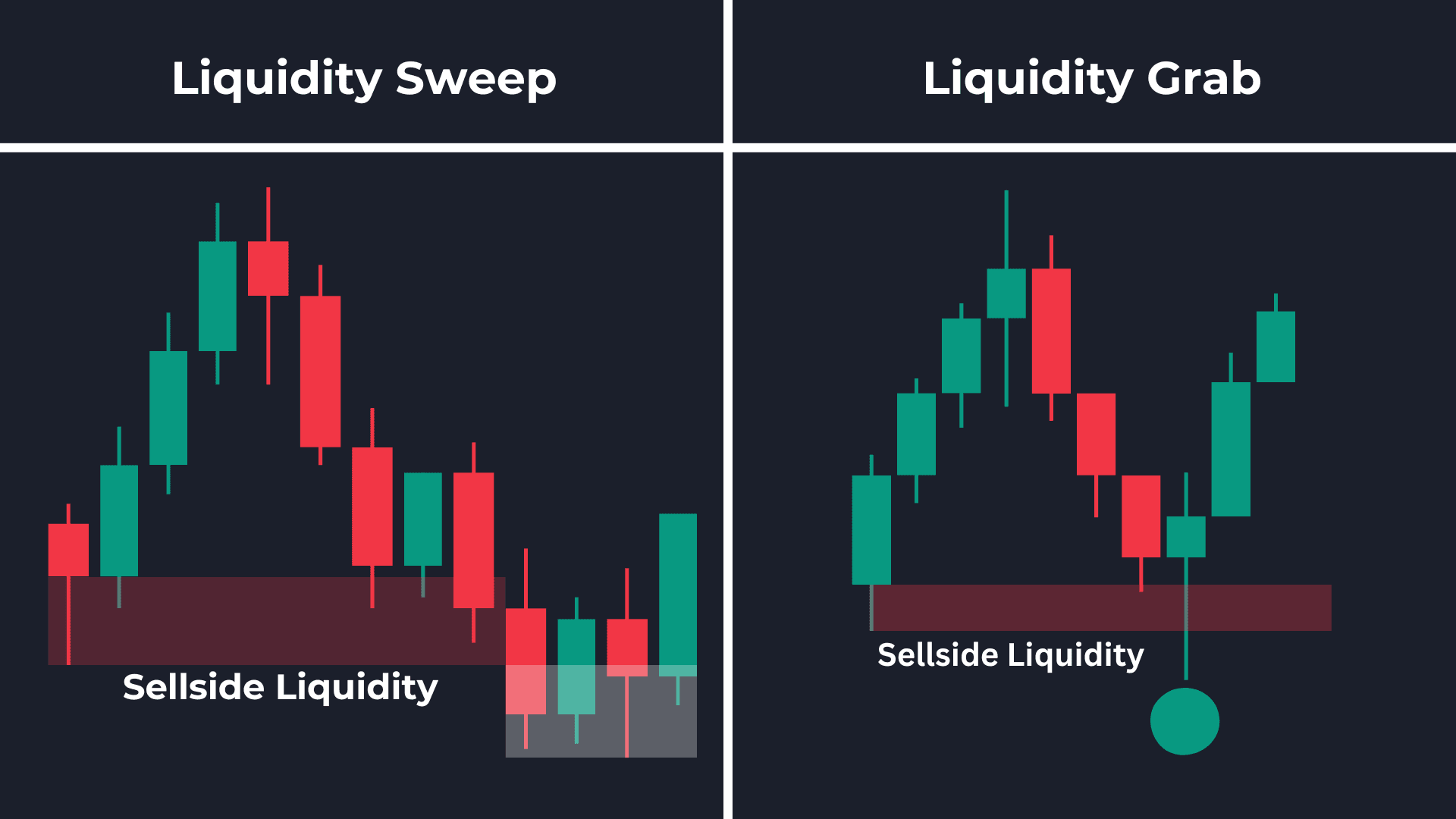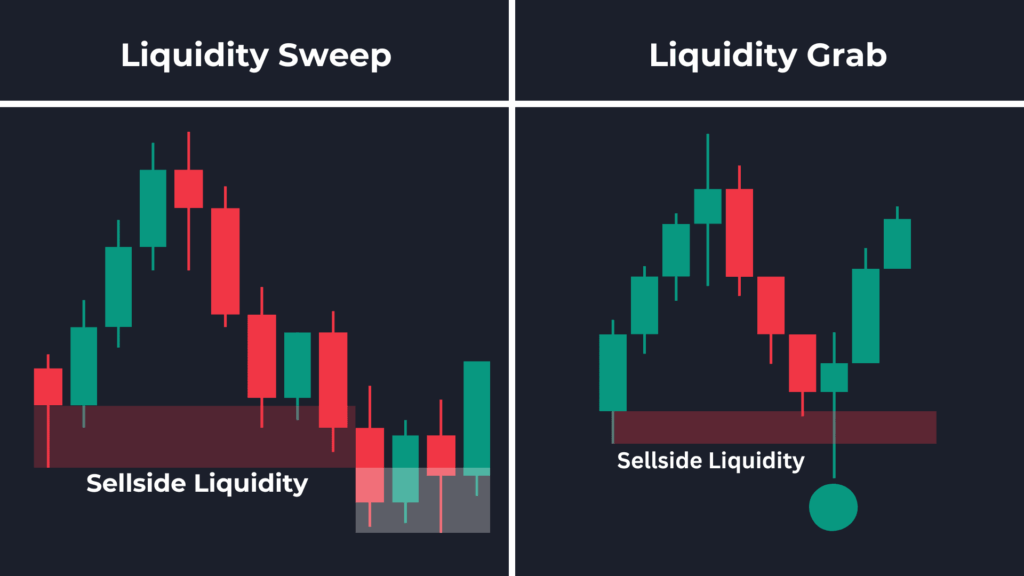
Unveiling Liquidity Sweep Trading: A Comprehensive Guide
In the dynamic world of financial markets, traders constantly seek strategies to capitalize on price movements and market inefficiencies. One such strategy is liquidity sweep trading, a technique that aims to profit from the rapid execution of large orders that consume available liquidity at specific price levels. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of liquidity sweep trading, exploring its mechanics, advantages, risks, and practical applications.
What is Liquidity Sweep Trading?
Liquidity sweep trading, also known as iceberg order execution or stop-hunt trading by some, involves placing large market orders designed to quickly fill at the best available prices. These orders are intended to exhaust the readily available liquidity at a particular price point, often triggering stop-loss orders and initiating a cascade of further price movement. The core principle behind liquidity sweep trading is to exploit the imbalance between supply and demand, profiting from the subsequent price shift.
Understanding Liquidity
Before diving deeper, it’s crucial to grasp the concept of liquidity. In financial markets, liquidity refers to the ease with which an asset can be bought or sold without significantly affecting its price. High liquidity implies a large number of buyers and sellers, allowing for quick and efficient transactions. Conversely, low liquidity means fewer participants, making it harder to execute large orders without causing substantial price fluctuations. Liquidity sweeps target areas where liquidity is perceived to be high, aiming to trigger a rapid price movement.
How Liquidity Sweep Trading Works
The mechanics of liquidity sweep trading can be broken down into several key steps:
- Identification of Liquidity Zones: Traders identify price levels where significant liquidity is expected to be present. These areas often coincide with support and resistance levels, trendlines, or areas where stop-loss orders are clustered.
- Placement of Large Market Orders: Once a liquidity zone is identified, a large market order is placed in the direction of the anticipated price movement. This order is designed to consume all available limit orders at that price level.
- Triggering Stop-Loss Orders: As the market order executes, it triggers stop-loss orders placed by other traders who were positioned against the anticipated price move.
- Cascade Effect and Price Movement: The triggered stop-loss orders further fuel the price movement, creating a cascade effect as more and more traders are forced to exit their positions.
- Profit Taking: The liquidity sweep trader then aims to profit from this rapid price movement by closing their position at a favorable price.
For example, imagine a stock trading at $50 with a large number of stop-loss orders clustered just below $49.90. A liquidity sweep trader might place a large sell order at $49.90, intending to trigger those stop-loss orders and drive the price even lower, allowing them to profit from the short-term downward momentum.
