Hedge Fund vs. Mutual Fund: Understanding the Key Differences
Navigating the world of investments can feel like traversing a complex maze. Two prominent players in this arena are hedge funds and mutual funds. Both offer avenues for investors to grow their wealth, but they operate under different structures, cater to different clientele, and employ vastly different strategies. Understanding the distinctions between a hedge fund vs. mutual fund is crucial for making informed investment decisions. This article aims to provide a clear and concise comparison, highlighting the key differences and helping you determine which option, if either, aligns with your financial goals and risk tolerance.
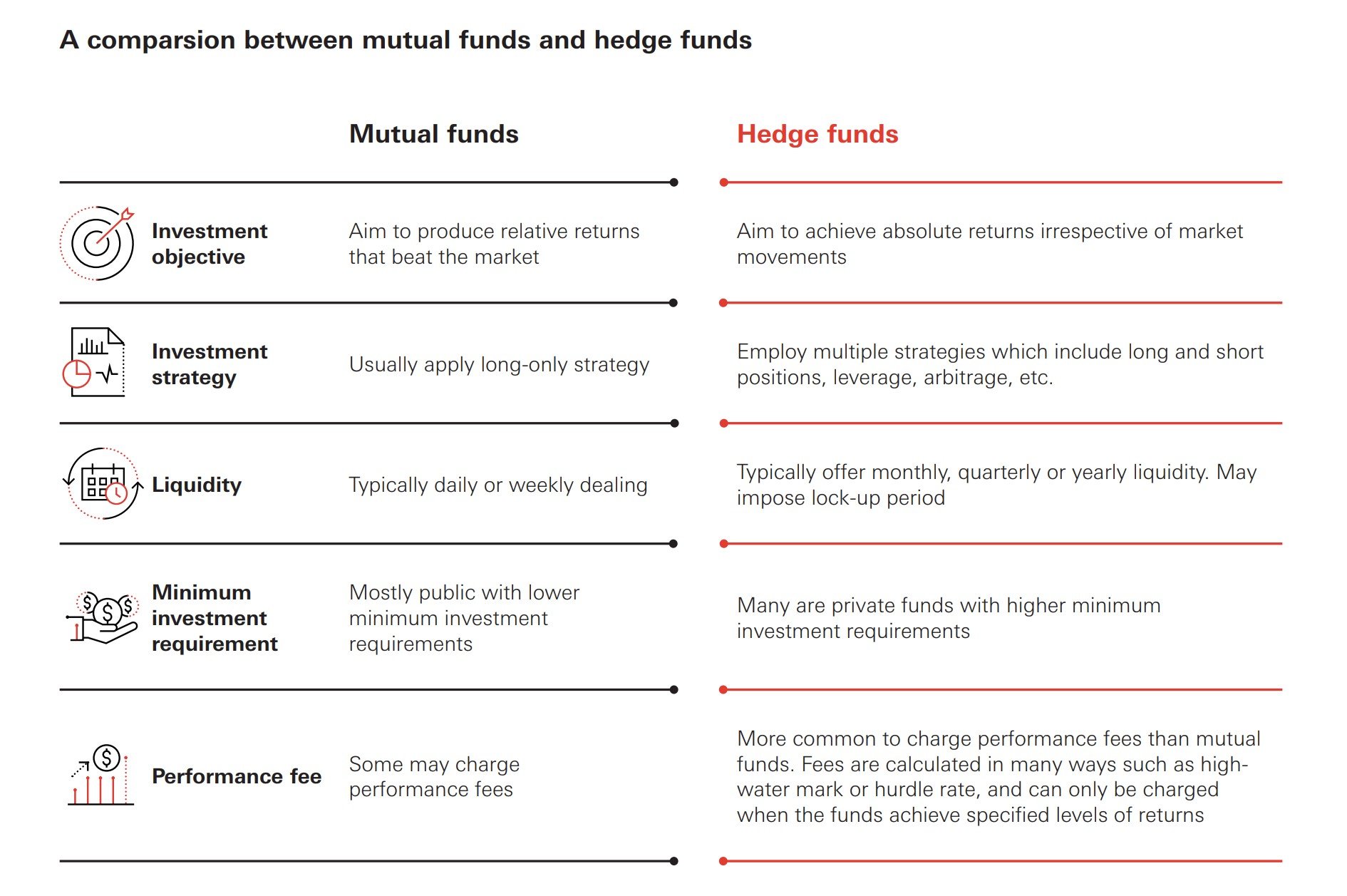
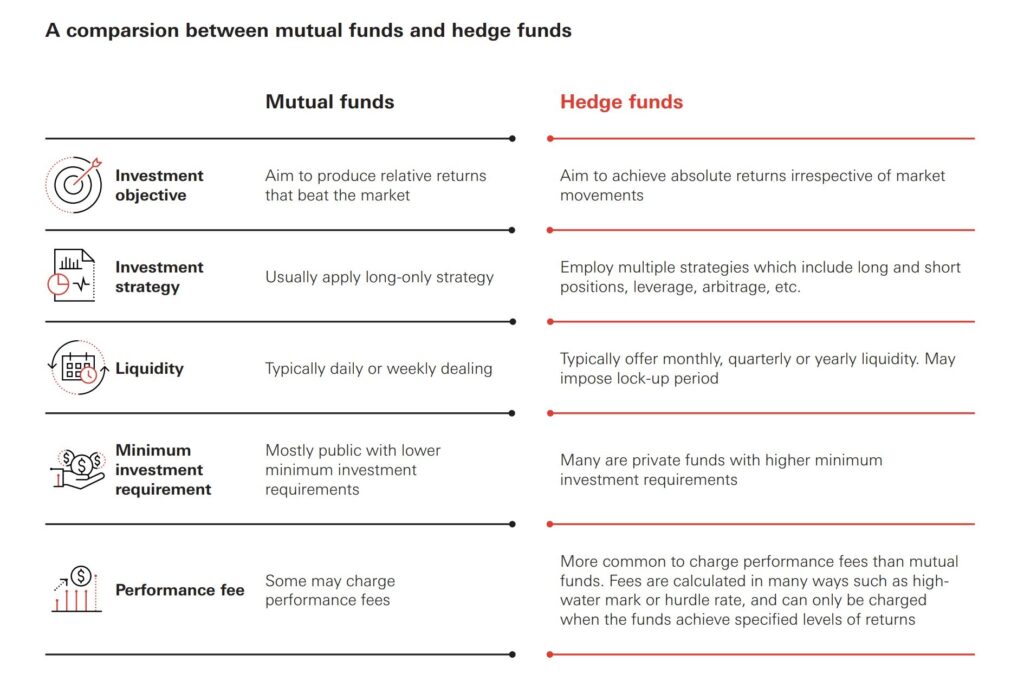
What is a Mutual Fund?
A mutual fund is a type of investment vehicle that pools money from many investors to purchase a diversified portfolio of stocks, bonds, or other assets. The fund is managed by a professional fund manager who makes investment decisions on behalf of the investors. Mutual funds are regulated by government agencies like the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) to protect investors.
Key Characteristics of Mutual Funds:
- Accessibility: Mutual funds are generally accessible to a wide range of investors, including those with relatively small amounts of capital.
- Regulation: They are heavily regulated to ensure transparency and investor protection.
- Diversification: Mutual funds offer instant diversification, spreading risk across a variety of assets.
- Liquidity: Investors can typically buy or sell shares of a mutual fund on any business day.
