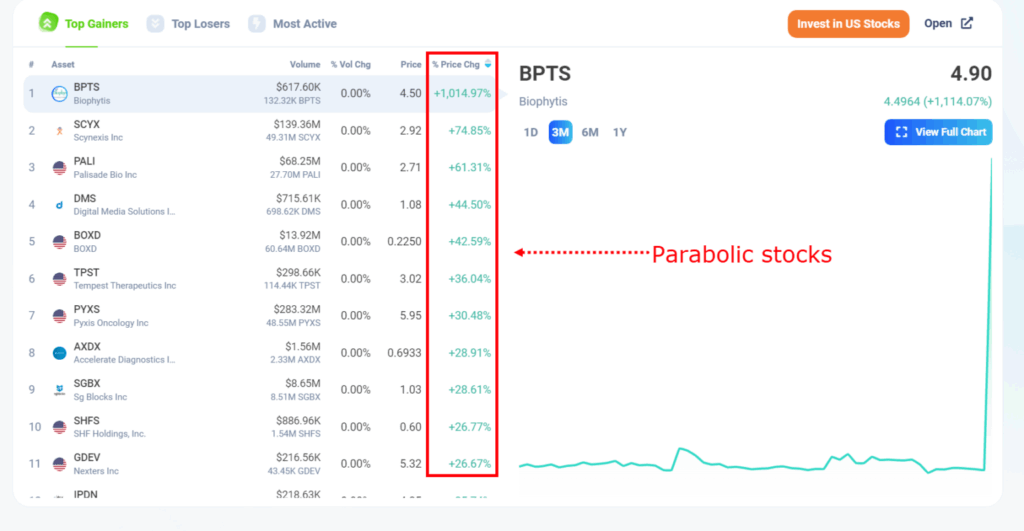
Understanding Parabolic Meaning in Stocks: A Comprehensive Guide
In the world of stock trading, understanding chart patterns and technical indicators is crucial for making informed decisions. One such pattern, often discussed and sometimes feared, is the parabolic move. The parabolic meaning in stocks refers to a rapid and often unsustainable price increase that resembles a parabola on a stock chart. This article delves into the intricacies of this pattern, exploring its characteristics, causes, implications, and strategies for navigating it.
What is a Parabolic Move in Stocks?
A parabolic move in stocks is characterized by a sharp, almost vertical, increase in price over a relatively short period. The price action, when plotted on a chart, forms a curve that resembles a parabola. This type of movement typically occurs due to intense buying pressure, often fueled by hype, speculation, or a significant positive catalyst.
The key characteristics of a parabolic stock include:
- Rapid Price Increase: The price rises dramatically and quickly.
- High Volume: Trading volume is significantly higher than usual.
- Steep Trendline: The trendline connecting the lows of the price action becomes very steep.
- Unsustainable Growth: The rate of increase is unlikely to be maintained in the long term.
Causes of Parabolic Moves
Several factors can contribute to a parabolic move in a stock. Understanding these causes can help traders identify potential parabolic setups and anticipate their consequences.
Hype and Speculation
One of the primary drivers of parabolic moves is hype and speculation. This often occurs when a stock becomes popular on social media, online forums, or through word-of-mouth. As more and more investors pile into the stock, the price is driven higher, creating a self-fulfilling prophecy. Examples include meme stocks like GameStop and AMC, which experienced parabolic surges due to coordinated buying efforts by retail investors.
Positive News and Catalysts
Significant positive news or catalysts can also trigger a parabolic move. This could include a breakthrough product announcement, a major contract win, or a positive earnings report. If the news is perceived as highly impactful, investors may rush to buy the stock, driving the price sharply higher. These catalysts often justify the initial price increase, but the subsequent parabolic move can be overextended.
Short Squeezes
A short squeeze occurs when a heavily shorted stock experiences a rapid price increase, forcing short sellers to cover their positions by buying back the stock. This buying pressure further drives the price higher, exacerbating the parabolic move. Short squeezes are often associated with meme stocks and can lead to dramatic and unpredictable price swings.
Low Float Stocks
Stocks with a low float (i.e., a small number of shares available for trading) are more susceptible to parabolic moves. With fewer shares available, it takes less buying pressure to drive the price significantly higher. These stocks can be highly volatile and prone to rapid price increases and declines.
The Risks of Trading Parabolic Stocks
While the potential for quick profits may be tempting, trading parabolic stocks involves significant risks. The unsustainable nature of these moves means that the price is likely to eventually correct sharply, often leading to substantial losses for those who buy in at the peak.
The Inevitable Correction
The most significant risk is the inevitable correction. What goes up must come down, and parabolic stocks are no exception. The higher the price climbs, the greater the potential for a sharp and sudden decline. This correction can be triggered by various factors, including profit-taking, negative news, or a shift in market sentiment.
