Riding the Rocket: Understanding and Identifying Parabolic Stocks
The allure of quick, substantial gains in the stock market is undeniable. Among the various investment strategies, identifying and trading parabolic stocks stands out for its potential for rapid profit. However, this potential comes with significant risk. Understanding what constitutes a parabolic stock, the factors that drive its ascent, and the risks involved are crucial for any investor considering this high-stakes game.
What are Parabolic Stocks?
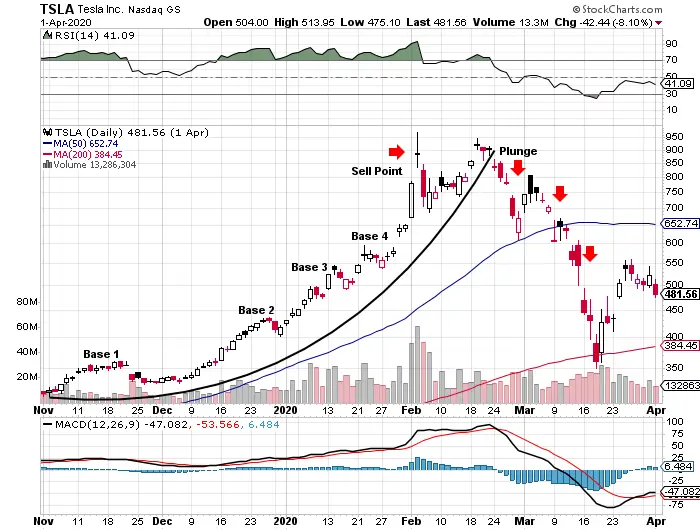
A parabolic stock is characterized by a dramatic and exponential increase in its price over a relatively short period. The price chart resembles a parabola, hence the name. This rapid ascent is often fueled by a combination of factors, including positive news, market hype, short squeezes, or a fundamental shift in the company’s prospects. Unlike stocks with steady, gradual growth, parabolic stocks experience a surge that defies conventional valuation metrics. These stocks are often heavily traded and generate significant buzz within the investor community.
Factors Driving Parabolic Movements
Positive News and Catalysts
Breakthrough announcements, such as FDA approval for a new drug, a major contract win, or a revolutionary product launch, can trigger a surge in investor interest and drive the stock price into a parabolic trajectory. The news acts as a catalyst, attracting both institutional and retail investors who believe the company’s future prospects have significantly improved.
Market Hype and Social Media Frenzy
In the age of social media, investment decisions are increasingly influenced by online trends and discussions. A stock that gains traction on platforms like Reddit, Twitter, or other investment forums can experience a rapid influx of new investors, pushing the price higher and creating a self-fulfilling prophecy. This ‘meme stock’ phenomenon underscores the power of collective sentiment in driving parabolic movements, though often divorced from fundamental analysis.
Short Squeezes
A short squeeze occurs when a heavily shorted stock begins to rise in price, forcing short sellers to cover their positions by buying back shares. This buying pressure exacerbates the price increase, creating a parabolic move. The more heavily shorted the stock, the more dramatic the potential short squeeze. [See also: Understanding Short Squeezes]
Fundamental Shifts
Occasionally, a genuine and significant change in a company’s underlying business can justify a parabolic rise. This could involve a disruptive technology, a successful turnaround strategy, or a major shift in market dynamics that benefits the company. However, it is crucial to distinguish between genuine fundamental improvements and temporary hype.
Identifying Potential Parabolic Stocks
Spotting parabolic stocks before they peak is challenging, but certain indicators can help investors identify potential candidates:
- Volume Surge: A significant increase in trading volume often accompanies the initial stages of a parabolic move.
- Price Momentum: Look for stocks exhibiting strong upward momentum, consistently making new highs.
- News and Sentiment: Monitor news feeds, social media, and investment forums for any catalysts that could drive further price appreciation.
- Technical Indicators: Utilize technical indicators like the Relative Strength Index (RSI) and Moving Average Convergence Divergence (MACD) to assess overbought conditions and potential reversal points.
The Risks of Trading Parabolic Stocks
While the potential for quick profits is alluring, trading parabolic stocks is inherently risky. The rapid ascent is often unsustainable, and the inevitable correction can be swift and severe. Here are some key risks to consider:
The Inevitable Correction
What goes up must come down. Parabolic moves are rarely sustainable in the long term. The higher the stock climbs, the greater the risk of a sharp correction. Investors who buy at the peak often face substantial losses when the bubble bursts.
Emotional Trading
The fear of missing out (FOMO) can drive investors to make irrational decisions, buying into parabolic stocks at inflated prices. Emotional trading can lead to poor judgment and significant financial losses. It’s crucial to maintain discipline and adhere to a well-defined trading plan.
Limited Liquidity
During the peak of a parabolic move, liquidity can become scarce. Selling large positions may be difficult, and prices can fluctuate wildly. This can exacerbate losses if the stock begins to decline rapidly.
Market Manipulation
Some parabolic moves are driven by market manipulation, such as pump-and-dump schemes. Unscrupulous individuals or groups artificially inflate the stock price through misleading information and coordinated buying, only to sell their shares at a profit before the price collapses. [See also: Understanding Market Manipulation]
Strategies for Trading Parabolic Stocks
If you choose to trade parabolic stocks, it’s essential to have a well-defined strategy and manage your risk effectively:
- Set Stop-Loss Orders: Protect your capital by setting stop-loss orders to automatically sell your shares if the price falls below a certain level.
- Take Profits Regularly: Don’t get greedy. Take profits as the stock rises to lock in gains and reduce your exposure to potential losses.
- Diversify Your Portfolio: Avoid putting all your eggs in one basket. Diversify your portfolio to mitigate the risk of losses from any single parabolic stock.
- Conduct Thorough Research: Before investing in any stock, conduct thorough research on the company’s fundamentals, industry trends, and potential risks.
- Understand Your Risk Tolerance: Be honest with yourself about your risk tolerance. Parabolic stocks are not suitable for risk-averse investors.
Examples of Parabolic Stocks in Recent History
Several stocks have experienced parabolic movements in recent years, often fueled by social media hype and speculative trading. Examples include GameStop (GME) and AMC Entertainment (AMC), which saw dramatic price increases driven by retail investors coordinating through online forums. While some investors made substantial profits, many others lost money when the prices eventually crashed. These examples highlight the volatile nature of parabolic stocks and the importance of managing risk.
The Psychology of Parabolic Stock Trading
Understanding the psychology behind parabolic stock trading is crucial for making informed decisions. The fear of missing out (FOMO) and the allure of quick profits can cloud judgment and lead to impulsive behavior. It’s important to remain rational and objective, focusing on fundamental analysis and risk management rather than succumbing to emotional pressures. Recognizing the psychological biases that can influence trading decisions can help investors avoid costly mistakes.
Conclusion
Parabolic stocks offer the potential for rapid gains, but they also carry significant risks. Identifying these stocks requires a keen understanding of market dynamics, technical indicators, and investor sentiment. However, even with the best analysis, predicting the peak of a parabolic move is nearly impossible. Therefore, a disciplined approach to risk management, including setting stop-loss orders and taking profits regularly, is essential for protecting capital. Ultimately, trading parabolic stocks is a high-risk, high-reward game that requires careful consideration and a strong stomach. Before investing in any parabolic stock, investors should conduct thorough research, understand their risk tolerance, and seek advice from a qualified financial advisor.
Remember, while the allure of a quick win is tempting, a sustainable investment strategy built on fundamental analysis and diversification is more likely to lead to long-term success. Approach parabolic stocks with caution and a healthy dose of skepticism.
