Hedge Funds vs. Mutual Funds: Understanding the Key Differences
When navigating the world of investments, two common options often arise: hedge funds and mutual funds. While both serve as investment vehicles pooling capital from various investors, significant differences between hedge funds and mutual funds exist in their structure, investment strategies, regulation, and investor accessibility. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for making informed investment decisions aligned with your financial goals and risk tolerance.
What are Mutual Funds?
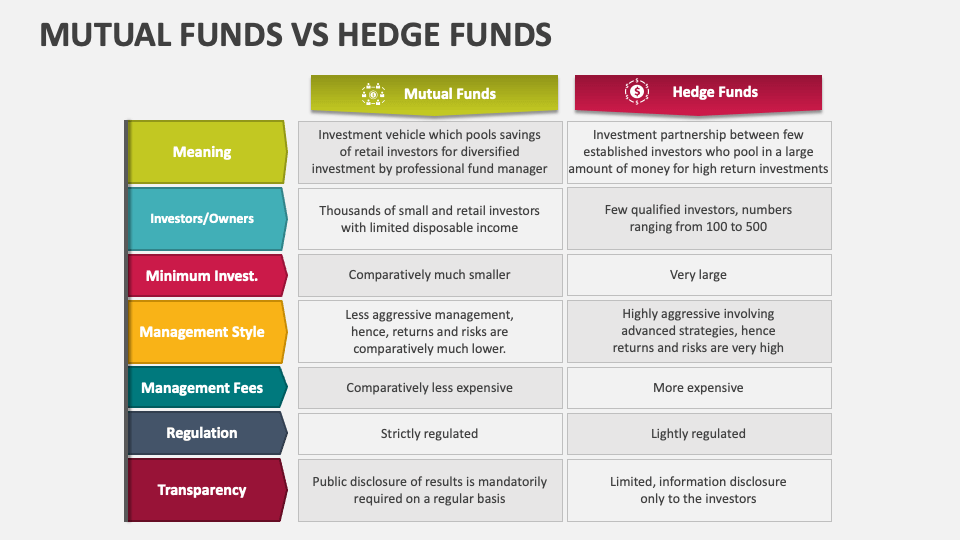
Mutual funds are investment vehicles that pool money from many investors to purchase a diversified portfolio of stocks, bonds, or other assets. They are managed by professional fund managers who aim to achieve specific investment objectives outlined in the fund’s prospectus. Mutual funds are typically regulated by government agencies like the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) in the United States, providing a level of investor protection and transparency.
Key Characteristics of Mutual Funds:
- Diversification: Mutual funds offer instant diversification by investing in a basket of securities, reducing the risk associated with individual investments.
- Liquidity: Investors can typically buy or sell mutual fund shares daily at the fund’s net asset value (NAV).
- Regulation: Mutual funds are subject to strict regulatory oversight, ensuring transparency and protecting investors.
- Accessibility: Mutual funds are widely accessible to retail investors with relatively low minimum investment requirements.
- Transparency: Mutual funds are required to disclose their holdings and performance regularly.
What are Hedge Funds?
Hedge funds, on the other hand, are investment partnerships that employ more complex and often riskier investment strategies to generate higher returns. They are typically available only to accredited investors, such as high-net-worth individuals and institutional investors, due to their higher minimum investment requirements and greater risk profile. The differences between hedge funds and mutual funds are vast.
Key Characteristics of Hedge Funds:
- Sophisticated Strategies: Hedge funds utilize a wide range of investment strategies, including short-selling, leverage, derivatives, and arbitrage, which can be more complex and speculative than those used by mutual funds.
- Limited Liquidity: Hedge funds often have lock-up periods, restricting investors from withdrawing their funds for a specified period.
- Less Regulation: Hedge funds are subject to less regulatory oversight than mutual funds, allowing them greater flexibility in their investment strategies but also exposing investors to higher risks.
- Accredited Investors Only: Hedge funds are typically only accessible to accredited investors who meet specific income or net worth requirements.
- Performance Fees: Hedge funds typically charge performance fees, often a percentage of the profits generated, in addition to management fees.