Volatility
Parabolic stocks are highly volatile, meaning that their prices can fluctuate wildly in a short period. This volatility can make it difficult to manage risk and can lead to emotional decision-making. Traders may be tempted to hold on to losing positions in the hope of a rebound, only to see their losses deepen.
False Breakouts
Parabolic moves can also be characterized by false breakouts. A false breakout occurs when the price temporarily breaks through a key resistance level but then quickly reverses direction. This can trap traders who buy in anticipation of further gains, leading to losses when the price falls back below the resistance level. Identifying the parabolic meaning and its potential reversal is crucial.
Strategies for Trading Parabolic Stocks
Despite the risks, some traders attempt to profit from parabolic stocks using various strategies. However, it’s important to approach these strategies with caution and to have a well-defined risk management plan in place.
Riding the Momentum
One strategy is to ride the momentum by buying the stock as it’s moving higher. This requires quick decision-making and the ability to identify entry and exit points. Traders using this strategy often employ technical indicators such as moving averages and relative strength index (RSI) to gauge the strength of the trend and to identify potential overbought conditions.
Shorting the Peak
Another strategy is to short the stock at the peak of the parabolic move. This is a high-risk, high-reward strategy that involves betting against the prevailing trend. Traders using this strategy look for signs of exhaustion, such as decreasing volume or bearish candlestick patterns, to identify potential reversal points. Shorting requires a deep understanding of market dynamics and the ability to manage risk effectively.
Waiting for the Correction
A more conservative approach is to wait for the correction and then buy the stock at a lower price. This strategy involves identifying fundamentally sound companies that have experienced a parabolic move due to temporary hype or speculation. By waiting for the price to correct, traders can potentially buy the stock at a more attractive valuation.
Risk Management for Parabolic Stocks
Regardless of the strategy used, risk management is paramount when trading parabolic stocks. Here are some key risk management techniques:
- Stop-Loss Orders: Use stop-loss orders to limit potential losses. A stop-loss order automatically sells the stock if it falls below a certain price.
- Position Sizing: Limit the size of your position to avoid excessive risk. Do not allocate a large percentage of your capital to a single parabolic stock.
- Diversification: Diversify your portfolio to reduce overall risk. Do not put all your eggs in one basket.
- Emotional Control: Avoid making emotional decisions based on fear or greed. Stick to your trading plan and do not deviate from your risk management rules.
Examples of Parabolic Stocks
Throughout history, there have been numerous examples of stocks that have experienced parabolic moves. Some notable examples include:
- GameStop (GME): In early 2021, GameStop experienced a massive parabolic surge due to a coordinated buying effort by retail investors.
- AMC Entertainment (AMC): Like GameStop, AMC also experienced a parabolic move in 2021 due to similar factors.
- Tesla (TSLA): While not a pure parabolic move, Tesla’s stock price experienced significant growth over several years, exhibiting characteristics of parabolic growth at times.
These examples illustrate the potential for both profit and loss when trading parabolic stocks. Understanding the underlying dynamics and managing risk effectively are crucial for success.
Conclusion
The parabolic meaning in stocks refers to a rapid and unsustainable price increase that can be both exciting and dangerous for traders. While the potential for quick profits may be tempting, it’s important to understand the risks involved and to have a well-defined risk management plan in place. By understanding the causes of parabolic moves, implementing effective risk management techniques, and choosing appropriate trading strategies, traders can potentially navigate these volatile situations and avoid significant losses. Remember to always conduct thorough research and to consult with a financial advisor before making any investment decisions. Recognizing a parabolic trend early can be the difference between profit and loss. [See also: Understanding Stock Market Corrections] Always remember that the parabolic meaning often implies an unsustainable trend. The rise can be exhilarating, but the fall can be devastating. Approach parabolic stocks with caution and a sound strategy. Consider the parabolic meaning within the broader market context. Does the overall market sentiment support such a rapid rise? The parabolic meaning should always be weighed against fundamental analysis. Is the company’s performance justifying the price surge? Ignoring the parabolic meaning can lead to significant financial losses. Always be aware of the potential for a correction. The parabolic meaning is often associated with high volatility. Be prepared for rapid price swings. The parabolic meaning can be a valuable tool for experienced traders. However, it requires discipline and a strong understanding of risk management. The parabolic meaning highlights the importance of staying informed and adaptable in the stock market. Market conditions can change quickly, so it’s crucial to be prepared to adjust your strategy as needed. The parabolic meaning serves as a reminder of the potential for both opportunity and risk in the stock market. Approach every investment with caution and a well-thought-out plan. Understanding the parabolic meaning is just one piece of the puzzle. Continuous learning and adaptation are essential for long-term success in the stock market. The parabolic meaning is a concept that every investor should be familiar with, regardless of their experience level. It’s a reminder that the stock market is not always rational and that prices can sometimes deviate significantly from fundamental value. The parabolic meaning underscores the importance of due diligence and critical thinking. Don’t simply follow the crowd; do your own research and make informed decisions based on your own analysis.

