Leverage Calculator: Maximize Your Investments with Precision
In the world of finance and trading, leverage is a powerful tool that can amplify both potential gains and potential losses. Understanding how to use leverage effectively is crucial for any investor or trader. A leverage calculator is an indispensable tool in this process, allowing individuals to assess the impact of leverage on their investments and make informed decisions. This article delves into the intricacies of leverage, exploring what it is, how it works, and how a leverage calculator can be used to optimize your investment strategies.
What is Leverage?
Leverage, in its simplest form, is the use of borrowed capital to increase the potential return of an investment. It allows you to control a larger position in the market than you could with your own capital alone. For example, if you have $1,000 and leverage of 10:1, you can control a position worth $10,000. This means that any gains or losses are calculated on the $10,000 position, not just your initial $1,000.
Leverage is commonly used in various financial markets, including:
- Forex (Foreign Exchange): Forex trading often involves high leverage ratios due to the relatively small price movements.
- Stocks: Margin accounts allow investors to borrow money from their broker to buy stocks.
- Commodities: Futures contracts often require a margin deposit, which represents a leveraged position in the underlying commodity.
- Real Estate: Mortgages allow individuals to purchase properties with a relatively small down payment, leveraging the bank’s capital.
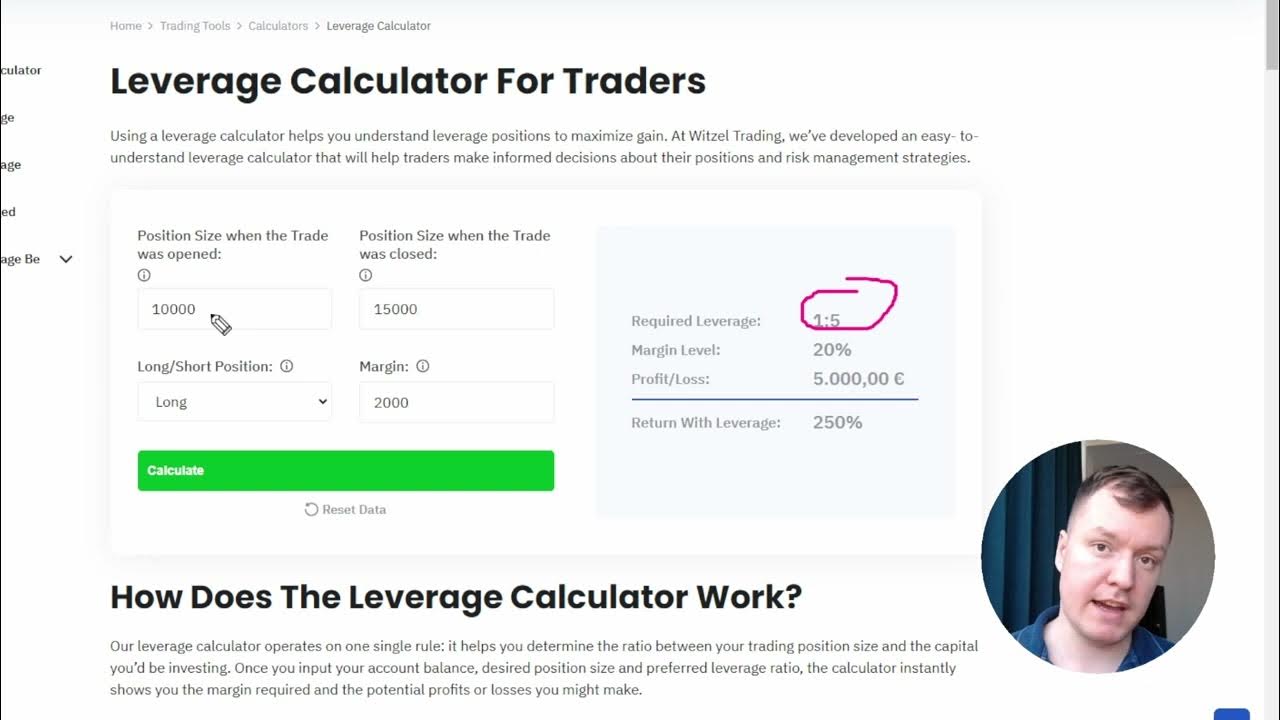
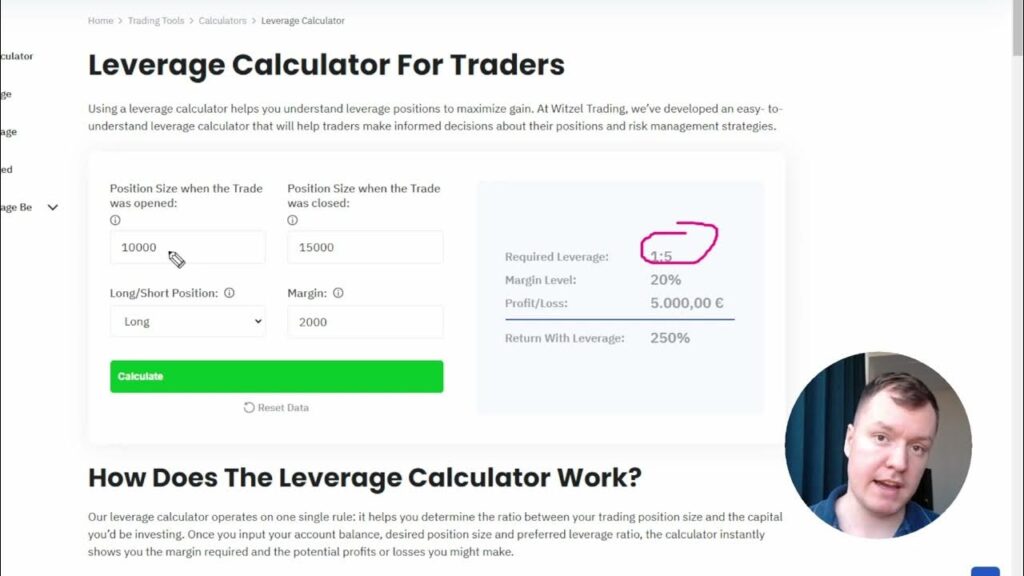
How a Leverage Calculator Works
A leverage calculator is a simple yet powerful tool that helps traders and investors understand the impact of leverage on their positions. It typically requires a few key inputs:
- Account Balance: The amount of capital you have available for trading or investment.
- Leverage Ratio: The ratio of borrowed capital to your own capital (e.g., 1:10, 1:50, 1:100).
- Position Size: The total value of the position you want to control.
- Asset Price: The current price of the asset you are trading.
Based on these inputs, the leverage calculator will provide you with the following information:
- Margin Required: The amount of capital you need to deposit to open the position.
- Potential Profit or Loss: The potential gain or loss based on a specific price movement.