Detailed Differences Between Hedge Funds and Mutual Funds
To further clarify the differences between hedge funds and mutual funds, let’s delve into a detailed comparison across several key aspects:
Investor Eligibility
Mutual funds are designed for a broad range of investors, including retail investors with varying levels of investment experience. Hedge funds, however, are typically restricted to accredited investors, defined as individuals with a net worth exceeding $1 million (excluding their primary residence) or an annual income of at least $200,000 (or $300,000 combined with a spouse) for the past two years, with a reasonable expectation of reaching the same income level in the current year. This restriction is in place because hedge funds are considered riskier investments, and regulators believe that only sophisticated investors with the financial resources to withstand potential losses should participate.
Investment Strategies
Mutual funds generally adhere to more conservative investment strategies, focusing on long-term growth and diversification. They often invest in a broad range of stocks and bonds, aiming to match or outperform a specific market index. Hedge funds, on the other hand, employ a much wider range of investment strategies, including short-selling, leverage, arbitrage, and derivatives trading. These strategies are designed to generate higher returns, regardless of market direction, but they also carry significantly higher risks. The differences between hedge funds and mutual funds in strategies is substantial.
Regulation and Transparency
Mutual funds are subject to extensive regulation by government agencies like the SEC. This regulation aims to protect investors by ensuring transparency, requiring regular disclosure of fund holdings and performance, and limiting the types of investments funds can make. Hedge funds are subject to less regulatory oversight, giving them greater flexibility in their investment strategies but also reducing transparency for investors. This lack of transparency can make it more difficult for investors to assess the risks associated with hedge fund investments. [See also: Understanding Investment Risks]
Fees and Expenses
Mutual funds typically charge management fees, which are a percentage of the fund’s assets under management (AUM). These fees cover the costs of managing the fund and are typically disclosed in the fund’s prospectus. Hedge funds typically charge both management fees and performance fees. Management fees are similar to those charged by mutual funds, but performance fees are a percentage of the profits generated by the fund. This fee structure incentivizes hedge fund managers to generate higher returns, but it also means that investors pay a higher price for successful performance. The structure of fees is one of the key differences between hedge funds and mutual funds.
Liquidity
Mutual funds offer high liquidity, allowing investors to buy or sell shares daily at the fund’s NAV. This liquidity makes it easy for investors to access their funds when needed. Hedge funds often have lock-up periods, restricting investors from withdrawing their funds for a specified period, typically several months or years. This lack of liquidity can be a disadvantage for investors who may need to access their funds quickly. The illiquidity is another of the key differences between hedge funds and mutual funds.
Risk Profile
Mutual funds are generally considered less risky than hedge funds due to their diversified portfolios and adherence to more conservative investment strategies. However, the risk profile of a mutual fund can vary depending on its investment objectives. For example, a bond fund is typically less risky than a stock fund. Hedge funds are generally considered riskier investments due to their use of complex investment strategies and leverage. These strategies can generate higher returns, but they also carry a greater risk of losses. The level of risk is a major factor when considering the differences between hedge funds and mutual funds.
Hedge Funds vs. Mutual Funds: A Summary Table
| Feature | Mutual Funds | Hedge Funds |
|---|---|---|
| Investor Eligibility | All investors | Accredited investors only |
| Investment Strategies | Conservative, diversified | Complex, potentially risky |
| Regulation | Highly regulated | Less regulated |
| Fees | Management fees | Management and performance fees |
| Liquidity | High | Low |
| Risk Profile | Lower | Higher |
Choosing Between Hedge Funds and Mutual Funds
The choice between hedge funds and mutual funds depends on your individual investment goals, risk tolerance, and financial situation. If you are a retail investor seeking diversified exposure to the market with relatively low risk, mutual funds may be a suitable option. If you are an accredited investor with a high-risk tolerance and a desire for potentially higher returns, hedge funds may be worth considering. However, it is crucial to conduct thorough due diligence and understand the risks associated with hedge fund investments before making any decisions. The differences between hedge funds and mutual funds are so significant that they attract different kinds of investors.
Conclusion
Understanding the differences between hedge funds and mutual funds is essential for making informed investment decisions. Mutual funds offer diversification, liquidity, and transparency, making them suitable for a wide range of investors. Hedge funds offer the potential for higher returns but come with higher risks, less liquidity, and limited accessibility. By carefully evaluating your investment goals, risk tolerance, and financial situation, you can determine which type of investment vehicle is right for you. Remember to consult with a qualified financial advisor before making any investment decisions. Consider all the differences between hedge funds and mutual funds before investing. Both offer advantages, but one might be better suited than the other.
