Unlocking Financial Power: A Comprehensive Guide to the Leverage Calculator
In the dynamic world of finance, understanding and effectively utilizing leverage is crucial for both individuals and businesses aiming to amplify their investment returns. A leverage calculator serves as an indispensable tool in this process, enabling users to quantify the potential impact of debt on their financial outcomes. This article delves into the intricacies of leverage, exploring its definition, benefits, risks, and practical applications through the use of a leverage calculator.
What is Leverage?
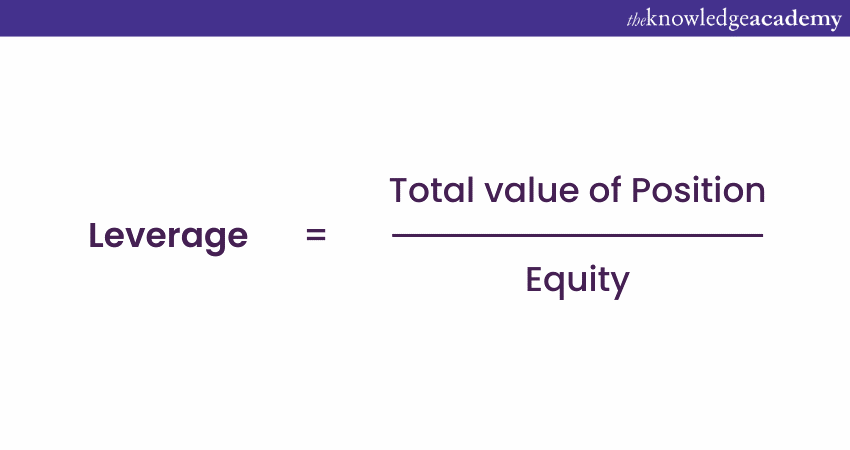
Leverage, in its simplest form, involves using borrowed capital to increase the potential return of an investment. Think of it as using a small amount of your own money to control a much larger asset. This can significantly magnify both profits and losses. Common examples include using a mortgage to buy a house, or margin trading in the stock market. The key is understanding the risk-reward ratio before employing leverage.
The Importance of a Leverage Calculator
A leverage calculator is a specialized tool designed to help investors and business owners determine the optimal level of debt to use in a specific investment or project. It takes into account various factors such as the initial investment, the cost of borrowing (interest rates), and the anticipated return on investment to provide a clear picture of the potential financial outcomes. Without a leverage calculator, making informed decisions about leverage becomes significantly more challenging, increasing the risk of over-leveraging and potential financial distress.
Benefits of Using Leverage
- Amplified Returns: The primary benefit of leverage is the potential to generate higher returns on investment. By using borrowed funds, investors can control larger assets and potentially reap greater profits.
- Increased Investment Capacity: Leverage allows investors to participate in opportunities that would otherwise be beyond their financial reach. This opens up a wider range of investment possibilities and can accelerate wealth accumulation.
- Tax Advantages: In some cases, interest paid on borrowed funds may be tax-deductible, further enhancing the attractiveness of leverage. Consult with a tax professional to determine the specific tax implications in your jurisdiction.
Risks Associated with Leverage
- Magnified Losses: While leverage can amplify profits, it can also magnify losses. If an investment performs poorly, the investor is still responsible for repaying the borrowed funds, potentially leading to significant financial losses.
- Increased Financial Risk: Over-leveraging can increase the risk of financial distress and even bankruptcy. It’s crucial to carefully assess the risk-reward ratio and ensure that the investment has the potential to generate sufficient returns to cover the cost of borrowing.
- Interest Rate Risk: Changes in interest rates can impact the cost of borrowing and the overall profitability of a leveraged investment. Rising interest rates can erode profits and increase the burden of debt repayment.
Understanding the Components of a Leverage Calculator
Most leverage calculators require several key inputs to provide accurate results. These typically include:
- Initial Investment: The amount of capital the investor is contributing from their own funds.
- Borrowed Funds: The amount of debt being used to finance the investment.
- Interest Rate: The cost of borrowing, expressed as an annual percentage.
- Investment Return: The anticipated return on the investment, expressed as a percentage.
- Time Horizon: The length of time the investment is expected to generate returns.
