Unveiling Trading Liquidity Sweeps: A Comprehensive Guide for Traders
In the dynamic world of trading, understanding market mechanics is crucial for success. One such mechanism is the trading liquidity sweep. A trading liquidity sweep, often simply referred to as a liquidity sweep, is a market event where a large order rapidly consumes available liquidity at multiple price levels. This phenomenon can have significant implications for traders, influencing price action and potentially creating both opportunities and risks. This guide aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of trading liquidity sweeps, exploring their causes, characteristics, and strategic implications for traders of all levels.
Understanding Liquidity in Trading
Before delving into the specifics of trading liquidity sweeps, it’s essential to grasp the concept of liquidity itself. Liquidity refers to the ease with which an asset can be bought or sold without significantly affecting its price. A market with high liquidity has numerous buyers and sellers, ensuring that orders can be executed quickly and efficiently. Conversely, a market with low liquidity may experience significant price fluctuations when large orders are placed.
Order books visually represent liquidity. They display the available buy (bid) and sell (ask) orders at various price points. The depth of the order book indicates the amount of liquidity available at each price level. A trading liquidity sweep occurs when a large order depletes these existing orders, often triggering further price movement.
What is a Trading Liquidity Sweep?
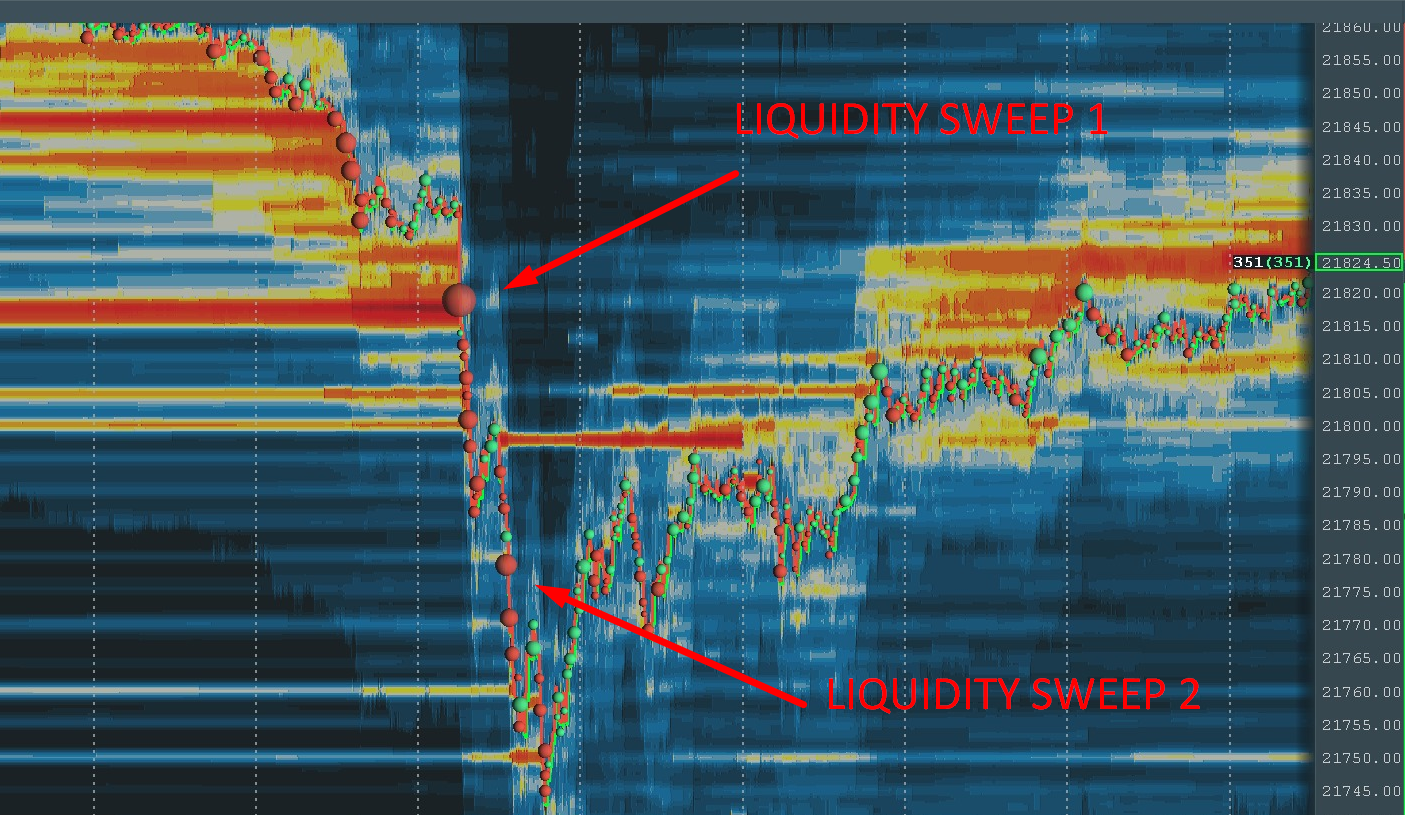
A trading liquidity sweep is characterized by a rapid and aggressive execution of a large order that consumes available liquidity across multiple price levels in the order book. Imagine a scenario where a trader wants to buy a significant amount of a particular asset. Instead of placing a single large order at the current ask price, they strategically break it down into smaller orders that are executed sequentially, each targeting the next available level of liquidity. This aggressive buying (or selling, in the case of a short position) can create a domino effect, triggering stop-loss orders and attracting other traders to join the movement.
The visual effect on a price chart is often a sharp, sudden spike or drop, followed by a period of consolidation or retracement. This volatility can be both profitable and risky, depending on a trader’s position and strategy.
