Unlocking Market Secrets: Mastering the Bollinger Squeeze for Profitable Trading
In the dynamic world of financial markets, traders are constantly seeking reliable indicators to predict price movements and capitalize on profitable opportunities. Among the plethora of technical analysis tools available, the Bollinger Squeeze stands out as a powerful technique for identifying periods of low volatility that often precede significant price breakouts. This article delves into the intricacies of the Bollinger Squeeze, exploring its underlying principles, practical applications, and potential benefits for traders of all levels.
Understanding the Bollinger Squeeze
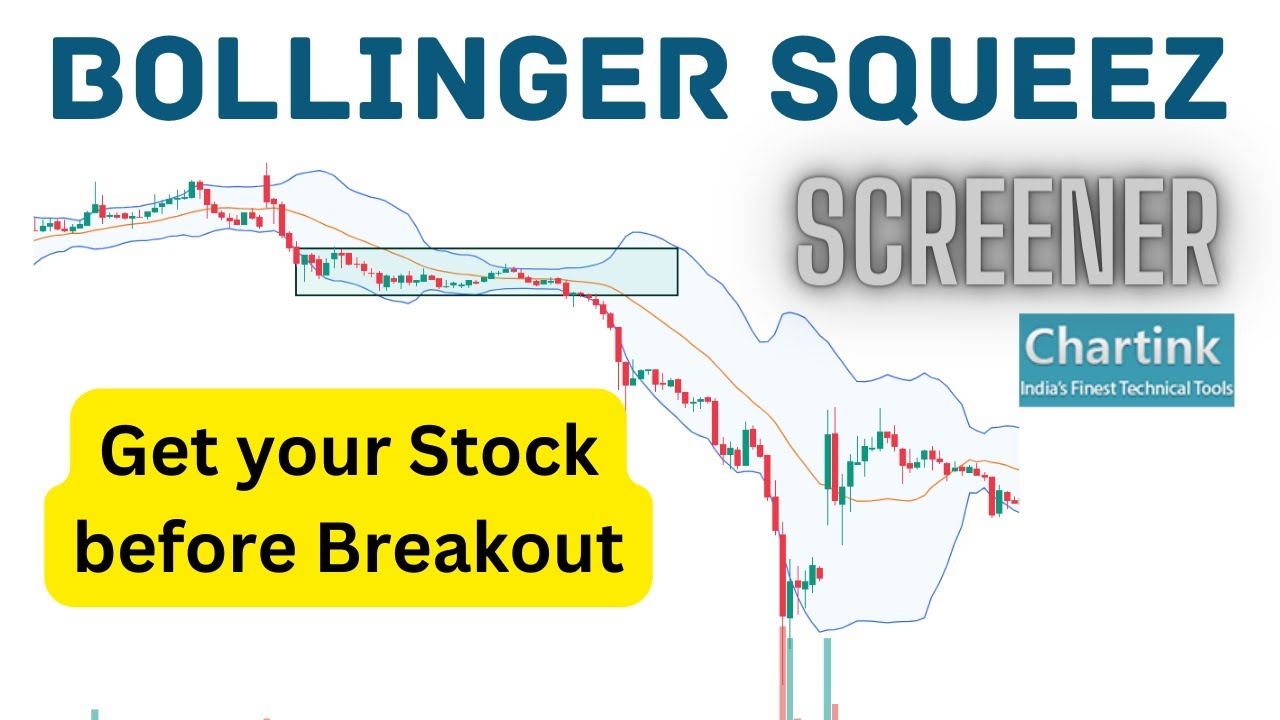
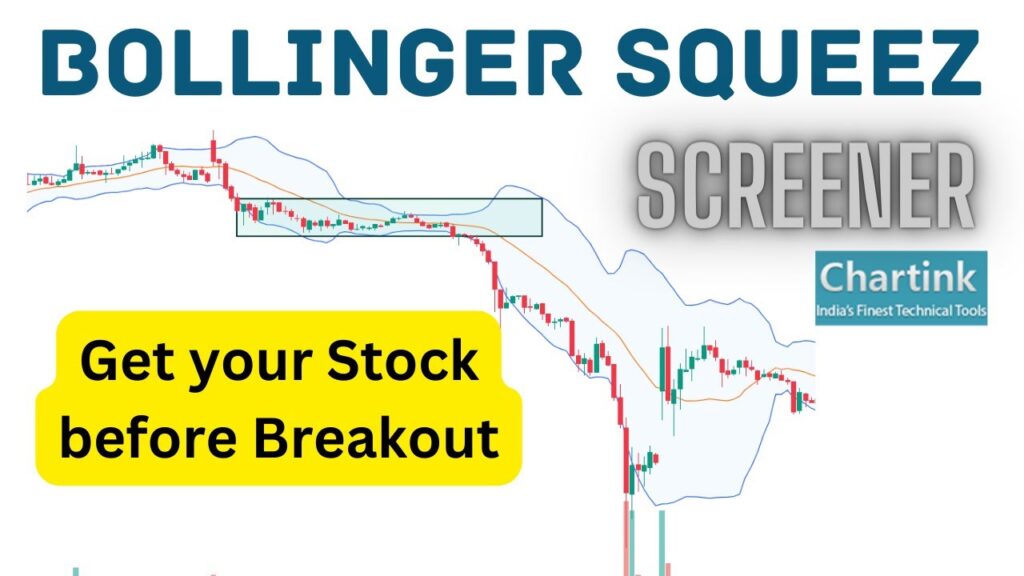
The Bollinger Squeeze is a volatility indicator derived from Bollinger Bands, a technical analysis tool developed by John Bollinger in the 1980s. Bollinger Bands consist of three lines plotted on a price chart: a simple moving average (SMA), an upper band calculated by adding a certain number of standard deviations to the SMA, and a lower band calculated by subtracting the same number of standard deviations from the SMA. The standard deviation is a measure of price volatility, reflecting how much the price deviates from its average value.
When the upper and lower Bollinger Bands move closer together, constricting the price action, it signals a period of low volatility. This contraction is known as the Bollinger Squeeze. The core principle behind the Bollinger Squeeze is that periods of low volatility are often followed by periods of high volatility, resulting in a significant price movement in either direction. Traders use the Bollinger Squeeze to identify potential breakout opportunities and prepare for a possible surge in price volatility. The Bollinger Squeeze is not a crystal ball, but it is a useful tool.
How the Bollinger Squeeze Works
The Bollinger Squeeze identifies moments when volatility reaches a relatively low point. This happens when the upper and lower bands converge, indicating that the price has been trading within a narrow range. This period of consolidation suggests that the market is in a state of equilibrium, and a significant price movement is likely to occur soon. The squeeze essentially ‘prepares’ the market for a breakout, but it doesn’t predict the direction of the breakout. Traders then look for additional confirmation signals to determine whether the price will break upward or downward.
