What is Marginal Analysis? A Comprehensive Guide for Decision-Making
In the realm of economics and business, informed decision-making is paramount. One critical tool that aids in this process is marginal analysis. But que es analisis marginal? It’s a method that examines the additional benefits of an activity compared to the additional costs incurred by that same activity. Companies use marginal analysis as a decision-making tool to help them maximize their potential profits. Understanding que es analisis marginal and how to apply it can significantly impact strategic choices, from production levels to pricing strategies.
Understanding the Basics of Marginal Analysis
At its core, marginal analysis is about evaluating the impact of small changes. Instead of looking at the overall picture, it focuses on the incremental effects. To fully grasp que es analisis marginal, consider these key components:
- Marginal Cost: The additional cost incurred by producing one more unit of a good or service.
- Marginal Revenue: The additional revenue generated by selling one more unit of a good or service.
- Marginal Benefit: The additional satisfaction or utility gained from consuming one more unit of a good or service.
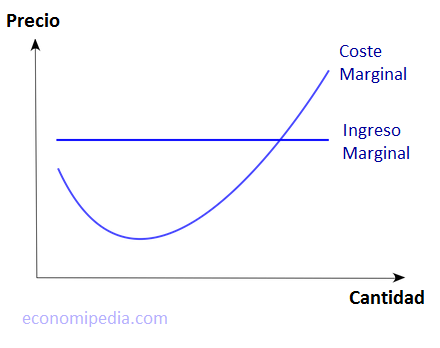
The central idea is that a decision is rational if the marginal benefits exceed the marginal costs. Conversely, if the marginal costs outweigh the marginal benefits, the decision should be reconsidered. Let’s dive deeper into how this works in practice.
How Marginal Analysis Works
The process of conducting a marginal analysis involves several steps. First, you need to identify the decision you’re trying to make. For example, a company might be deciding whether to increase production of a particular product. Next, you need to quantify the marginal costs and marginal benefits associated with that decision.
Calculating marginal cost often involves looking at variable costs, such as the cost of raw materials and labor. Fixed costs, like rent, are typically not included in the calculation because they don’t change with small variations in production. Marginal revenue, on the other hand, depends on the market price and the quantity sold. Finally, compare the marginal cost and marginal revenue. If the marginal revenue is greater than the marginal cost, increasing production is likely a good idea.
Example of Marginal Analysis
Imagine a bakery that sells cakes. Each cake costs $5 to make (marginal cost) and sells for $12 (marginal revenue). In this scenario, the marginal revenue ($12) exceeds the marginal cost ($5) by $7. Therefore, the bakery should continue producing and selling cakes because each additional cake adds to their profit.
However, let’s say the bakery starts experiencing diminishing returns. To sell more cakes, they need to lower the price to $8. Now, the marginal revenue ($8) still exceeds the marginal cost ($5), but the profit margin has shrunk. The bakery needs to carefully monitor the situation to determine the optimal production level.
Applications of Marginal Analysis in Business
Marginal analysis has a wide range of applications in the business world. It can be used to make decisions about:
- Production Levels: Determining the optimal quantity of goods or services to produce.
- Pricing Strategies: Setting prices that maximize profitability.
- Marketing Campaigns: Evaluating the effectiveness of advertising and promotional efforts.
- Investment Decisions: Assessing the potential return on investment for new projects.
- Hiring Decisions: Deciding whether to hire additional employees.
By carefully considering the marginal costs and marginal benefits of each decision, businesses can make more informed choices that lead to increased profitability and efficiency. Understanding que es analisis marginal enables strategic advantages in various business functions.
Benefits of Using Marginal Analysis
There are several benefits to using marginal analysis as a decision-making tool:
- Improved Decision-Making: Provides a structured framework for evaluating choices.
- Increased Profitability: Helps businesses optimize production levels and pricing strategies.
- Resource Allocation: Enables businesses to allocate resources more efficiently.
- Risk Reduction: Helps businesses avoid costly mistakes by carefully considering the potential consequences of their decisions.
By systematically analyzing the marginal costs and marginal benefits of different options, businesses can make more informed decisions that lead to better outcomes. Knowing que es analisis marginal and its advantages is crucial for business success.
