Mutual Funds vs. Hedge Funds: Understanding the Key Differences
Navigating the world of investments can be daunting, especially when confronted with terms like mutual funds and hedge funds. While both are investment vehicles that pool money from multiple investors, they operate under different structures, cater to different investor profiles, and employ vastly different investment strategies. Understanding the key differences between mutual funds and hedge funds is crucial for making informed investment decisions. This article aims to demystify these two investment options, providing a clear and concise comparison to help you determine which, if either, might be suitable for your financial goals.
What are Mutual Funds?
Mutual funds are investment vehicles that pool money from many investors to purchase a diversified portfolio of stocks, bonds, or other assets. They are managed by professional fund managers who make investment decisions based on the fund’s stated objectives. The primary goal of mutual funds is to provide investors with access to a diversified portfolio at a relatively low cost. Mutual funds are highly regulated and designed to be transparent and accessible to the general public.
Key Characteristics of Mutual Funds:
- Diversification: They offer instant diversification, reducing risk by spreading investments across numerous assets.
- Liquidity: Shares can typically be bought or sold daily at the fund’s net asset value (NAV).
- Regulation: Subject to strict regulatory oversight, providing investor protection.
- Accessibility: Generally accessible to all investors with relatively low minimum investment requirements.
- Transparency: Required to disclose their holdings and performance regularly.
What are Hedge Funds?