The key to understanding the Bollinger Squeeze lies in recognizing that volatility tends to oscillate between periods of expansion and contraction. When volatility is high, the bands widen to accommodate the price fluctuations. Conversely, when volatility is low, the bands narrow, creating the squeeze. This cyclical pattern provides traders with valuable insights into the market’s potential future movements. The Bollinger Squeeze is a visual representation of this volatility cycle.
Identifying a Bollinger Squeeze
Visually identifying a Bollinger Squeeze on a price chart is relatively straightforward. Look for periods where the upper and lower Bollinger Bands move closer together, narrowing the channel within which the price is trading. The tighter the squeeze, the more significant the potential breakout is likely to be. Some trading platforms offer automated tools that highlight Bollinger Squeeze occurrences, further simplifying the identification process.
However, it is important to note that not every instance of narrowing Bollinger Bands constitutes a valid Bollinger Squeeze. The squeeze should be accompanied by a sustained period of low volatility, indicating that the market is genuinely consolidating. Traders should also consider other technical indicators and chart patterns to confirm the validity of the squeeze and avoid false signals. [See also: Confirming Trading Signals with Technical Indicators]
Trading Strategies Using the Bollinger Squeeze
Once a Bollinger Squeeze has been identified, traders can employ various strategies to capitalize on the anticipated breakout. Here are some common approaches:
Breakout Confirmation
This strategy involves waiting for the price to break above the upper band or below the lower band before entering a trade. A break above the upper band suggests an upward breakout, while a break below the lower band suggests a downward breakout. Traders typically use stop-loss orders to manage risk and limit potential losses if the breakout fails.
Momentum Indicators
Traders often combine the Bollinger Squeeze with momentum indicators, such as the Relative Strength Index (RSI) or the Moving Average Convergence Divergence (MACD), to confirm the direction of the breakout. For example, if the price breaks above the upper band and the RSI is above 70, it suggests strong upward momentum and a higher probability of a successful breakout.