- Transparency: Mutual funds are required to disclose their holdings and performance regularly.
What is a Hedge Fund?
A hedge fund, in contrast, is a private investment partnership that uses more aggressive strategies to generate higher returns. These strategies can include short selling, leverage, derivatives, and arbitrage. Hedge funds are typically open only to accredited investors, meaning those with high net worth or income. Because they cater to sophisticated investors, hedge funds face fewer regulatory constraints than mutual funds.
Key Characteristics of Hedge Funds:
- Exclusivity: Hedge funds are primarily accessible to accredited investors due to high minimum investment requirements.
- Less Regulation: They are subject to less stringent regulations compared to mutual funds.
- Complex Strategies: Hedge funds employ complex and often risky investment strategies.
- Lower Liquidity: Investors may face restrictions on when they can withdraw their money. Lock-up periods are common.
- Higher Fees: Hedge funds typically charge higher fees, including management fees and performance fees (often referred to as the “2 and 20” model).
Hedge Fund vs. Mutual Fund: A Detailed Comparison
Let’s delve deeper into the specific differences between a hedge fund vs. mutual fund:
Investor Base
Mutual funds are designed for the average investor looking for a diversified and relatively safe investment option. Hedge funds, on the other hand, target high-net-worth individuals, institutional investors (like pension funds and endowments), and other sophisticated investors who can tolerate higher risk.
