Understanding Parabolic Price Movements: A Comprehensive Guide
In the dynamic world of financial markets, understanding price movements is crucial for making informed investment decisions. One particularly dramatic and potentially lucrative type of price action is the parabolic price movement. This article delves into the intricacies of parabolic price patterns, exploring what they are, how they form, their implications, and strategies for navigating them effectively. We will examine the characteristics, potential risks, and opportunities associated with parabolic price trends. Understanding parabolic price action can provide traders and investors with valuable insights into market sentiment and potential turning points. The allure of quick gains often accompanies these rapid ascents, but it’s crucial to approach them with caution and a well-defined strategy. Identifying a parabolic price trend early on can be challenging, but the rewards can be substantial. However, the risk of a sharp correction is always present. The concept of a parabolic price move is important to grasp for anyone looking to make money in the markets. Mastering the understanding of these patterns is a great way to improve your trading skills. Before making any investment decisions, it is important to conduct thorough research and seek professional advice. This article aims to provide a foundational understanding of parabolic price movements, equipping you with the knowledge to recognize and potentially profit from them, while also mitigating the inherent risks.
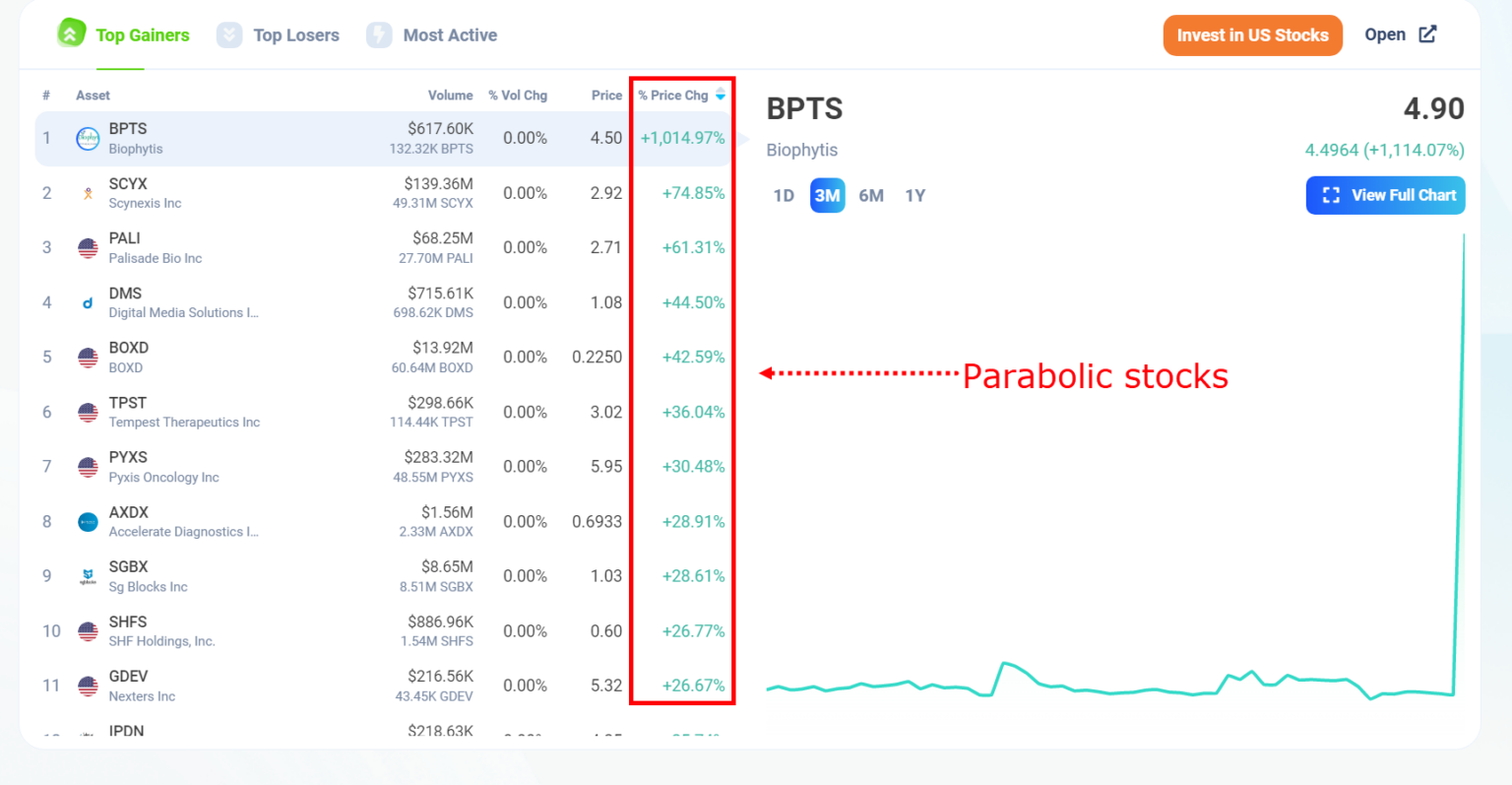
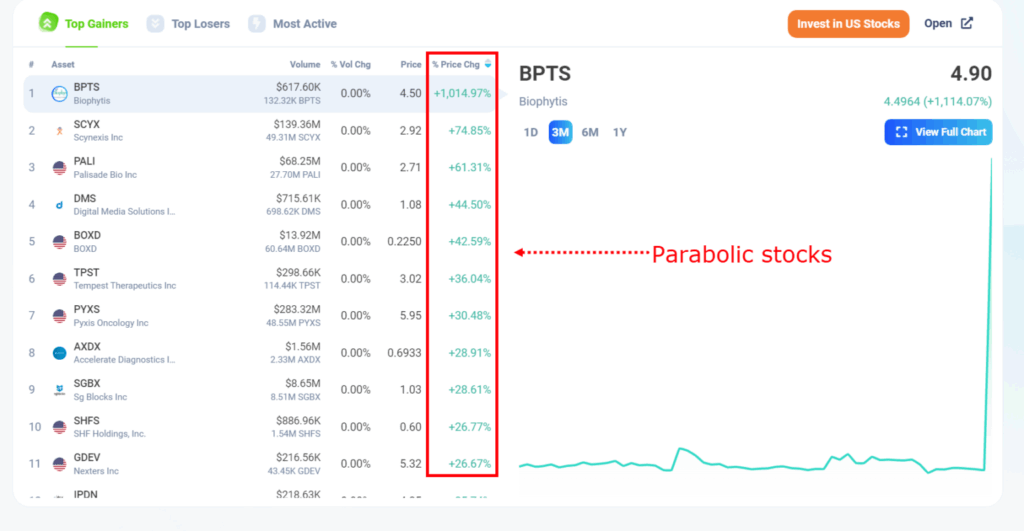
What is a Parabolic Price Movement?
A parabolic price movement is characterized by a rapid and exponential increase in the price of an asset over a relatively short period. This type of price action resembles a parabola when plotted on a chart, hence the name. It’s often fueled by strong bullish sentiment, speculation, and a fear of missing out (FOMO) among investors. These movements are unsustainable in the long run and typically end with a sharp correction or crash.