- Risk Exposure: An assessment of the potential risk associated with the leveraged position.
Benefits of Using a Leverage Calculator
Using a leverage calculator offers several significant benefits for traders and investors:
Risk Management
One of the primary benefits is improved risk management. By understanding the potential impact of leverage on your positions, you can make more informed decisions about position sizing and risk tolerance. A leverage calculator helps you visualize the worst-case scenarios and adjust your strategy accordingly. It allows you to answer questions like, “What if the market moves against me by x percent?” and prepare for that eventuality.
Informed Decision-Making
A leverage calculator provides you with the data you need to make informed decisions. Instead of relying on gut feelings or intuition, you can use concrete numbers to assess the potential risks and rewards of a trade. This data-driven approach can lead to more consistent and profitable trading outcomes. Knowing the exact margin requirements and potential profit/loss scenarios empowers you to trade with greater confidence.
Optimized Position Sizing
Proper position sizing is crucial for successful trading. A leverage calculator can help you determine the optimal position size based on your account balance, risk tolerance, and the leverage ratio. By correctly sizing your positions, you can avoid overexposing your capital and minimize the risk of significant losses. It also helps to avoid under-leveraging, ensuring that you maximize opportunities when they arise.
Understanding Margin Requirements
Margin requirements can be complex, especially for novice traders. A leverage calculator simplifies this process by clearly showing you the amount of capital you need to deposit to open a specific position. This helps you avoid unexpected margin calls and ensures that you always have sufficient funds to cover your positions. Understanding margin requirements is fundamental to responsible leverage use.
Scenario Analysis
A leverage calculator allows you to perform scenario analysis by simulating different price movements and their impact on your positions. This can help you prepare for various market conditions and develop contingency plans. For example, you can use the calculator to see how a 1% increase or decrease in the asset price would affect your profit or loss. This type of analysis is invaluable for stress-testing your trading strategies.
