerns about their use in tax evasion, money laundering, and terrorist financing began to mount. Because ownership was not recorded, it was difficult to track the flow of funds and identify the beneficial owners of the assets. This lack of transparency posed a significant challenge to law enforcement and regulatory agencies.
In response to these concerns, many countries began to phase out bearer bonds. The United States eliminated them for the most part in the 1980s, and other nations followed suit. The push for greater financial transparency, driven by international organizations such as the Financial Action Task Force (FATF), further accelerated their decline.
The Current Status: Do Bearer Bonds Still Exist?
So, do bearer bonds still exist today? The answer is complex. While they are not entirely extinct, their use is significantly restricted and regulated in most developed countries. New issuances of bearer bonds are generally prohibited. However, some bearer bonds issued before the regulatory changes may still be outstanding. These legacy bonds can still be traded, although their market is much smaller and less liquid than it once was.
Legal and Regulatory Restrictions
The regulatory landscape surrounding bearer bonds is complex and varies from country to country. In many jurisdictions, holding or trading bearer bonds is subject to strict reporting requirements. Financial institutions are required to conduct enhanced due diligence on customers who deal with these instruments to prevent money laundering and other illicit activities. Failure to comply with these regulations can result in severe penalties.
Furthermore, some countries have imposed outright bans on the possession or transfer of bearer bonds. These measures are designed to eliminate the anonymity associated with these instruments and make it more difficult for criminals to use them to conceal their assets. The goal is to promote greater transparency and accountability in the financial system.
Practical Implications
For investors, the decline of bearer bonds has several practical implications. First, it means that it is becoming increasingly difficult to find and trade these instruments. The market for bearer bonds is shrinking, and liquidity is limited. This can make it challenging to buy or sell them at a fair price.
Second, investors who hold bearer bonds may face increased scrutiny from financial institutions and regulatory authorities. They may be required to provide additional documentation to prove the legitimacy of their holdings and comply with anti-money laundering regulations. Failure to do so could result in the freezing or seizure of their assets.
Alternatives to Bearer Bonds
Given the restrictions and risks associated with bearer bonds, investors seeking privacy and flexibility have turned to alternative instruments. These include:
- Nominee accounts: These accounts allow investors to hold assets in the name of a nominee, providing a degree of privacy. However, the beneficial owner is still ultimately identifiable.
- Offshore companies: Setting up a company in a tax haven can provide a layer of anonymity. However, this approach is subject to increasing scrutiny and regulation.
- Cryptocurrencies: Digital currencies like Bitcoin offer a degree of anonymity, although transactions are recorded on a public ledger. [See also: Cryptocurrency Regulations]
It is important to note that these alternatives also come with their own set of risks and regulations. Investors should carefully consider their options and seek professional advice before making any decisions.
The Future of Financial Transparency
The decline of bearer bonds is part of a broader trend towards greater financial transparency. Governments and international organizations are working together to combat tax evasion, money laundering, and terrorist financing. This includes measures such as:
- Automatic exchange of information: Agreements like the Common Reporting Standard (CRS) require financial institutions to automatically exchange information about their customers with tax authorities in other countries.
- Beneficial ownership registers: These registers require companies to disclose the identities of their ultimate beneficial owners, making it more difficult to hide assets behind shell corporations.
- Enhanced due diligence: Financial institutions are required to conduct more thorough due diligence on their customers to identify and prevent illicit activities.
These measures are designed to create a more transparent and accountable financial system, making it more difficult for criminals and tax evaders to operate. While privacy remains an important value, it is increasingly balanced against the need to combat financial crime.
Conclusion
So, to reiterate: Do bearer bonds still exist? Yes, but their prevalence is significantly diminished. While legacy bearer bonds may still be in circulation, new issuances are largely prohibited, and existing bonds are subject to strict regulations. The rise and fall of bearer bonds reflect a broader shift towards greater financial transparency and a crackdown on illicit financial activities. While they once played a significant role in international finance, their anonymity has made them a target for regulatory scrutiny. As governments and international organizations continue to prioritize financial transparency, the future of bearer bonds looks increasingly uncertain. Investors should be aware of the risks and regulations associated with these instruments and consider alternative options that comply with current legal and regulatory requirements. The era of easy anonymity in finance is fading, replaced by a new emphasis on accountability and transparency. Understanding the history of bearer bonds provides a valuable perspective on this evolving landscape.
The question of whether bearer bonds still exist is therefore best answered with a nuanced understanding of their historical context, regulatory treatment, and the broader movement toward financial transparency. [See also: Anti-Money Laundering Regulations]