What is a Liquidity Sweep in Trading? A Comprehensive Guide
In the fast-paced world of financial markets, understanding the nuances of trading strategies and market mechanics is crucial for success. One such concept that traders often encounter is the liquidity sweep. This article aims to provide a comprehensive overview of what a liquidity sweep is, how it works, its implications, and how traders can potentially leverage it for their benefit. We’ll delve into the mechanics behind this phenomenon, explore real-world examples, and discuss strategies for navigating the complexities of liquidity sweeps.
Understanding Liquidity in Trading
Before diving into the specifics of a liquidity sweep, it’s essential to grasp the fundamental concept of liquidity in the context of trading. Liquidity refers to the ease with which an asset can be bought or sold without causing a significant change in its price. A highly liquid market has many buyers and sellers, ensuring that orders can be executed quickly and efficiently.
Conversely, an illiquid market has fewer participants, making it more challenging to find counterparties for trades. This can lead to larger price swings and increased volatility. Understanding the level of liquidity in a particular market is crucial for traders to assess the risk associated with their positions.
Defining a Liquidity Sweep
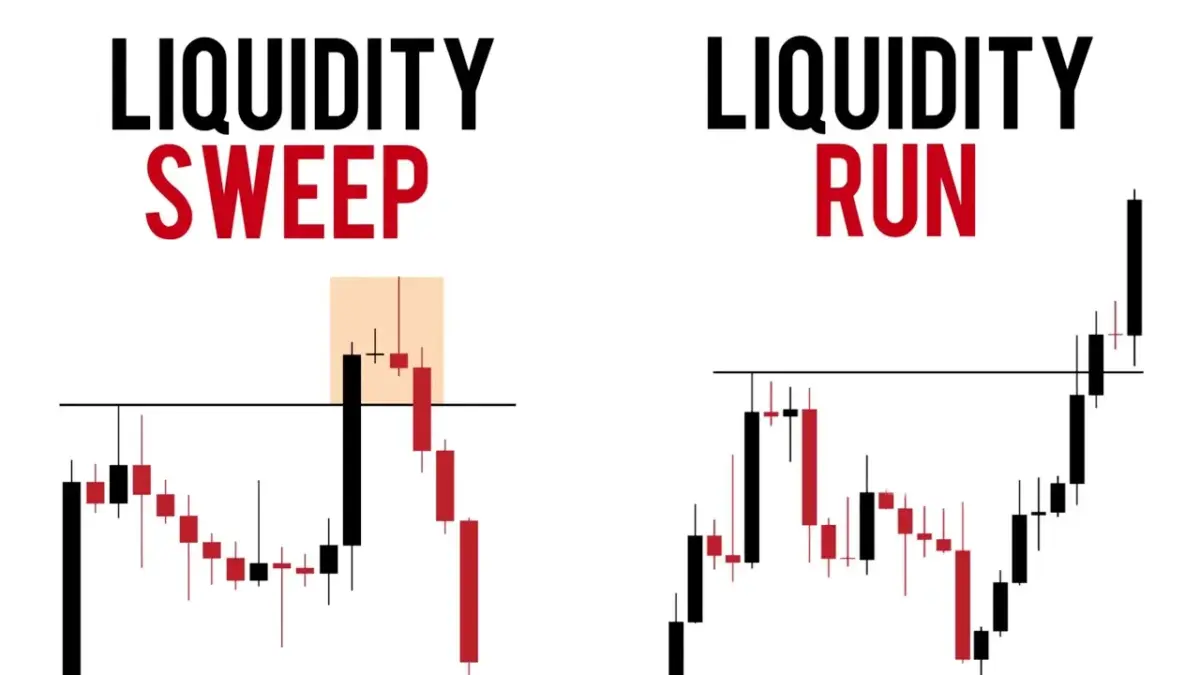
A liquidity sweep is a market event characterized by a rapid and significant movement in price, often triggered by a large order or a series of orders that quickly consume available liquidity at specific price levels. This can result in a sudden spike or drop in price as the market searches for new buyers or sellers to match the demand or supply imbalance.
