Grid Trading: A Comprehensive Guide to Automated Forex Strategies
In the dynamic world of forex trading, automated strategies are gaining prominence. Among these, grid trading stands out as a systematic approach to capitalize on market volatility. This article provides a comprehensive overview of grid trading, exploring its mechanics, advantages, disadvantages, and practical applications. Whether you’re a seasoned trader or just starting, understanding grid trading can offer valuable insights into navigating the complexities of the forex market.
Understanding Grid Trading
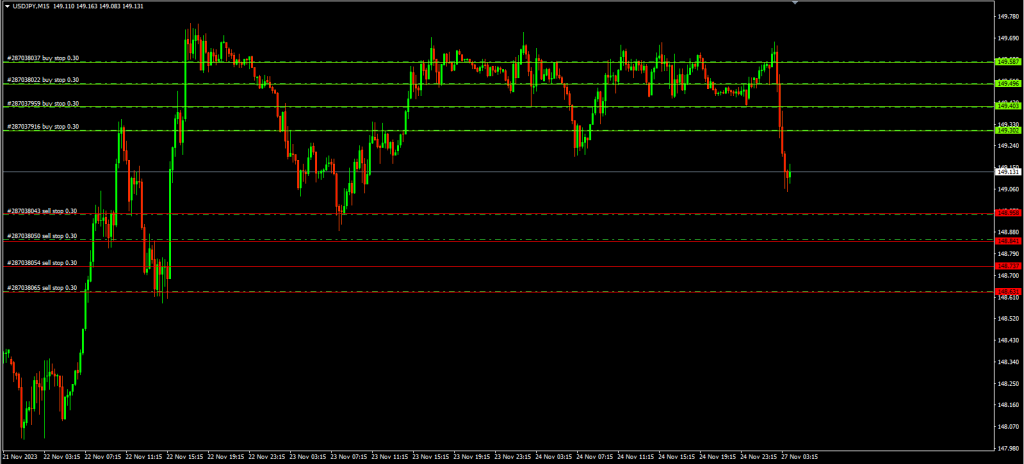
Grid trading is a quantitative trading strategy that involves placing buy and sell orders at regular intervals above and below a predefined price level. These orders create a ‘grid’ of potential entry points. The core idea is to profit from small price movements within a specific range, regardless of the overall market direction. Unlike directional strategies that rely on predicting market trends, grid trading aims to capture gains from sideways or range-bound markets.
The grid is typically established using a series of limit orders. As the price fluctuates within the grid, orders are executed, and profits are realized on each trade. The strategy relies on the assumption that prices will oscillate within the grid, triggering both buy and sell orders repeatedly. Effective grid trading requires careful consideration of the grid spacing, position sizing, and risk management parameters.
How Grid Trading Works
The implementation of grid trading involves several key steps:
Defining the Grid Range
The first step is to determine the upper and lower boundaries of the grid. This range should be based on historical price data, volatility analysis, and expected market conditions. Identifying support and resistance levels can help define a realistic and profitable grid range. A wider grid allows for greater price fluctuations but may require larger capital reserves. A narrower grid generates more frequent trades but is more susceptible to being breached by sudden price movements. [See also: Support and Resistance Trading Strategies]
Setting Grid Spacing
Grid spacing refers to the distance between each buy and sell order within the grid. The optimal spacing depends on the volatility of the asset being traded. Higher volatility warrants wider spacing to avoid excessive transaction costs and false signals. Lower volatility allows for narrower spacing to capture smaller price movements. Backtesting different spacing parameters can help identify the most profitable setting for a given market.
Position Sizing
Determining the appropriate position size for each order is crucial for risk management. Position sizing should be based on the trader’s risk tolerance and the overall capital allocated to the grid trading strategy. Smaller position sizes reduce the potential losses from adverse price movements, while larger position sizes amplify both profits and losses. It is essential to maintain a balanced approach to position sizing to ensure the sustainability of the strategy. [See also: Risk Management in Forex Trading]
Order Placement
Once the grid range, spacing, and position size have been determined, the next step is to place the buy and sell orders. Buy orders are typically placed below the current price, while sell orders are placed above the current price. These orders are set as limit orders, which are executed only when the price reaches the specified level. The number of orders placed depends on the grid range and spacing. It’s important to use a reliable trading platform that supports automated order placement and execution.