Hedge funds are investment partnerships that also pool money from investors, but they are structured very differently from mutual funds. They are typically managed by experienced portfolio managers and employ more aggressive and complex investment strategies, including short-selling, leverage, and derivatives, with the goal of generating higher returns. Hedge funds are largely unregulated and are usually only accessible to accredited investors – those with high net worth and income. The term ‘hedge’ refers to the original intention of reducing risk but many hedge funds today seek absolute returns, regardless of market direction.
Key Characteristics of Hedge Funds:
- Complex Strategies: Utilize sophisticated investment techniques to generate returns.
- Limited Regulation: Subject to less regulatory oversight than mutual funds.
- Accredited Investors Only: Typically only available to high-net-worth individuals and institutional investors.
- Higher Fees: Charge higher management and performance fees (e.g., the “2 and 20” model).
- Lower Liquidity: May have restrictions on when and how frequently investors can redeem their shares.
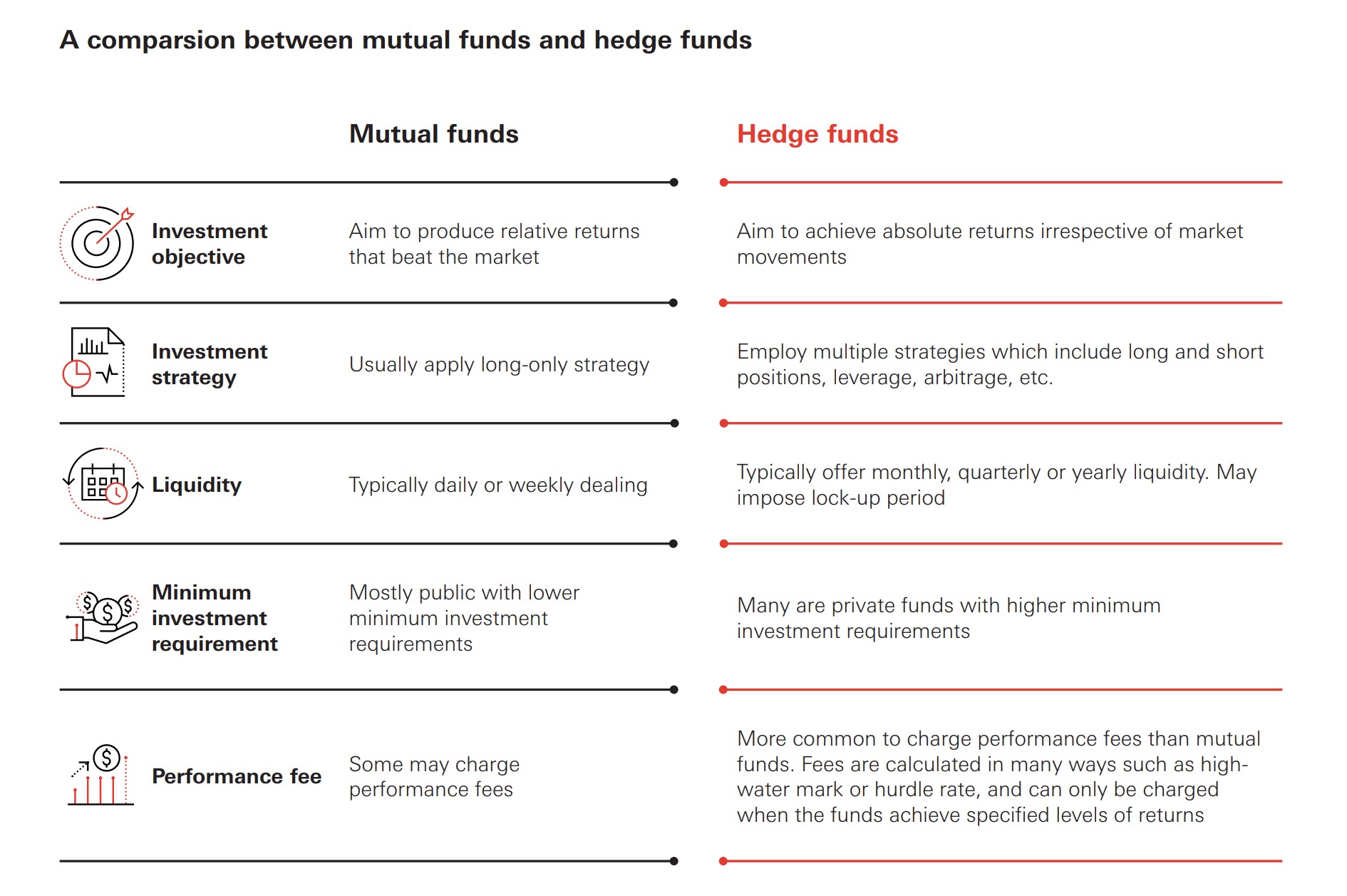
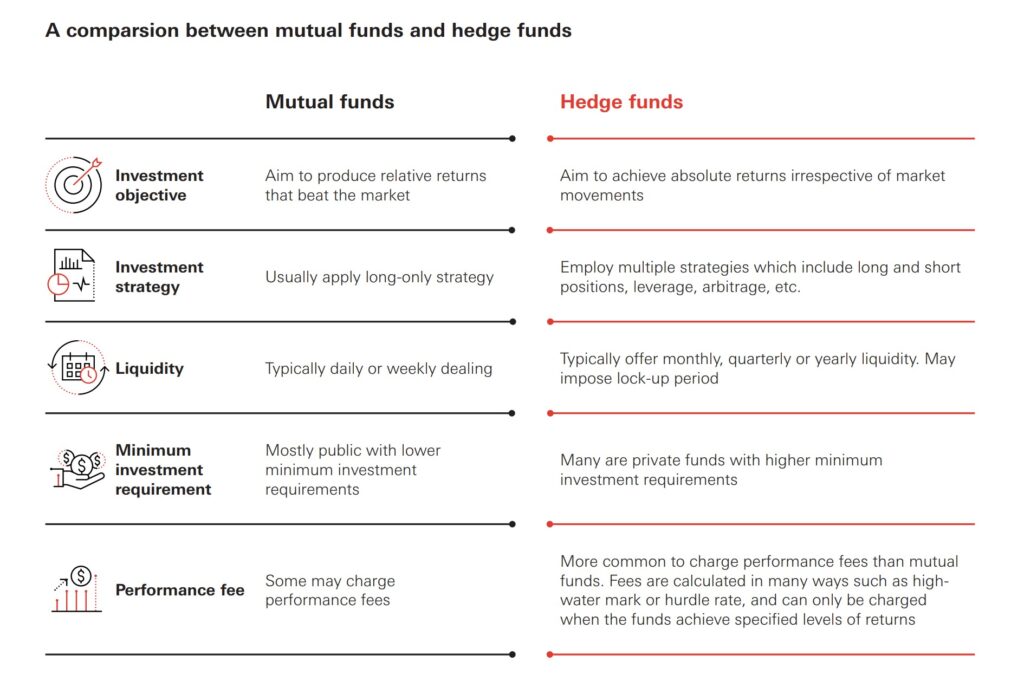
Mutual Funds vs. Hedge Funds: A Detailed Comparison
To further clarify the differences, let’s delve into a detailed comparison across several key aspects:
Investor Eligibility
Mutual funds are designed for the average investor. They are readily available to anyone with a brokerage account and often have low minimum investment requirements. Hedge funds, on the other hand, are primarily targeted at accredited investors. This means individuals with a net worth exceeding $1 million (excluding their primary residence) or an annual income of at least $200,000 (or $300,000 combined with a spouse) for the past two years, with a reasonable expectation of reaching the same income level in the current year. This restriction is in place due to the higher risk and complexity associated with hedge fund investments.