The key features of a parabolic price trend include:
- Rapid Price Increase: The asset’s price rises at an accelerating pace.
- Steep Trendline: The trendline connecting the price lows becomes increasingly steep.
- High Volume: Trading volume often increases significantly as the price rises.
- Euphoria: Market sentiment becomes extremely bullish, with widespread optimism.
- Unsustainable: The rapid price increase is not supported by underlying fundamentals.
How Parabolic Price Movements Form
Several factors can contribute to the formation of a parabolic price movement:
- Strong Demand: A sudden surge in demand for the asset, often driven by positive news or events.
- Limited Supply: A scarcity of the asset, which can exacerbate the price increase.
- Speculation: Investors buying the asset with the expectation of selling it at a higher price.
- FOMO: The fear of missing out on potential gains, which encourages more investors to buy.
- Leverage: The use of borrowed funds to amplify potential profits (and losses).
The process typically begins with a gradual uptrend, which then accelerates as more investors become aware of the asset’s potential. As the price rises, media coverage increases, attracting even more buyers. This creates a self-fulfilling prophecy, where the rising price reinforces the bullish sentiment and attracts further investment. Eventually, the price reaches an unsustainable level, and the bubble bursts.
Identifying Parabolic Price Patterns
Recognizing a parabolic price pattern early on can be challenging, but there are several indicators to look for:
- Trendline Analysis: Draw a trendline connecting the price lows. If the trendline becomes increasingly steep, it could be a sign of a parabolic price move.