Limitations of Marginal Analysis
While marginal analysis is a valuable tool, it’s important to be aware of its limitations:
- Difficulty Quantifying Costs and Benefits: Some costs and benefits are difficult to measure accurately.
- Assumptions of Rationality: Assumes that decision-makers are always rational, which may not always be the case.
- Short-Term Focus: Primarily focuses on short-term effects and may not adequately consider long-term consequences.
- External Factors: Doesn’t always account for external factors that can impact costs and benefits, such as changes in market conditions or government regulations.
Despite these limitations, marginal analysis remains a powerful tool when used in conjunction with other decision-making techniques and a thorough understanding of the business environment.
Marginal Analysis vs. Cost-Benefit Analysis
It’s important to distinguish marginal analysis from cost-benefit analysis. While both methods involve comparing costs and benefits, they differ in their scope and focus. Cost-benefit analysis typically looks at the overall costs and benefits of a project or decision, while marginal analysis focuses on the incremental costs and benefits of small changes.
Cost-benefit analysis is often used for large-scale projects with significant upfront investments, such as building a new factory or launching a new product line. Marginal analysis, on the other hand, is more suitable for day-to-day operational decisions, such as adjusting production levels or pricing strategies. Both techniques can be valuable tools for decision-making, but they should be used in different contexts. Understanding que es analisis marginal helps to differentiate it from other analysis methods.
How to Perform a Marginal Analysis
Performing a marginal analysis involves a structured approach. Here are the steps:
- Define the Decision: Clearly identify the decision you’re trying to make.
- Identify Costs: Determine all relevant costs associated with the decision.
- Identify Benefits: Determine all relevant benefits associated with the decision.
- Quantify Costs and Benefits: Assign monetary values to the costs and benefits.
- Calculate Marginal Cost: Determine the additional cost of one more unit.
- Calculate Marginal Revenue/Benefit: Determine the additional revenue or benefit of one more unit.
- Compare Marginal Cost and Marginal Revenue/Benefit: If the marginal revenue/benefit is greater than the marginal cost, proceed with the decision. If not, reconsider.
- Consider Qualitative Factors: Take into account any qualitative factors that may not be easily quantifiable.
- Make a Decision: Based on the analysis, make an informed decision.
- Monitor Results: Track the results of your decision and make adjustments as needed.
By following these steps, you can conduct a thorough marginal analysis and make more informed decisions. Remember, a key part of que es analisis marginal involves constant monitoring and adjustment.
Real-World Examples of Marginal Analysis
Let’s look at a few real-world examples of how marginal analysis is used in practice:
- Airline Pricing: Airlines use marginal analysis to determine the optimal price for each seat on a flight. They consider the marginal cost of filling an empty seat (which is very low) and the potential marginal revenue from selling that seat.
- Retail Inventory: Retailers use marginal analysis to determine the optimal level of inventory to hold. They consider the marginal cost of holding additional inventory (storage costs, spoilage) and the potential marginal revenue from selling that inventory.
- Restaurant Menu Pricing: Restaurants use marginal analysis to set prices for their menu items. They consider the marginal cost of preparing each dish (ingredients, labor) and the potential marginal revenue from selling that dish.
These examples illustrate how marginal analysis can be applied in a variety of industries to make informed decisions about pricing, production, and inventory management. Understanding que es analisis marginal is key for making these decisions.
Conclusion
Marginal analysis is a powerful tool for making informed decisions in economics and business. By carefully considering the marginal costs and marginal benefits of different options, individuals and organizations can make choices that lead to better outcomes. While it has limitations, when used appropriately and in conjunction with other decision-making techniques, marginal analysis can significantly improve profitability, efficiency, and resource allocation. Understanding que es analisis marginal is essential for anyone seeking to make sound economic decisions.
From production levels to pricing strategies, the application of marginal analysis provides a structured framework for evaluating choices, ultimately leading to more informed and profitable outcomes. So, the next time you’re faced with a decision, remember to ask yourself: what are the marginal costs and benefits? Answering this question can help you make the best possible choice. The essence of que es analisis marginal lies in this simple yet powerful question.
[See also: Cost-Benefit Analysis: A Practical Guide]
[See also: Understanding Economic Principles]
