Mutual Funds vs. Hedge Funds: Understanding the Key Differences
Navigating the world of investment can be daunting, especially when faced with a plethora of options. Two prominent investment vehicles often compared are mutual funds and hedge funds. While both pool capital from investors, their operational strategies, risk profiles, and accessibility differ significantly. This article delves into the key differences between mutual funds and hedge funds, providing a clear understanding for potential investors.
What are Mutual Funds?
A mutual fund is a type of investment vehicle that pools money from many investors to purchase a diversified portfolio of stocks, bonds, or other assets. These funds are managed by professional money managers who aim to achieve a specific investment objective, such as growth, income, or capital preservation. Mutual funds are regulated and offer transparency, making them accessible to a wide range of investors.
Key Characteristics of Mutual Funds:
- Diversification: Mutual funds invest in a variety of assets, reducing the risk associated with investing in individual securities.
- Liquidity: Investors can typically buy or sell shares of a mutual fund at the end of each trading day.
- Regulation: Mutual funds are heavily regulated by government agencies like the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC), ensuring investor protection.
- Accessibility: Mutual funds are generally accessible to all investors, with relatively low minimum investment amounts.
- Transparency: Mutual funds are required to disclose their holdings and performance regularly, providing investors with clear information.
What are Hedge Funds?
A hedge fund is a privately managed investment fund that employs a variety of sophisticated investment strategies to generate returns. Unlike mutual funds, hedge funds are less regulated and often target high-net-worth individuals and institutional investors. They typically use leverage, short-selling, and other complex techniques to maximize profits, which also increases risk.
Key Characteristics of Hedge Funds:
- Sophisticated Strategies: Hedge funds use a wide range of complex investment strategies, including arbitrage, event-driven investing, and global macro strategies.
- Limited Regulation: Hedge funds are subject to less stringent regulations compared to mutual funds.
- High Minimum Investments: Hedge funds typically require substantial minimum investments, often hundreds of thousands or even millions of dollars.
- Limited Liquidity: Investors may face restrictions on when they can withdraw their money from a hedge fund, with lock-up periods and redemption fees.
- Performance-Based Fees: Hedge fund managers often charge performance-based fees, such as a percentage of the profits generated, in addition to management fees.
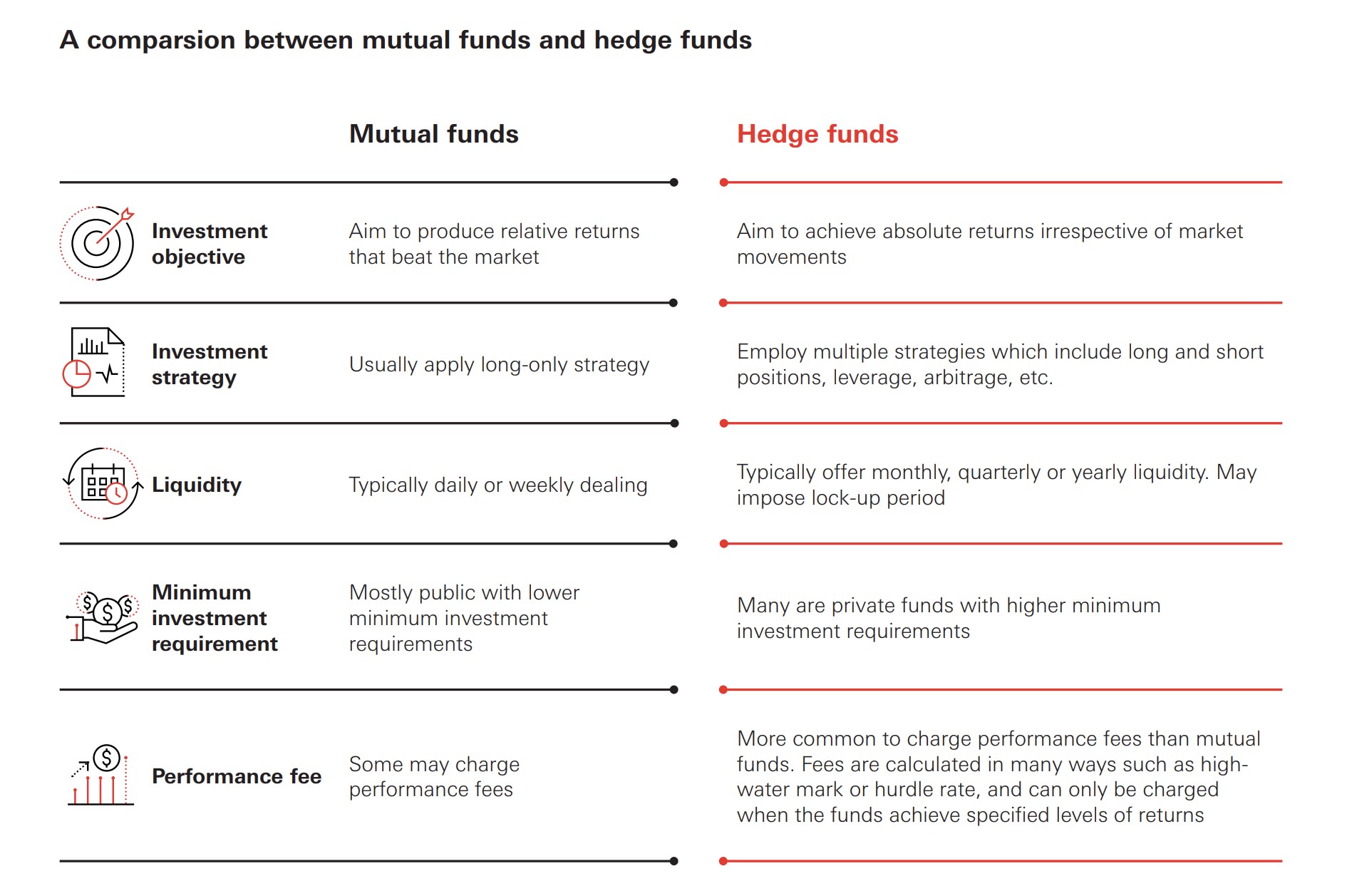
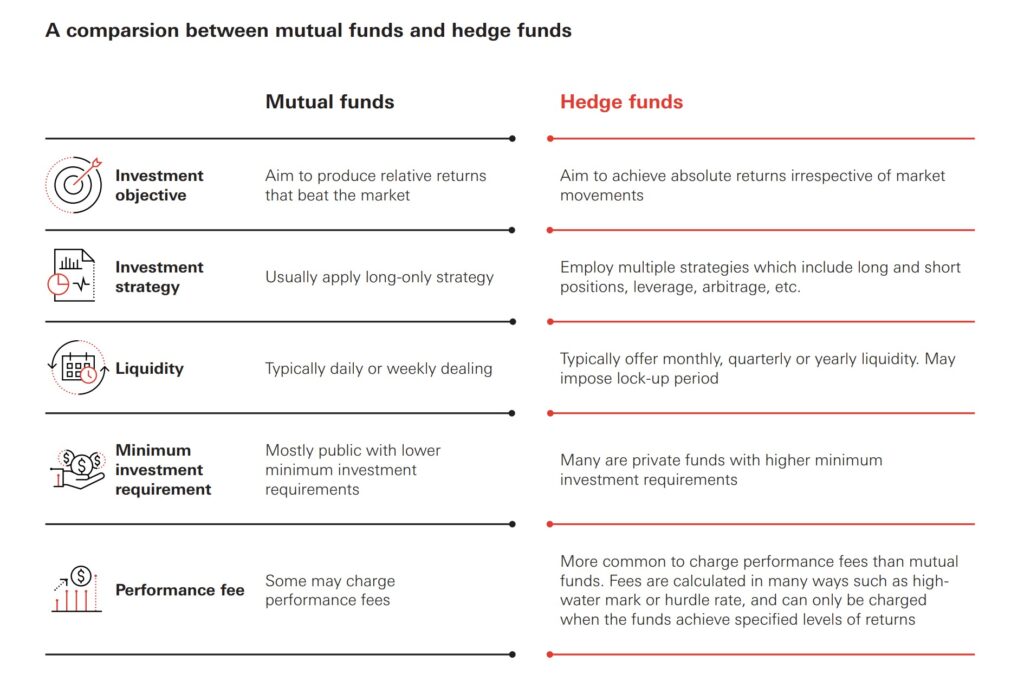
Mutual Funds vs. Hedge Funds: A Detailed Comparison
To further clarify the differences, let’s examine a side-by-side comparison of mutual funds and hedge funds across several key factors.