Causes of Trading Liquidity Sweeps
Several factors can contribute to the occurrence of trading liquidity sweeps:
- Large Institutional Orders: Institutional investors, such as hedge funds, pension funds, and mutual funds, often execute large orders that can trigger liquidity sweeps. Their trading activity has a substantial impact on market dynamics.
- Algorithmic Trading: Automated trading systems, or algorithms, are designed to identify and capitalize on market inefficiencies. Some algorithms are specifically programmed to trigger liquidity sweeps by strategically placing orders to exploit imbalances in the order book.
- News Events: Major economic announcements, geopolitical events, or unexpected news releases can create sudden surges in trading volume and volatility, leading to liquidity sweeps. Traders often react quickly to news, placing orders that can quickly deplete available liquidity.
- Stop-Loss Hunting: Some traders or institutions may intentionally trigger liquidity sweeps to activate stop-loss orders placed by other traders. This tactic, known as stop-loss hunting, aims to profit from the resulting price movement.
- Market Manipulation: In some cases, liquidity sweeps can be used as a form of market manipulation. By placing large orders to artificially inflate or deflate the price of an asset, manipulators can profit from the resulting trading activity.
Characteristics of Trading Liquidity Sweeps
Identifying a trading liquidity sweep requires careful observation and analysis of market data. Some key characteristics include:
- Rapid Price Movement: A sudden and significant price spike or drop is a hallmark of a liquidity sweep. This movement is typically faster and more pronounced than normal price fluctuations.
- High Trading Volume: Liquidity sweeps are often accompanied by a surge in trading volume, as large orders are executed and other traders react to the price movement.
- Order Book Imbalance: Before a liquidity sweep, there is often an imbalance in the order book, with a significantly larger number of buy or sell orders at certain price levels. This imbalance creates an opportunity for a large order to trigger a sweep.
- Activation of Stop-Loss Orders: As the price moves rapidly, stop-loss orders are triggered, further accelerating the price movement and amplifying the effect of the liquidity sweep.
- Retracement or Consolidation: After the initial price spike or drop, the price often retraces or consolidates as the market adjusts to the new level.
Strategic Implications for Traders
Understanding trading liquidity sweeps can provide valuable insights for traders and inform their trading strategies. Here are some key considerations:
- Risk Management: Liquidity sweeps can be highly volatile events, and traders should implement robust risk management strategies to protect their capital. This includes setting appropriate stop-loss orders and managing position sizes.
- Identifying Entry and Exit Points: Recognizing the patterns associated with liquidity sweeps can help traders identify potential entry and exit points. For example, a trader might look to enter a position after a liquidity sweep has occurred, anticipating a retracement or consolidation.
- Understanding Market Sentiment: Liquidity sweeps can provide insights into market sentiment. A strong upward liquidity sweep might indicate bullish sentiment, while a downward sweep might suggest bearish sentiment.
- Avoiding Stop-Loss Hunting: Traders should be aware of the potential for stop-loss hunting and avoid placing stop-loss orders too close to key price levels. Consider using wider stop-loss orders or alternative risk management techniques.
- Using Limit Orders: Employing limit orders instead of market orders can help traders avoid being caught in a liquidity sweep. Limit orders allow traders to specify the price at which they are willing to buy or sell, providing greater control over their execution.
Examples of Trading Liquidity Sweeps
To illustrate the concept of trading liquidity sweeps, consider the following examples:
Example 1: Cryptocurrency Market
In the cryptocurrency market, a large whale (a trader with a significant amount of cryptocurrency) places a massive buy order for Bitcoin, triggering a liquidity sweep. The price of Bitcoin rapidly spikes upward as the whale consumes all available sell orders at multiple price levels. This triggers stop-loss orders from short sellers, further accelerating the price increase. Traders who were long on Bitcoin profit from the surge, while those who were short experience losses.
Example 2: Forex Market
A major economic announcement, such as the release of US employment data, triggers a liquidity sweep in the EUR/USD currency pair. The announcement is unexpectedly positive, leading to a surge in demand for the US dollar. Large institutional investors quickly buy US dollars, consuming all available sell orders for EUR/USD. The price of EUR/USD plummets as the liquidity sweep unfolds. Traders who anticipated the positive announcement and positioned themselves accordingly profit from the move.
Tools and Resources for Identifying Liquidity Sweeps
Several tools and resources can help traders identify and analyze liquidity sweeps:
- Order Book Analysis Tools: These tools provide a real-time view of the order book, allowing traders to see the depth of liquidity at various price levels.
- Volume Analysis Tools: Volume analysis tools track trading volume over time, helping traders identify surges in volume that may indicate a liquidity sweep.
- Price Charts: Price charts provide a visual representation of price movements, allowing traders to identify rapid price spikes or drops that are characteristic of liquidity sweeps.
- News Feeds: Staying informed about major economic announcements and geopolitical events can help traders anticipate potential liquidity sweeps.
- Market Scanners: Market scanners can be programmed to identify stocks or other assets that are experiencing unusual price or volume activity, potentially indicating a liquidity sweep.
Conclusion
Trading liquidity sweeps are a significant market phenomenon that can have a profound impact on price action. By understanding the causes, characteristics, and strategic implications of liquidity sweeps, traders can better manage their risk, identify potential trading opportunities, and improve their overall trading performance. While liquidity sweeps can present challenges, they also offer opportunities for informed and prepared traders. Continuous learning and adaptation are key to navigating the complexities of the market and profiting from these events. Remember to always practice responsible trading and manage your risk effectively. Understanding trading liquidity sweeps is a valuable tool in any trader’s arsenal. Further research into order book dynamics and algorithmic trading strategies can also be beneficial. [See also: Algorithmic Trading Strategies] and [See also: Understanding Order Book Dynamics]