By inputting these values into the leverage calculator, users can gain insights into the potential profit or loss, the return on equity, and the break-even point for the investment.
How to Use a Leverage Calculator Effectively
Using a leverage calculator is relatively straightforward, but it’s important to interpret the results carefully and consider all relevant factors. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
- Gather Your Data: Collect all the necessary information, including the initial investment, borrowed funds, interest rate, and anticipated return on investment.
- Input the Data: Enter the data into the leverage calculator. Most calculators are user-friendly and provide clear instructions.
- Analyze the Results: Review the results carefully, paying attention to the potential profit or loss, return on equity, and break-even point.
- Consider Different Scenarios: Experiment with different input values to see how changes in interest rates or investment returns could impact the outcome.
- Make Informed Decisions: Use the information provided by the leverage calculator to make informed decisions about the appropriate level of leverage to use in your investment.
Examples of Leverage in Different Scenarios
Real Estate: A common example of leverage is using a mortgage to purchase a property. The investor puts down a small percentage of the purchase price as a down payment and borrows the remaining amount from a lender. If the property appreciates in value, the investor can realize a significant return on their initial investment. However, if the property declines in value, the investor is still responsible for repaying the mortgage, potentially leading to financial losses. Using a leverage calculator can help determine how much mortgage to take on.
Stock Market: Margin trading involves borrowing funds from a brokerage firm to purchase stocks. This allows investors to control a larger number of shares than they could otherwise afford. If the stock price increases, the investor can realize a substantial profit. However, if the stock price decreases, the investor is still responsible for repaying the borrowed funds, potentially leading to significant losses. Calculating your potential gains and losses is easily achieved with a leverage calculator.
Business Operations: Businesses often use leverage to finance expansion or acquire new assets. This can involve taking out loans or issuing bonds. If the business is successful, the increased revenue can generate higher profits for the owners. However, if the business struggles, the debt repayment obligations can strain its financial resources.
Choosing the Right Leverage Calculator
Numerous leverage calculators are available online, ranging from simple tools to more sophisticated platforms. When choosing a leverage calculator, consider the following factors:
- Accuracy: Ensure that the calculator uses accurate formulas and provides reliable results.
- User-Friendliness: Choose a calculator that is easy to use and understand.
- Features: Look for a calculator that offers the features you need, such as the ability to analyze different scenarios or generate detailed reports.
- Cost: Some leverage calculators are free, while others require a subscription or one-time fee. Choose a calculator that fits your budget and provides the value you need.
Leverage and Risk Management
Effective risk management is essential when using leverage. Here are some key strategies to consider:
- Diversification: Spread your investments across different asset classes to reduce the impact of any single investment performing poorly.
- Stop-Loss Orders: Use stop-loss orders to limit potential losses on leveraged investments.
- Regular Monitoring: Monitor your investments regularly and adjust your leverage as needed.
- Professional Advice: Seek advice from a financial advisor to ensure that you are using leverage appropriately and managing your risk effectively.
The Future of Leverage Calculators
As financial markets become increasingly complex, leverage calculators are likely to become even more sophisticated. Future calculators may incorporate advanced features such as:
- Artificial Intelligence: AI-powered calculators could provide more personalized and accurate recommendations based on individual risk profiles and investment goals.
- Real-Time Data: Calculators could integrate with real-time market data to provide up-to-date insights into investment opportunities.
- Scenario Planning: Calculators could offer more advanced scenario planning capabilities, allowing users to simulate the impact of various economic conditions on their leveraged investments.
Conclusion
The leverage calculator is a powerful tool that can help investors and business owners make informed decisions about the use of debt. By understanding the benefits and risks of leverage and using a leverage calculator effectively, individuals can potentially amplify their investment returns and achieve their financial goals. However, it’s crucial to remember that leverage is a double-edged sword, and effective risk management is essential to avoid potential financial distress. Always consult with a financial advisor before making any significant investment decisions.
Leverage can be a powerful tool if understood and used correctly. This guide provides a solid understanding to help you get started. Remember to always calculate your risks when using leverage.
[See also: Understanding Financial Ratios] [See also: Investment Strategies for Beginners] [See also: Risk Management in Investing]