Examples of Leverage in Action
Let’s look at a few examples to illustrate how leverage works and how a leverage calculator can be used in different scenarios:
Example 1: Forex Trading
Suppose you have an account balance of $5,000 and you want to trade EUR/USD with a leverage ratio of 1:50. You want to open a position of 1 lot (100,000 EUR). Using a leverage calculator, you can determine the margin required:
Margin Required = (Position Size / Leverage Ratio) = (100,000 EUR / 50) = 2,000 EUR
This means you need to deposit 2,000 EUR (approximately $2,200 USD) to open the position. The leverage calculator also helps you determine the potential profit or loss based on price movements. If EUR/USD moves by 100 pips (0.0100), your profit or loss would be $1,000.
Example 2: Stock Trading
You want to buy 100 shares of a stock priced at $100 per share, totaling $10,000. You have a margin account with a leverage ratio of 2:1. Using a leverage calculator:
Margin Required = (Total Position Value / Leverage Ratio) = ($10,000 / 2) = $5,000
You need to deposit $5,000 to buy the shares. If the stock price increases by 10% to $110 per share, your profit would be $1,000, representing a 20% return on your margin deposit. However, if the stock price decreases by 10% to $90 per share, your loss would also be $1,000, representing a 20% loss on your margin deposit. The leverage calculator makes these outcomes clear before you commit capital.
Example 3: Real Estate Investment
You want to purchase a property for $500,000 and you secure a mortgage with a 20% down payment. This means you are leveraging the bank’s capital for 80% of the purchase price. While a traditional leverage calculator might not apply directly, the concept of leverage is the same. Your initial investment (down payment) is $100,000, and you are controlling an asset worth $500,000. If the property value increases by 10% to $550,000, your equity increases by $50,000, representing a 50% return on your initial investment (excluding mortgage payments and other expenses).
Choosing the Right Leverage Calculator
Several leverage calculators are available online, each with its own features and functionalities. When choosing a leverage calculator, consider the following factors:
- Accuracy: Ensure that the calculator provides accurate calculations based on the inputs you provide.
- User-Friendliness: Look for a calculator that is easy to use and understand, with a clear and intuitive interface.
- Customization: Choose a calculator that allows you to customize the inputs and outputs to suit your specific needs.
- Additional Features: Some calculators offer additional features such as risk assessment tools, position sizing recommendations, and scenario analysis capabilities.
The Risks of Leverage
While leverage can amplify potential gains, it also amplifies potential losses. It’s crucial to understand the risks associated with leverage before using it in your trading or investment strategies. Some of the key risks include:
- Magnified Losses: As mentioned earlier, leverage can magnify losses, potentially leading to significant financial setbacks.
- Margin Calls: If your positions move against you and your account balance falls below the required margin, your broker may issue a margin call, requiring you to deposit additional funds to cover the losses.
- Increased Volatility: Leveraged positions are more sensitive to market volatility, which can lead to rapid and unpredictable price swings.
- Emotional Trading: The pressure of managing leveraged positions can lead to emotional trading decisions, which can further exacerbate losses.
To mitigate these risks, it’s essential to use leverage responsibly and implement effective risk management strategies. This includes setting stop-loss orders, diversifying your portfolio, and avoiding over-leveraging your account. [See also: Risk Management Strategies for Traders]
Best Practices for Using Leverage
To use leverage effectively and responsibly, consider the following best practices:
- Understand Your Risk Tolerance: Before using leverage, assess your risk tolerance and determine how much capital you are willing to risk on each trade.
- Use Stop-Loss Orders: Always use stop-loss orders to limit your potential losses. A stop-loss order is an instruction to your broker to automatically close your position if the price reaches a certain level.
- Diversify Your Portfolio: Avoid putting all your eggs in one basket. Diversify your portfolio across different asset classes and markets to reduce your overall risk exposure.
- Avoid Over-Leveraging: Don’t over-leverage your account. Use a leverage calculator to determine the appropriate position size based on your account balance and risk tolerance.
- Stay Informed: Stay informed about market conditions and economic events that could impact your positions.
- Practice with a Demo Account: Before trading with real money, practice using leverage with a demo account to familiarize yourself with the risks and rewards.
Conclusion
A leverage calculator is an essential tool for any trader or investor who wants to use leverage effectively and responsibly. By understanding the impact of leverage on your positions, you can make more informed decisions, manage your risk, and optimize your investment strategies. However, it’s crucial to remember that leverage is a double-edged sword, and it’s essential to use it with caution and implement effective risk management strategies. By following the best practices outlined in this article, you can harness the power of leverage to maximize your investment potential while minimizing your risk exposure. [See also: Advanced Trading Techniques]