Essentially, a liquidity sweep occurs when the price moves through multiple levels of resting orders, such as stop-loss orders or limit orders, triggering their execution and further accelerating the price movement. This can create a cascading effect as each triggered order contributes to the overall momentum.
Key Characteristics of a Liquidity Sweep
- Rapid Price Movement: The most defining characteristic is the speed at which the price moves. This movement is often much faster than typical market fluctuations.
- High Volume: Liquidity sweeps are usually accompanied by a surge in trading volume, indicating increased activity and participation.
- Triggered Orders: The event often triggers a series of stop-loss and limit orders, exacerbating the price movement.
- Temporary Imbalance: Liquidity sweeps typically represent a temporary imbalance between buyers and sellers, which is eventually corrected as the market finds equilibrium.
How Liquidity Sweeps Work
The mechanics of a liquidity sweep can be complex, but the underlying principle is relatively straightforward. It begins with a lack of sufficient orders on one side of the market (either buy or sell). When a large order is placed on the opposite side, it quickly exhausts the available liquidity at the current price level. As the order continues to execute, it moves through successive price levels, triggering any resting orders along the way.
For example, imagine a stock trading at $50 with a significant number of stop-loss orders clustered around $49.50. If a large sell order is placed, it will quickly consume all the buy orders at $50 and begin to push the price lower. As the price reaches $49.50, the stop-loss orders are triggered, adding further selling pressure and accelerating the downward movement. This continues until the market finds enough buyers to absorb the selling pressure.
Factors Contributing to Liquidity Sweeps
- Order Book Depth: The depth of the order book, which shows the number of buy and sell orders at different price levels, plays a crucial role. A shallow order book with limited liquidity makes the market more susceptible to liquidity sweeps.
- Algorithmic Trading: Automated trading systems, or algorithms, can exacerbate liquidity sweeps by rapidly executing large orders based on pre-defined criteria. These algorithms can detect areas of low liquidity and exploit them to generate profits.
- News Events: Unexpected news events, such as earnings announcements or economic data releases, can trigger sudden shifts in market sentiment and lead to liquidity sweeps.
- Market Manipulation: In some cases, liquidity sweeps can be intentionally orchestrated by large market participants to manipulate prices and profit from the resulting volatility. This is illegal and subject to regulatory scrutiny.
Examples of Liquidity Sweeps in Trading
Liquidity sweeps can occur in various markets, including stocks, currencies, and commodities. Here are a few examples to illustrate the concept:
- Flash Crash: The “Flash Crash” of May 6, 2010, is a prime example of a liquidity sweep. A large sell order in the E-Mini S&P 500 futures contract triggered a rapid and dramatic decline in stock prices, wiping out billions of dollars in market value within minutes. While the exact cause is still debated, many experts believe that algorithmic trading and a lack of liquidity contributed to the event.
- Currency Markets: In the foreign exchange (forex) market, liquidity sweeps can occur during periods of low trading volume, such as overnight sessions. A large order can quickly move the price of a currency pair, triggering stop-loss orders and creating volatility.
- Cryptocurrency Markets: The cryptocurrency market is particularly prone to liquidity sweeps due to its relatively low liquidity and high volatility. Large sell orders can quickly drive down the price of a cryptocurrency, triggering cascading liquidations of leveraged positions.
Implications for Traders
Liquidity sweeps can have significant implications for traders, both positive and negative. On the one hand, they can present opportunities for quick profits if traders are able to anticipate and capitalize on the price movement. On the other hand, they can lead to substantial losses if traders are caught on the wrong side of the sweep.
Here are some of the key implications for traders:
- Increased Volatility: Liquidity sweeps contribute to increased market volatility, making it more challenging to predict price movements and manage risk.
