Spread Betting vs. CFD Trading: Understanding the Key Differences
When navigating the world of financial trading, two popular instruments often come up: spread betting and Contracts for Difference (CFDs). Both offer a way to speculate on the price movements of various assets without actually owning them. However, significant differences exist between spread betting and CFD trading, impacting taxation, market access, and overall suitability for different traders. This article delves into a detailed comparison of spread betting and CFDs, highlighting their nuances to help you make an informed decision.
What is Spread Betting?
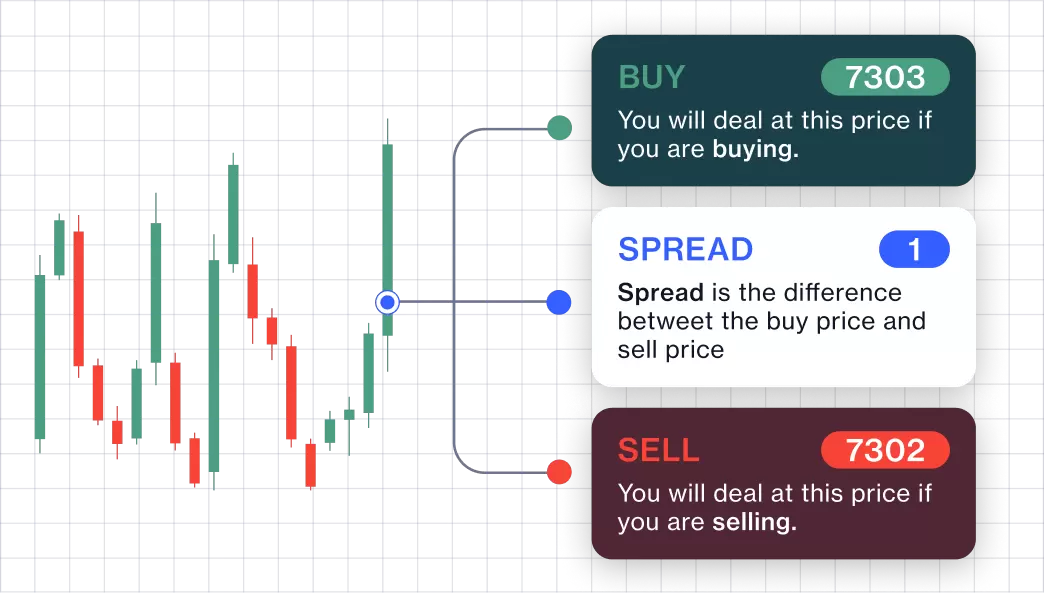
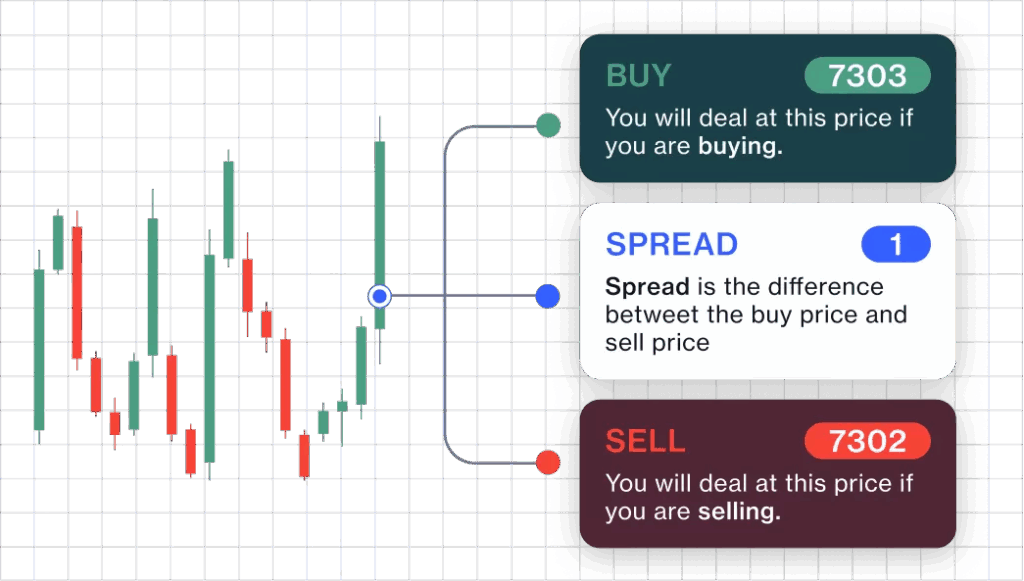
Spread betting is a form of speculation where you bet on the direction of a market’s price movement without owning the underlying asset. The ‘spread’ refers to the difference between the buying and selling price quoted by the broker. Your profit or loss is determined by the accuracy of your prediction and the size of your stake. In the UK and Ireland, spread betting profits are often tax-free, making it an attractive option for some traders.
- Tax Advantages: Typically tax-free profits in the UK and Ireland.