Advantages of Liquidity Sweep Trading
Liquidity sweep trading offers several potential advantages:
- Profit Potential: The rapid price movements generated by liquidity sweeps can lead to quick and substantial profits.
- Relatively Short Timeframe: Liquidity sweep trades typically occur over a short timeframe, allowing traders to capitalize on immediate market opportunities.
- Versatility: This strategy can be applied to various asset classes, including stocks, forex, and cryptocurrencies.
Risks of Liquidity Sweep Trading
Despite its potential benefits, liquidity sweep trading is a high-risk strategy with several inherent challenges:
- Market Manipulation Concerns: Critics argue that liquidity sweep trading can be used for market manipulation, as large players may intentionally trigger stop-loss orders to profit at the expense of other traders.
- Unpredictable Market Conditions: Market conditions can change rapidly, and a liquidity sweep may not always unfold as expected. Unexpected news events or shifts in market sentiment can invalidate the trade setup.
- Slippage: Slippage, the difference between the expected price and the actual execution price, can erode profits, especially when dealing with large orders in volatile markets.
- False Signals: Sometimes, what appears to be a liquidity zone can be a false signal, leading to losses if the price doesn’t move as anticipated.
- Requires Significant Capital: Successfully executing a liquidity sweep often requires substantial capital to place large orders that can move the market.
Liquidity Sweep Trading in Different Markets
The application of liquidity sweep trading can vary depending on the specific market:
Forex Market
In the forex market, liquidity sweeps often target areas around key psychological levels (e.g., 1.2000 for EUR/USD) or major support and resistance levels. The high leverage available in forex trading can amplify both profits and losses associated with this strategy. [See also: Forex Trading Strategies]
Stock Market
In the stock market, liquidity sweeps may target areas where institutional investors are expected to accumulate or distribute shares. Identifying these areas requires a deep understanding of order book dynamics and market microstructure. [See also: Understanding Stock Market Order Books]
Cryptocurrency Market
The cryptocurrency market, known for its volatility and relatively low liquidity compared to traditional markets, can be particularly susceptible to liquidity sweeps. Traders should exercise extreme caution when employing this strategy in crypto, as the risks are often magnified. [See also: Cryptocurrency Trading Risks]
Tools and Techniques for Liquidity Sweep Trading
Successful liquidity sweep trading requires a combination of technical analysis skills, market awareness, and specialized tools:
- Order Book Analysis: Understanding the order book, which displays the current buy and sell orders at different price levels, is crucial for identifying potential liquidity zones.
- Volume Analysis: Analyzing trading volume can help confirm the presence of significant buying or selling pressure, supporting the likelihood of a liquidity sweep.
- Technical Indicators: Indicators such as volume price trend (VPT) and on-balance volume (OBV) can provide insights into the strength of price movements and potential liquidity imbalances.
- Trading Platforms: Access to advanced trading platforms with order routing capabilities and real-time market data is essential for executing liquidity sweep trades effectively.
Ethical Considerations
The ethical implications of liquidity sweep trading are a subject of ongoing debate. While some argue that it’s a legitimate trading strategy, others view it as a form of market manipulation that exploits other traders. It’s crucial to consider the ethical implications and adhere to all applicable regulations when engaging in liquidity sweep trading.
Conclusion
Liquidity sweep trading is a complex and high-risk strategy that requires a deep understanding of market dynamics and sophisticated trading skills. While it offers the potential for significant profits, it also carries substantial risks, including market manipulation concerns, unpredictable market conditions, and slippage. Traders considering this strategy should carefully weigh the potential benefits against the inherent risks and ensure they have the necessary knowledge, tools, and capital to execute it effectively. As with any trading strategy, proper risk management and a disciplined approach are essential for long-term success. Understanding the nuances of liquidity sweeps can provide a competitive edge, but always trade responsibly and be aware of the potential pitfalls.
Before attempting liquidity sweep trading, consider consulting with a financial advisor to determine if it aligns with your risk tolerance and investment goals. Remember that past performance is not indicative of future results, and all trading involves risk of loss.