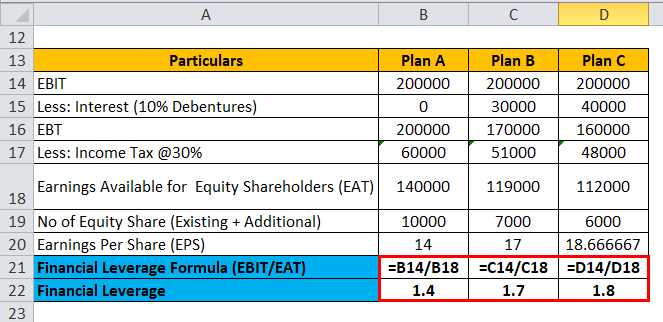
Leverage Calculator: Understanding and Utilizing Financial Leverage
In the world of finance, leverage is a powerful tool that can amplify both gains and losses. Understanding how leverage works and how to calculate its potential impact is crucial for making informed investment and financial decisions. A leverage calculator is an invaluable resource for anyone looking to understand and utilize financial leverage effectively. This article delves into the concept of leverage, explores the functionality of a leverage calculator, and provides insights into how it can be used to optimize financial strategies.
What is Leverage?
Leverage, in simple terms, is the use of borrowed capital to increase the potential return of an investment. It allows individuals or businesses to control a larger asset base with a smaller amount of their own capital. While leverage can significantly enhance profits, it also magnifies potential losses, making it a double-edged sword.
Common forms of leverage include:
- Debt Financing: Borrowing money to invest in a business or project.
- Margin Trading: Borrowing funds from a broker to trade securities.
- Derivatives: Using financial instruments like options and futures to control a larger underlying asset.
Understanding the Leverage Calculator
A leverage calculator is a tool designed to help users quantify the potential impact of leverage on their investments or financial positions. These calculators typically require several inputs, such as the initial investment, the amount of borrowed capital, and the expected return on investment. The calculator then provides outputs like the potential profit or loss, the return on equity, and the leverage ratio.
Key Components of a Leverage Calculator
A comprehensive leverage calculator often includes the following features:
- Initial Investment: The amount of capital the user is willing to invest.
- Borrowed Capital: The amount of money the user borrows to increase their investment capacity.
- Interest Rate: The cost of borrowing the capital, expressed as an annual percentage.
- Expected Return on Investment: The anticipated percentage return on the total investment (including borrowed capital).
- Leverage Ratio: A measure of how much debt is used to finance assets, calculated as total assets divided by equity.
How to Use a Leverage Calculator
Using a leverage calculator is straightforward. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
- Input the Initial Investment: Enter the amount of your own capital you are investing.
- Enter the Borrowed Capital: Input the amount of money you are borrowing.
- Specify the Interest Rate: Enter the interest rate on the borrowed capital.
- Enter the Expected Return on Investment: Input your estimated return on the total investment.
- Calculate and Analyze: The calculator will then compute the potential profit or loss, return on equity, and leverage ratio. Analyze these results to understand the potential risks and rewards.
Benefits of Using a Leverage Calculator
Employing a leverage calculator offers several advantages for investors and financial managers:
Risk Assessment
One of the primary benefits is the ability to assess the potential risks associated with leverage. By inputting different scenarios, users can see how changes in the expected return can impact their overall profitability and potential losses. This helps in making more informed decisions and setting appropriate risk management strategies.
Return on Equity Analysis
A leverage calculator helps in understanding how leverage affects the return on equity (ROE). ROE is a key metric for evaluating the profitability of a company or investment relative to the amount of equity invested. By calculating ROE with and without leverage, users can determine whether the use of leverage is truly beneficial.
Financial Planning
For businesses, a leverage calculator is an essential tool for financial planning. It can help in determining the optimal level of debt financing to maximize shareholder value while maintaining a healthy financial position. It also aids in evaluating the impact of different debt structures on the company’s financial performance.
Investment Decisions
Investors can use a leverage calculator to evaluate the potential returns and risks of leveraged investments, such as margin trading or real estate investments. This allows them to make more informed decisions and avoid overleveraging, which can lead to significant financial losses. Understanding the impact of a leverage calculator can be extremely helpful.