- Potential for Stop-Loss Hunting: Sophisticated traders may attempt to trigger liquidity sweeps to activate stop-loss orders and profit from the resulting price movement. This is known as “stop-loss hunting.”
- Opportunities for Scalping: Skilled scalpers can take advantage of the rapid price movements during liquidity sweeps to generate small profits on short-term trades.
- Risk of Unexpected Losses: Traders who are not aware of the potential for liquidity sweeps may be caught off guard and suffer unexpected losses.
Strategies for Navigating Liquidity Sweeps
While it is impossible to completely avoid the impact of liquidity sweeps, there are several strategies that traders can use to mitigate the risks and potentially profit from them:
- Monitor Order Book Depth: Pay attention to the depth of the order book to identify areas of low liquidity and potential vulnerability to liquidity sweeps.
- Use Limit Orders: Limit orders, which specify the price at which you are willing to buy or sell, can help you avoid being caught in a liquidity sweep by ensuring that your order is only executed at a favorable price.
- Avoid Tight Stop-Loss Orders: Placing stop-loss orders too close to the current price increases the risk of being triggered by a liquidity sweep. Consider using wider stop-loss orders that allow for more price fluctuation.
- Trade During Liquid Hours: Trade during periods of high trading volume to minimize the risk of liquidity sweeps. Avoid trading during overnight sessions or holidays when liquidity is typically lower.
- Stay Informed: Keep abreast of market news and events that could potentially trigger liquidity sweeps. Be prepared to adjust your trading strategy accordingly.
- Implement Risk Management: Proper risk management techniques, such as position sizing and diversification, can help you limit your losses in the event of a liquidity sweep.
- Consider Using Guaranteed Stop-Loss Orders: Some brokers offer guaranteed stop-loss orders, which ensure that your order will be executed at the specified price, even during periods of high volatility. However, these orders typically come with a higher cost.
The Role of Market Makers
Market makers play a crucial role in maintaining liquidity in financial markets. They provide buy and sell quotes for various assets, ensuring that there are always counterparties available for trades. In the absence of market makers, liquidity sweeps would likely be more frequent and severe.
Market makers use sophisticated algorithms to manage their inventory and adjust their quotes based on market conditions. They also monitor the order book for signs of potential liquidity sweeps and adjust their strategies accordingly.
Liquidity Sweeps and Algorithmic Trading
Algorithmic trading has significantly impacted the frequency and intensity of liquidity sweeps. While algorithms can improve market efficiency and liquidity under normal conditions, they can also exacerbate liquidity sweeps by rapidly executing large orders and triggering cascading effects.
Some algorithms are specifically designed to detect and exploit areas of low liquidity, contributing to the phenomenon of “stop-loss hunting.” Regulators are closely monitoring algorithmic trading practices to ensure that they do not contribute to market manipulation or instability.
Regulation and Oversight
Regulators around the world are increasingly focused on monitoring and regulating market practices that could contribute to liquidity sweeps. This includes scrutinizing algorithmic trading strategies, enforcing rules against market manipulation, and promoting transparency in order book data.
The goal of regulation is to ensure that markets are fair, efficient, and resilient to shocks. By promoting transparency and accountability, regulators can help to reduce the risk of liquidity sweeps and protect investors from undue harm.
Conclusion
Understanding what a liquidity sweep is and how it works is essential for navigating the complexities of financial markets. While liquidity sweeps can present both risks and opportunities, traders who are aware of the phenomenon and employ appropriate risk management strategies can mitigate the potential for losses and potentially profit from the resulting volatility. By monitoring order book depth, using limit orders, and staying informed about market news and events, traders can increase their chances of success in the face of liquidity sweeps.
Ultimately, a comprehensive understanding of market mechanics, combined with sound risk management practices, is the key to navigating the challenges and opportunities presented by liquidity sweeps in the dynamic world of trading. Remember to always conduct thorough research and seek professional advice before making any investment decisions. [See also: Understanding Market Volatility] [See also: Risk Management Strategies for Traders]