Volume Analysis
Volume plays a crucial role in confirming the validity of a Bollinger Squeeze breakout. A significant increase in volume during the breakout indicates strong participation and confirms that the price movement is likely to be sustained. Conversely, a breakout with low volume may be a false signal and should be approached with caution. [See also: Volume Analysis in Trading]
Using Stop-Loss Orders
Regardless of the specific strategy employed, it is essential to use stop-loss orders to manage risk. Stop-loss orders automatically close a trade if the price moves against the trader’s position, limiting potential losses. The placement of stop-loss orders should be based on the trader’s risk tolerance and the volatility of the market.
Advantages of Using the Bollinger Squeeze
The Bollinger Squeeze offers several advantages for traders:
- Early Identification of Potential Breakouts: The Bollinger Squeeze allows traders to identify potential breakout opportunities before they occur, giving them a head start in capitalizing on the subsequent price movement.
- Objective Indicator: The Bollinger Squeeze is based on mathematical calculations and provides an objective assessment of market volatility, reducing the influence of subjective biases.
- Versatility: The Bollinger Squeeze can be applied to various markets and timeframes, making it a versatile tool for traders of all styles.
- Easy to Understand: The concept of the Bollinger Squeeze is relatively easy to grasp, even for novice traders.
Limitations of Using the Bollinger Squeeze
Despite its advantages, the Bollinger Squeeze also has some limitations:
- False Signals: The Bollinger Squeeze can generate false signals, especially in choppy or sideways markets.
- Directional Ambiguity: The Bollinger Squeeze does not predict the direction of the breakout, requiring traders to use additional indicators or analysis to determine the likely direction.
- Lagging Indicator: The Bollinger Squeeze is a lagging indicator, meaning that it provides information about past price movements rather than predicting future movements with certainty.
- Requires Confirmation: It’s crucial to confirm signals from the Bollinger Squeeze with other technical indicators or chart patterns to increase the probability of a successful trade.
Real-World Examples of Bollinger Squeeze in Action
Numerous examples demonstrate the effectiveness of the Bollinger Squeeze in identifying profitable trading opportunities. Consider a stock that has been trading within a narrow range for several weeks, with the Bollinger Bands gradually narrowing. As the bands tighten, a Bollinger Squeeze forms, indicating that a significant price movement is imminent. If the stock subsequently breaks above the upper band with a surge in volume, it confirms an upward breakout, and traders can enter a long position to profit from the anticipated price increase. Conversely, if the stock breaks below the lower band, traders can enter a short position. [See also: Case Studies in Technical Analysis]
Tips for Using the Bollinger Squeeze Effectively
To maximize the effectiveness of the Bollinger Squeeze, consider the following tips:
- Use Multiple Timeframes: Analyze the Bollinger Squeeze on multiple timeframes to gain a more comprehensive understanding of the market’s volatility and potential breakout opportunities.
- Combine with Other Indicators: Combine the Bollinger Squeeze with other technical indicators, such as momentum indicators and volume analysis, to confirm signals and improve the accuracy of your trading decisions.
- Practice Risk Management: Always use stop-loss orders to manage risk and limit potential losses.
- Backtest Your Strategies: Backtest your Bollinger Squeeze trading strategies on historical data to evaluate their effectiveness and identify potential weaknesses.
- Stay Informed: Keep abreast of market news and events that may impact volatility and influence the outcome of Bollinger Squeeze breakouts.
Conclusion
The Bollinger Squeeze is a valuable tool for traders seeking to identify periods of low volatility that often precede significant price movements. By understanding the underlying principles of the Bollinger Squeeze and applying it in conjunction with other technical analysis techniques, traders can enhance their ability to anticipate breakouts and capitalize on profitable opportunities. However, it is crucial to remember that the Bollinger Squeeze is not a foolproof indicator and should be used with caution and in conjunction with sound risk management practices. The Bollinger Squeeze is a powerful weapon in a trader’s arsenal when used correctly. Mastering the Bollinger Squeeze, with its nuances and best practices, can lead to more informed and profitable trading decisions. Trading is a complex endeavor, and continuous learning and adaptation are key to long-term success. The Bollinger Squeeze, when properly understood and applied, can be a significant asset in navigating the markets.