Profit Taking and Stop-Loss
Grid trading strategies often incorporate profit-taking and stop-loss mechanisms to manage risk and secure profits. Profit targets are usually set at a fixed level above or below the entry price of each order. Stop-loss orders are placed to limit potential losses if the price moves against the grid. The placement of stop-loss orders is critical to protecting capital and preventing significant drawdowns. Some traders also use trailing stop-loss orders, which adjust dynamically as the price moves in their favor.
Advantages of Grid Trading
Grid trading offers several advantages that make it an attractive strategy for certain traders:
- Profiting in Range-Bound Markets: Grid trading excels in markets with limited directional movement. It can generate consistent profits by capturing small price fluctuations within a defined range.
- Automated Execution: The strategy can be fully automated using trading robots or expert advisors (EAs). This eliminates the need for constant monitoring and allows traders to execute trades around the clock.
- Flexibility: Grid trading can be adapted to various currency pairs and timeframes. Traders can adjust the grid parameters to suit their risk tolerance and market conditions.
- Reduced Emotional Bias: By automating the trading process, grid trading minimizes the impact of emotional decision-making. This can lead to more consistent and rational trading outcomes.
Disadvantages of Grid Trading
Despite its advantages, grid trading also has several drawbacks that traders should be aware of:
- Risk of Drawdown: If the price moves significantly against the grid, the strategy can incur substantial losses. This is particularly true in trending markets where the price breaks out of the defined range.
- High Transaction Costs: Frequent trading can lead to high transaction costs, including spreads and commissions. These costs can erode profits, especially with narrow grid spacing.
- Complexity: Implementing and managing a grid trading strategy requires a good understanding of market dynamics, risk management, and trading platform functionality.
- Over-Optimization: It is possible to over-optimize the grid parameters to fit historical data. This can lead to poor performance in live trading due to changing market conditions.
Implementing a Grid Trading Strategy
To successfully implement a grid trading strategy, consider the following steps:
- Choose a Suitable Market: Select a currency pair or other asset that tends to trade within a defined range. Avoid markets that are prone to strong trends.
- Backtest the Strategy: Use historical data to test the performance of the grid trading strategy with different parameters. This will help identify the optimal grid range, spacing, and position size.
- Use a Reliable Trading Platform: Choose a trading platform that supports automated order placement and execution. Ensure that the platform offers robust risk management tools.
- Monitor the Strategy: Regularly monitor the performance of the grid trading strategy and adjust the parameters as needed. Be prepared to modify the grid range or stop the strategy if market conditions change.
- Manage Risk: Implement strict risk management controls, including stop-loss orders and position sizing limits. Never risk more capital than you can afford to lose.
Advanced Grid Trading Techniques
Experienced traders may explore advanced grid trading techniques to enhance their strategy:
Dynamic Grid Adjustment
This technique involves adjusting the grid range and spacing based on changing market conditions. For example, if volatility increases, the grid spacing can be widened to reduce the frequency of trades. Dynamic grid adjustment requires real-time market analysis and sophisticated trading algorithms. [See also: Algorithmic Trading Strategies]
Hedging Strategies
Hedging involves taking offsetting positions to reduce the risk of adverse price movements. In grid trading, hedging can be used to protect against significant drawdowns if the price breaks out of the grid range. For example, a trader might place a stop order to automatically initiate a short position if the price falls below the lower boundary of the grid.
Combining with Technical Indicators
Grid trading can be combined with technical indicators to improve the accuracy of order placement. For example, traders might use moving averages or oscillators to identify potential entry points within the grid. This can help to filter out false signals and increase the probability of profitable trades.
The Future of Grid Trading
As technology continues to evolve, grid trading is likely to become even more sophisticated and accessible. The development of advanced trading platforms and artificial intelligence (AI) will enable traders to automate and optimize their grid trading strategies with greater precision. AI-powered algorithms can analyze vast amounts of market data to identify optimal grid parameters and dynamically adjust the grid based on real-time conditions. Furthermore, the increasing availability of historical data and backtesting tools will allow traders to refine their strategies and improve their performance.
Conclusion
Grid trading is a powerful automated trading strategy that can be effective in range-bound markets. By understanding the mechanics, advantages, and disadvantages of grid trading, traders can make informed decisions about whether to incorporate it into their trading arsenal. While grid trading offers the potential for consistent profits, it also carries inherent risks. Proper risk management, thorough backtesting, and continuous monitoring are essential for successful implementation. As the forex market continues to evolve, grid trading will likely remain a valuable tool for traders seeking to capitalize on market volatility and generate consistent returns.