Investment Strategies
Mutual funds generally follow a more conservative investment approach, focusing on long-term growth and diversification. They typically invest in a broad range of stocks and bonds, aiming to mirror the performance of a specific market index or benchmark. Hedge funds employ a wider range of strategies, including short selling (betting against stocks), leverage (borrowing money to amplify returns), and derivatives (contracts whose value is derived from an underlying asset). These strategies can generate higher returns but also carry significantly higher risk.
Regulation
Mutual funds are heavily regulated by the SEC to protect investors. Regulations cover areas such as disclosure requirements, fund governance, and investment restrictions. Hedge funds are subject to fewer regulations, giving them greater flexibility in their investment strategies. However, this also means less oversight and potentially higher risk for investors. This lack of oversight is a key differentiator in the hedge fund vs. mutual fund comparison.
Fees
Mutual funds typically charge lower fees than hedge funds. The most common fee is an expense ratio, which covers the fund’s operating expenses. Hedge funds often charge a management fee (typically around 2% of assets under management) and a performance fee (typically around 20% of profits). This “2 and 20” model can result in significantly higher fees for hedge fund investors, especially if the fund performs well.
Liquidity
Mutual funds offer high liquidity, allowing investors to buy or sell shares on any business day. Hedge funds often have lock-up periods, restricting when investors can withdraw their money. This lack of liquidity can be a significant drawback for some investors. Consider the liquidity differences when evaluating a hedge fund vs. mutual fund.
Transparency
Mutual funds are required to disclose their holdings and performance regularly, providing investors with a clear picture of their investments. Hedge funds are less transparent, providing less information to investors about their strategies and holdings. This lack of transparency can make it difficult for investors to assess the risk and potential return of a hedge fund.
Examples of Investment Strategies
To further illustrate the differences, here are some specific examples:
- Long-Short Equity: A hedge fund strategy that involves taking long positions in stocks expected to rise in value and short positions in stocks expected to decline. A mutual fund might only take long positions.
- Fixed Income Arbitrage: A hedge fund strategy that exploits price discrepancies in fixed income securities. Mutual funds typically don’t engage in arbitrage strategies.
- Global Macro: A hedge fund strategy that makes investment decisions based on macroeconomic trends. While some mutual funds consider macroeconomic factors, they typically don’t make highly speculative bets based on these trends.
Which is Right for You?
The choice between a hedge fund vs. mutual fund depends on your individual circumstances, financial goals, and risk tolerance. If you are a retail investor looking for a diversified and relatively safe investment option, a mutual fund is likely the better choice. If you are an accredited investor with a high risk tolerance and a desire for potentially higher returns, a hedge fund may be worth considering. However, it’s crucial to thoroughly research any hedge fund before investing and to understand the risks involved.
Consider these factors when making your decision:
- Investment Goals: What are you trying to achieve with your investments?
- Risk Tolerance: How much risk are you willing to take?
- Investment Horizon: How long do you plan to invest your money?
- Financial Situation: Can you afford the high minimum investment requirements and fees associated with hedge funds?
- Liquidity Needs: Do you need easy access to your money?
The Future of Hedge Funds and Mutual Funds
Both hedge funds and mutual funds continue to evolve in response to changing market conditions and investor demands. The rise of passive investing and exchange-traded funds (ETFs) has put pressure on actively managed mutual funds to justify their fees. Hedge funds are facing increased scrutiny from regulators and investors regarding transparency and performance. The hedge fund vs. mutual fund dynamic is constantly shifting as both industries adapt. [See also: Understanding ETF Investing Strategies]
Conclusion
Understanding the differences between a hedge fund vs. mutual fund is essential for making informed investment decisions. Mutual funds offer accessibility, diversification, and regulation, making them suitable for a wide range of investors. Hedge funds provide the potential for higher returns through complex strategies but come with higher risk, higher fees, and less liquidity. Carefully consider your individual circumstances and consult with a financial advisor before making any investment decisions. Ultimately, the best investment vehicle is the one that aligns with your specific needs and goals. Before making a decision, analyze your risk profile and goals. The difference between a hedge fund vs. mutual fund can significantly impact your investment outcome. Remember to research and understand all fees associated with each option. Many investors start with mutual funds before exploring hedge funds. The choice is yours based on your financial situation and risk appetite.