Spread Betting vs. CFD Trading: Understanding the Key Differences
For individuals seeking to participate in the financial markets, two popular methods are spread betting and Contract for Difference (CFD) trading. While both offer leveraged access to a wide range of assets, including stocks, indices, commodities, and currencies, they operate under different regulatory frameworks and have distinct tax implications. Understanding the spread betting CFD difference is crucial for making informed decisions about which approach best suits your trading style and financial goals. This article will delve into the nuances of each, providing a comprehensive comparison to help you navigate the complexities of leveraged trading.
What is Spread Betting?
Spread betting is a form of speculation on the price movement of financial instruments. Instead of buying or selling the underlying asset, you’re betting on whether the price will rise (going long) or fall (going short). The ‘spread’ represents the difference between the buy and sell price quoted by the broker. Your profit or loss is determined by the accuracy of your prediction and the size of your stake per point movement.
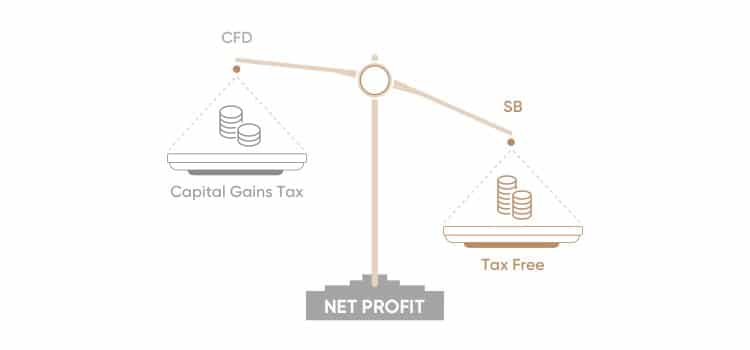
Spread betting is particularly popular in the UK and Ireland due to its tax advantages. Profits generated from spread betting are generally exempt from capital gains tax. However, losses are also not tax deductible. This tax treatment is a significant spread betting CFD difference. It’s crucial to verify the specific tax regulations in your jurisdiction with a qualified tax advisor.
Key Features of Spread Betting:
- Tax Advantages: Typically tax-free profits in the UK and Ireland.
- Leverage: Amplifies both potential profits and losses.
- Simplified Trading: Easy to understand and execute trades.
- Fixed Spreads: Some brokers offer fixed spreads, providing price certainty.
What is CFD Trading?
CFD trading, or Contract for Difference trading, allows you to speculate on the price movements of various financial assets without owning the underlying asset. A CFD is a contract between you and your broker to exchange the difference in the asset’s price from the time the contract is opened until it’s closed. Like spread betting, CFDs are leveraged products, meaning you only need to deposit a small percentage of the total trade value (known as margin) to control a much larger position.
CFD trading is globally accessible and subject to capital gains tax on profits in many jurisdictions. Losses are generally tax deductible. This contrasts sharply with the tax treatment of spread betting, highlighting another key spread betting CFD difference.
Key Features of CFD Trading:
- Global Availability: Widely available across different countries.
- Leverage: Similar to spread betting, offering amplified trading exposure.
- Diverse Markets: Access to a wide range of financial instruments.
- Tax Implications: Profits are typically subject to capital gains tax.
Spread Betting CFD Difference: A Detailed Comparison
The primary spread betting CFD difference lies in their tax treatment. However, there are other subtle distinctions to consider:
Taxation
As mentioned earlier, spread betting profits are often tax-free in the UK and Ireland, whereas CFD profits are subject to capital gains tax. This is perhaps the most significant spread betting CFD difference and a major factor for many traders.
Regulation
Both spread betting and CFD trading are regulated by financial authorities. In the UK, both are regulated by the Financial Conduct Authority (FCA). However, the specific regulations and protections may vary slightly. It is essential to choose a broker regulated by a reputable authority to ensure the safety of your funds.
Market Access
Both spread betting and CFD trading offer access to a broad range of markets, including stocks, indices, commodities, and currencies. The specific instruments available may vary depending on the broker.
Spreads and Commissions
Both spread betting and CFD brokers make money through the spread – the difference between the buying and selling price. Some CFD brokers may also charge commissions on trades. The size of the spread can vary depending on the asset, the broker, and market volatility. Comparing spreads across different brokers is essential to minimize trading costs. Understanding the impact of spreads is a key aspect of grasping the spread betting CFD difference in practical terms.
Leverage
Both spread betting and CFD trading offer leveraged trading. Leverage allows you to control a large position with a smaller amount of capital. While leverage can amplify profits, it can also magnify losses. It’s crucial to manage leverage carefully and use risk management tools such as stop-loss orders to protect your capital. The level of leverage offered can vary between brokers and is often subject to regulatory restrictions.