Examples of Leverage Calculation
Let’s consider a couple of examples to illustrate how a leverage calculator can be used in practice.
Example 1: Margin Trading
Suppose an investor wants to buy shares worth $10,000 and uses margin trading with a 50% margin requirement. This means they need to put up $5,000 of their own money and borrow the remaining $5,000 from the broker. If the shares increase in value by 10%, the total value of the shares becomes $11,000. After repaying the borrowed $5,000 (plus interest), the investor is left with a profit. A leverage calculator can quickly compute the return on equity in this scenario, accounting for the interest paid on the borrowed funds.
Example 2: Real Estate Investment
An individual purchases a property for $500,000, making a down payment of $100,000 and taking out a mortgage for $400,000. If the property appreciates in value by 5%, it is now worth $525,000. The investor’s equity has increased by $25,000. A leverage calculator can help determine the return on investment, taking into account mortgage payments, property taxes, and other expenses. The leverage calculator provides a clear picture of the potential profitability of the investment.
Risks Associated with Leverage
While leverage can enhance returns, it also comes with significant risks:
- Magnified Losses: Just as leverage can amplify profits, it can also magnify losses. If an investment performs poorly, the losses can quickly erode the investor’s equity.
- Interest Costs: Borrowed capital comes with interest costs, which can reduce the overall profitability of the investment.
- Margin Calls: In margin trading, if the value of the securities falls below a certain level, the broker may issue a margin call, requiring the investor to deposit additional funds to cover the losses.
- Financial Distress: Excessive leverage can lead to financial distress, making it difficult to meet debt obligations and potentially leading to bankruptcy.
Advanced Features of Leverage Calculators
Some advanced leverage calculators offer additional features that can provide even more detailed insights:
- Sensitivity Analysis: This feature allows users to assess how the results change based on different input values, such as varying interest rates or expected returns.
- Scenario Planning: Users can create multiple scenarios to evaluate the potential outcomes under different economic conditions or investment strategies.
- Tax Considerations: Some calculators incorporate tax considerations to provide a more accurate picture of the after-tax profitability of leveraged investments.
Choosing the Right Leverage Calculator
When selecting a leverage calculator, consider the following factors:
- Accuracy: Ensure that the calculator is accurate and uses the correct formulas and assumptions.
- Ease of Use: The calculator should be user-friendly and easy to navigate.
- Features: Look for a calculator that offers the features you need, such as sensitivity analysis or scenario planning.
- Credibility: Choose a calculator from a reputable source to ensure its reliability.
Leverage Calculator in Corporate Finance
In corporate finance, the leverage calculator is an indispensable tool. Companies use it to determine the optimal capital structure, balancing debt and equity to maximize shareholder value. Too much debt can increase the risk of financial distress, while too little debt may result in missed opportunities for growth and increased returns. A leverage calculator assists in finding the sweet spot.
Financial analysts also use leverage calculators to assess the financial health of a company. Key ratios like debt-to-equity and debt-to-asset are easily computed using a leverage calculator, providing insights into the company’s risk profile and its ability to meet its financial obligations. [See also: Understanding Debt-to-Equity Ratio]
The Future of Leverage Calculation
As financial markets become more complex, the sophistication of leverage calculators will continue to evolve. We can expect to see more advanced features, such as:
- Integration with Real-Time Data: Calculators will be able to pull real-time market data to provide more accurate and up-to-date results.
- AI-Powered Analysis: Artificial intelligence and machine learning will be used to provide more sophisticated risk assessments and investment recommendations.
- Customizable Models: Users will be able to create custom models that incorporate their specific financial goals and risk tolerance.
Conclusion
A leverage calculator is an essential tool for anyone involved in finance, whether they are individual investors, financial managers, or corporate executives. By understanding how leverage works and using a calculator to quantify its potential impact, individuals and businesses can make more informed decisions and optimize their financial strategies. While leverage can be a powerful tool for enhancing returns, it is crucial to be aware of the associated risks and to use it responsibly. Ultimately, a well-informed approach to leverage, guided by a reliable leverage calculator, can lead to greater financial success.