Investment Strategies
Mutual funds typically follow more straightforward and transparent investment strategies. They often focus on long-term growth or income through investments in stocks, bonds, or a combination of both. Their strategies are usually aligned with the fund’s stated investment objective and are easily understood by investors.
Hedge funds, on the other hand, employ a broader range of complex and often opaque strategies. These may include short-selling, leverage, derivatives, and arbitrage, which can generate higher returns but also carry greater risk. The strategies used by hedge funds are often tailored to specific market conditions and may change frequently.
Regulation and Transparency
Mutual funds are subject to strict regulations by the SEC, designed to protect investors. These regulations mandate transparency in reporting fund holdings, performance, and fees. Mutual funds must also adhere to specific rules regarding valuation, liquidity, and conflicts of interest.
Hedge funds operate with significantly less regulatory oversight. This allows them greater flexibility in their investment strategies but also exposes investors to higher levels of risk. The lack of transparency can make it difficult for investors to fully understand the risks involved and the fund’s performance drivers.
Investor Eligibility
Mutual funds are accessible to a wide range of investors, including individuals with modest investment amounts. The minimum investment requirements for mutual funds are typically low, making them an attractive option for those just starting to invest.
Hedge funds are generally limited to accredited investors, which include high-net-worth individuals and institutional investors. These investors are presumed to have the financial sophistication and risk tolerance necessary to invest in hedge funds. The high minimum investment requirements further restrict access to these funds.
Fees and Expenses
Mutual funds typically charge management fees, which are a percentage of the fund’s assets under management (AUM). These fees cover the costs of managing the fund, including research, trading, and administration. Expense ratios, which include management fees and other operating expenses, are generally lower for passively managed index funds compared to actively managed funds.
Hedge funds often charge a combination of management fees and performance-based fees. A common fee structure is the “2 and 20,” where the fund charges a 2% management fee and a 20% performance fee on any profits generated. These fees can be significantly higher than those charged by mutual funds.
Liquidity and Redemption
Mutual funds offer daily liquidity, allowing investors to buy or sell shares at the end of each trading day. This makes mutual funds a highly liquid investment option, suitable for investors who may need access to their funds on short notice.
Hedge funds typically have limited liquidity, with restrictions on when investors can redeem their shares. Lock-up periods, which prevent investors from withdrawing their money for a specified period, are common. Redemption fees may also apply, further limiting liquidity.
The Role of Risk Tolerance
When deciding between mutual funds and hedge funds, understanding your own risk tolerance is crucial. Mutual funds are generally considered less risky due to their diversification and regulatory oversight. They are a suitable option for investors seeking long-term growth or income with a moderate level of risk.
Hedge funds are inherently riskier investments due to their complex strategies and limited regulation. They are better suited for sophisticated investors with a high-risk tolerance and the ability to withstand potential losses. The potential for higher returns comes with the trade-off of increased volatility and the possibility of significant losses.
Making the Right Choice
The decision to invest in mutual funds or hedge funds depends on your individual investment goals, risk tolerance, and financial situation. Mutual funds offer diversification, liquidity, and transparency, making them a suitable option for a wide range of investors. Hedge funds, on the other hand, offer the potential for higher returns but come with increased risk and limited liquidity. It is essential to carefully consider all factors before making a decision and to seek professional financial advice if needed.
Ultimately, the choice between mutual funds and hedge funds is a personal one. By understanding the key differences between these two investment vehicles, you can make an informed decision that aligns with your financial objectives and risk profile. Remember to conduct thorough research and consult with a financial advisor to determine the best investment strategy for your specific needs. [See also: Understanding Investment Risks] [See also: Diversification Strategies for Beginners]
The Future of Mutual and Hedge Funds
The landscape of both mutual funds and hedge funds is constantly evolving. Technological advancements, regulatory changes, and shifting investor preferences are shaping the future of these investment vehicles. The rise of passive investing and exchange-traded funds (ETFs) has put pressure on actively managed mutual funds to justify their higher fees. At the same time, hedge funds are facing increasing scrutiny from regulators and investors alike, prompting them to enhance transparency and risk management practices.
As the investment industry continues to evolve, both mutual funds and hedge funds will need to adapt to meet the changing needs of investors. This may involve embracing new technologies, developing innovative investment strategies, and enhancing their commitment to transparency and investor protection. By staying ahead of the curve, these investment vehicles can continue to play a vital role in helping investors achieve their financial goals.