Investment Strategies
Mutual funds typically follow more conservative and transparent investment strategies. They are required to disclose their investment holdings regularly and adhere to specific investment guidelines. Hedge funds employ a wider range of strategies, often involving leverage, short-selling, derivatives, and arbitrage. These strategies aim to generate returns regardless of market conditions, but they also carry significantly higher risk. [See also: Understanding Investment Risk Tolerance] The use of these sophisticated strategies is a key differentiator between mutual funds and hedge funds.
Fees and Expenses
Mutual funds charge various fees, including management fees, operating expenses, and sometimes sales loads. These fees are generally lower than those charged by hedge funds. Hedge funds typically charge a “2 and 20” fee structure – a 2% management fee on assets under management and 20% of any profits generated. This performance-based fee structure incentivizes hedge fund managers to generate high returns, but it also means investors pay a substantial portion of the profits. The higher fee structure reflects the perceived higher value of the specialized expertise and potentially higher returns offered by hedge funds.
Regulation and Transparency
Mutual funds are heavily regulated by government agencies like the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC). This regulation provides investors with a level of protection and ensures transparency in fund operations. Hedge funds are subject to far less regulation. While they are required to register with the SEC, they are not subject to the same level of scrutiny as mutual funds. This lack of regulation allows hedge funds more flexibility in their investment strategies but also increases the risk for investors. The increased transparency of mutual funds makes them a more appealing option for risk-averse investors.
Liquidity
Mutual funds offer high liquidity. Investors can typically buy or sell shares daily at the fund’s net asset value (NAV). Hedge funds often have lock-up periods, meaning investors cannot redeem their shares for a specified period. They may also have restrictions on the frequency and amount of redemptions. This lower liquidity is a trade-off for the potential of higher returns and the illiquid nature of some of the assets they invest in. Understanding the liquidity constraints is crucial before investing in a hedge fund.
Which is Right for You?
The choice between mutual funds and hedge funds depends entirely on your individual financial situation, investment goals, and risk tolerance. If you are a retail investor seeking a diversified portfolio with relatively low risk and high liquidity, mutual funds are likely a more suitable option. They provide access to professional management and diversification at a reasonable cost.
If you are an accredited investor with a high-risk tolerance and a desire for potentially higher returns, hedge funds may be worth considering. However, it’s crucial to conduct thorough due diligence, understand the fund’s investment strategy, and be prepared for the possibility of significant losses. Hedge funds are not suitable for everyone, and it’s essential to seek professional financial advice before investing. Remember that past performance is not indicative of future results, and the higher fees associated with hedge funds can significantly impact overall returns.
The Role of Due Diligence
Regardless of whether you choose to invest in mutual funds or hedge funds, thorough due diligence is paramount. For mutual funds, carefully review the fund’s prospectus, which outlines its investment objectives, strategies, risks, and fees. Pay attention to the fund’s historical performance, but remember that past performance is not a guarantee of future results. [See also: How to Read a Fund Prospectus] For hedge funds, due diligence is even more critical due to the lack of regulation and transparency. Research the fund manager’s experience and track record, understand the fund’s investment strategy, and assess the fund’s risk management practices. Consider consulting with a financial advisor who specializes in alternative investments before making any decisions.
Conclusion
Mutual funds and hedge funds are distinct investment vehicles catering to different investor profiles and risk appetites. Mutual funds offer diversification, liquidity, and transparency, making them suitable for a wide range of investors. Hedge funds employ complex strategies and are typically reserved for accredited investors seeking potentially higher returns, but with higher risk. Understanding the key differences between these two investment options is essential for making informed decisions that align with your financial goals and risk tolerance. Remember to conduct thorough research and seek professional advice before investing in either mutual funds or hedge funds.