Direct Market Access
While most spread betting and CFD trading is done through brokers acting as market makers, some CFD brokers offer Direct Market Access (DMA). DMA allows you to trade directly on the order books of exchanges, potentially offering tighter spreads and faster execution. DMA is generally not available for spread betting.
Example Scenario: Spread Betting vs. CFD Trading
Let’s illustrate the spread betting CFD difference with an example. Suppose you believe the price of a particular stock, currently trading at £100, will increase. You decide to invest £1000 using leverage.
Spread Betting: You place a bet of £10 per point movement. If the stock price rises to £105, you make a profit of £50 (£10 x 5 points). If the stock price falls to £95, you incur a loss of £50 (£10 x 5 points).
CFD Trading: You buy 10 CFDs at £100 each. If the stock price rises to £105, you make a profit of £50 (10 CFDs x £5 difference). If the stock price falls to £95, you incur a loss of £50 (10 CFDs x £5 difference).
In this simplified example, the profit and loss potential are the same. However, the tax implications would differ significantly in the UK. The spread betting profit would be tax-free, while the CFD profit would be subject to capital gains tax. This simple example highlights the practical spread betting CFD difference.
Choosing Between Spread Betting and CFD Trading
The best choice between spread betting and CFD trading depends on your individual circumstances, trading style, and tax situation. Consider the following factors:
- Tax Implications: If you are a UK or Irish resident, the tax-free status of spread betting may be a significant advantage.
- Trading Style: Both methods are suitable for short-term and long-term trading strategies.
- Risk Tolerance: Leverage amplifies both profits and losses, so it’s crucial to manage risk carefully.
- Market Access: Ensure the broker offers access to the markets you want to trade.
- Costs: Compare spreads and commissions across different brokers.
Before engaging in either spread betting or CFD trading, it’s essential to thoroughly research and understand the risks involved. Consider practicing with a demo account to familiarize yourself with the platform and trading strategies. It is also wise to consult with a financial advisor to determine if leveraged trading is suitable for your financial situation. Understanding the nuances of the spread betting CFD difference is paramount to making informed trading decisions.
Risk Management in Spread Betting and CFD Trading
Effective risk management is paramount when engaging in leveraged trading activities such as spread betting and CFD trading. Due to the amplified nature of both potential profits and losses, implementing robust risk management strategies is crucial to protecting your capital.
Key Risk Management Techniques:
- Stop-Loss Orders: Automatically close your position when the price reaches a predetermined level, limiting potential losses.
- Take-Profit Orders: Automatically close your position when the price reaches a predetermined level, securing profits.
- Position Sizing: Carefully determine the size of your positions based on your risk tolerance and account balance.
- Leverage Management: Use leverage judiciously, understanding the potential for both gains and losses.
- Diversification: Spread your risk across multiple assets and markets.
- Emotional Control: Avoid making impulsive decisions based on fear or greed.
It’s crucial to remember that even with the best risk management strategies, losses are still possible. However, by implementing these techniques, you can significantly reduce the potential for catastrophic losses and protect your trading capital. The spread betting CFD difference in terms of risk management is negligible, as both require the same level of diligence and strategic planning.
The Future of Spread Betting and CFD Trading
The landscape of spread betting and CFD trading is constantly evolving, driven by technological advancements, regulatory changes, and shifting investor preferences. As online trading platforms become more sophisticated and accessible, more individuals are drawn to the potential opportunities offered by these leveraged products.
Regulatory bodies around the world are also continuously reviewing and updating regulations governing spread betting and CFD trading to protect investors and ensure market integrity. These regulations may include restrictions on leverage, mandatory risk warnings, and enhanced disclosure requirements. Staying informed about these regulatory changes is crucial for anyone involved in spread betting or CFD trading.
The ongoing debate surrounding the spread betting CFD difference, particularly regarding taxation, is likely to continue. Changes in tax laws could significantly impact the attractiveness of one method over the other. Therefore, it is essential to stay abreast of any potential changes in tax regulations that could affect your trading activities.
Conclusion
Understanding the spread betting CFD difference is essential for anyone considering leveraged trading. While both offer access to a wide range of markets and the potential for significant profits, they differ in their tax treatment and regulatory nuances. By carefully considering your individual circumstances, trading style, and risk tolerance, you can make an informed decision about which approach best suits your needs. Remember to prioritize risk management and stay informed about regulatory changes to ensure a successful and sustainable trading experience. [See also: Risk Management Strategies for CFD Trading] [See also: Understanding Leverage in Forex Trading]