- Volume Analysis: Look for a significant increase in trading volume as the price rises.
- Relative Strength Index (RSI): The RSI is a momentum indicator that measures the magnitude of recent price changes to evaluate overbought or oversold conditions. An RSI above 70 typically indicates an overbought condition, which could signal a potential reversal.
- Moving Averages: Compare the current price to its moving averages. If the price is significantly above its moving averages, it could be a sign of a parabolic price trend.
- Market Sentiment: Pay attention to market news and social media. If there is widespread euphoria and excessive optimism, it could be a warning sign.
The Risks of Investing in Parabolic Price Movements
Investing in parabolic price movements is inherently risky. The rapid price increase is unsustainable, and a sharp correction or crash is almost inevitable. The risks include:
- Sharp Corrections: The price can drop dramatically in a short period, leading to significant losses.
- Volatility: Parabolic price movements are characterized by high volatility, making it difficult to predict future price movements.
- Emotional Investing: FOMO can lead to impulsive investment decisions, which can be detrimental to your portfolio.
- Market Manipulation: Some parabolic price movements may be driven by market manipulation, which can lead to artificial price increases and subsequent crashes.
Strategies for Navigating Parabolic Price Movements
While investing in parabolic price movements is risky, there are strategies that can help mitigate the risks and potentially profit from these trends:
- Do Your Research: Before investing in any asset, conduct thorough research on its fundamentals and potential risks.
- Set Stop-Loss Orders: Use stop-loss orders to limit your potential losses in case of a price reversal.
- Take Profits: As the price rises, consider taking profits to secure your gains.
- Diversify Your Portfolio: Don’t put all your eggs in one basket. Diversify your portfolio across different assets to reduce your overall risk.
- Be Patient: Don’t rush into investments based on FOMO. Wait for a clear signal before entering a trade.
- Consider Shorting: Experienced traders might consider shorting the asset when they believe the parabolic price trend is nearing its end. However, this is a high-risk strategy that should only be attempted by experienced traders with a thorough understanding of risk management.
Examples of Parabolic Price Movements in History
Throughout history, there have been numerous examples of parabolic price movements, often followed by significant crashes. Some notable examples include:
- The Dot-Com Bubble (late 1990s): Internet stocks experienced a parabolic price increase, followed by a massive crash in the early 2000s.
- The Housing Bubble (mid-2000s): Real estate prices rose rapidly, fueled by easy credit and speculation. The bubble burst in 2008, triggering a global financial crisis.
- Bitcoin (2017): The price of Bitcoin surged dramatically in 2017, reaching a peak of nearly $20,000 before crashing in 2018.
- GameStop (2021): GameStop’s stock price experienced a parabolic price increase due to a short squeeze orchestrated by retail investors on social media.
The Psychology Behind Parabolic Price Action
Understanding the psychology behind parabolic price movements is crucial for navigating these trends. Several psychological factors contribute to the formation and eventual collapse of these bubbles:
- Greed: The desire to make quick profits can cloud judgment and lead to irrational investment decisions.
- Fear: The fear of missing out (FOMO) can drive investors to buy assets at inflated prices.
- Confirmation Bias: Investors tend to seek out information that confirms their existing beliefs, even if that information is inaccurate or misleading.
- Herd Mentality: Investors often follow the crowd, assuming that others know more than they do.
- Cognitive Dissonance: When an investment goes wrong, investors may try to justify their decision to avoid admitting they made a mistake.
Conclusion
Parabolic price movements are a fascinating and potentially lucrative phenomenon in financial markets. However, they are also inherently risky. By understanding the characteristics, causes, and risks associated with these trends, investors can make more informed decisions and potentially profit from them while mitigating the risk of significant losses. Remember to always conduct thorough research, set stop-loss orders, take profits, and diversify your portfolio. While the allure of quick gains is tempting, a disciplined and rational approach is essential for navigating the turbulent waters of parabolic price action. Understanding how a parabolic price trend can develop is essential in protecting your investments. [See also: Risk Management Strategies for Volatile Markets] and [See also: Understanding Market Bubbles and Crashes]. Keep in mind that past performance is not indicative of future results, and all investments carry risk. The best approach to trading parabolic price action is to be prepared and disciplined.