- Fixed Spreads: Some brokers offer fixed spreads, providing more predictability.
- Simplicity: Often perceived as simpler to understand than CFDs, particularly for beginners.
What are Contracts for Difference (CFDs)?
CFD trading involves an agreement to exchange the difference in the value of an asset between the time the contract is opened and closed. Like spread betting, you don’t own the underlying asset. CFDs are available on a wide range of markets, including stocks, indices, commodities, and currencies. Profits from CFDs are generally subject to capital gains tax.
- Wider Market Access: Access to a broader range of global markets.
- Flexibility: Greater flexibility in trade size and leverage options.
- Hedging: Useful for hedging existing investment portfolios.
Key Differences Between Spread Betting and CFDs
The core distinction between spread betting and CFDs lies in their tax treatment and pricing structure. While both allow leveraged trading, understanding these differences is crucial.
Taxation
As previously mentioned, a primary advantage of spread betting, especially in the UK and Ireland, is its tax-free status. Profits are generally exempt from capital gains tax. Conversely, profits from CFD trading are typically subject to capital gains tax. This difference can significantly impact overall profitability, particularly for frequent traders or those with substantial gains. It’s essential to consult with a tax advisor to understand your specific tax obligations.
Pricing and Spreads
While both instruments involve paying the spread (the difference between the buying and selling price), the way spreads are presented can differ. Spread betting brokers often quote a wider spread than CFD brokers. However, this wider spread may be offset by the tax advantages. CFD brokers typically offer tighter spreads but charge commissions on each trade. Therefore, it’s important to consider both the spread and any associated commissions when comparing the overall cost of trading.
Market Access
CFDs generally offer access to a broader range of markets compared to spread betting. While both provide exposure to major indices, currencies, and commodities, CFDs often include access to individual stocks from various global exchanges. This wider market access can be advantageous for traders seeking specific investment opportunities. [See also: Trading Strategies for Beginners]
Regulation
Both spread betting and CFD trading are regulated in most jurisdictions. In the UK, both are regulated by the Financial Conduct Authority (FCA). However, the specific regulations and protections afforded to traders may vary. It’s crucial to choose a regulated broker to ensure the safety of your funds and adherence to fair trading practices. Always verify the broker’s regulatory status before opening an account.
Leverage
Both spread betting and CFDs offer leveraged trading, allowing you to control a larger position with a smaller initial deposit. While leverage can amplify profits, it also magnifies losses. It’s essential to use leverage prudently and implement risk management strategies, such as stop-loss orders, to protect your capital. The FCA has implemented regulations to limit the amount of leverage offered to retail clients to mitigate the risks associated with leveraged trading. Understanding the implications of leverage is paramount before engaging in either spread betting or CFD trading.
Who are Spread Betting and CFDs Suitable For?
The choice between spread betting and CFDs depends on individual circumstances, trading style, and risk tolerance.
Spread Betting
Spread betting may be more suitable for:
- Traders based in the UK and Ireland who can benefit from the tax-free status.
- Beginners who prefer a simpler pricing structure.
- Traders who prefer fixed spreads.
CFDs
CFDs may be more suitable for:
- Traders seeking access to a wider range of global markets, including individual stocks.
- Traders who actively manage risk and require flexible trade sizes.
- Traders who wish to hedge existing investment portfolios.
Risk Management in Spread Betting and CFD Trading
Regardless of whether you choose spread betting or CFD trading, effective risk management is crucial. Both instruments involve leverage, which can amplify both profits and losses. Implement the following risk management strategies:
- Stop-Loss Orders: Automatically close your position if the price moves against you.
- Limit Orders: Automatically close your position when the price reaches a predetermined profit target.
- Position Sizing: Carefully determine the size of your trades based on your risk tolerance and account balance.
- Diversification: Spread your risk across multiple markets and asset classes.
- Stay Informed: Keep up-to-date with market news and economic events that could impact your trades.
Choosing a Broker
Selecting a reputable broker is essential for both spread betting and CFD trading. Consider the following factors when choosing a broker:
- Regulation: Ensure the broker is regulated by a reputable authority, such as the FCA.
- Spreads and Commissions: Compare the spreads and commissions offered by different brokers.
- Platform and Tools: Evaluate the broker’s trading platform and the tools and resources available.
- Customer Support: Check the availability and responsiveness of customer support.
- Account Options: Consider the different account options available and choose one that suits your needs.
Conclusion
Spread betting and CFD trading offer distinct advantages and disadvantages. Understanding the spread betting CFD difference, particularly regarding taxation and market access, is crucial for making an informed decision. Carefully consider your individual circumstances, trading style, and risk tolerance before choosing the instrument that best suits your needs. Remember to prioritize risk management and choose a reputable broker to enhance your trading experience. Whether you opt for spread betting or CFDs, continuous learning and adaptation are key to success in the financial markets. Always conduct thorough research and seek professional advice before making any trading decisions. Spread betting and CFD trading can be complex, so ensure you fully understand the risks involved. [See also: Advanced Trading Techniques]