Why is GBP Falling? Understanding the Pound’s Recent Weakness
The British Pound (GBP), also known as Sterling, has experienced significant volatility in recent times, prompting widespread concern and speculation. Understanding why is GBP falling requires a multi-faceted approach, considering economic indicators, political events, and global market dynamics. This article delves into the key factors contributing to the pound’s recent weakness, providing a comprehensive analysis for those seeking clarity on this crucial economic issue.
Economic Factors Influencing GBP’s Decline
Several fundamental economic factors are exerting downward pressure on the British Pound. These include:
Inflation and Cost of Living Crisis
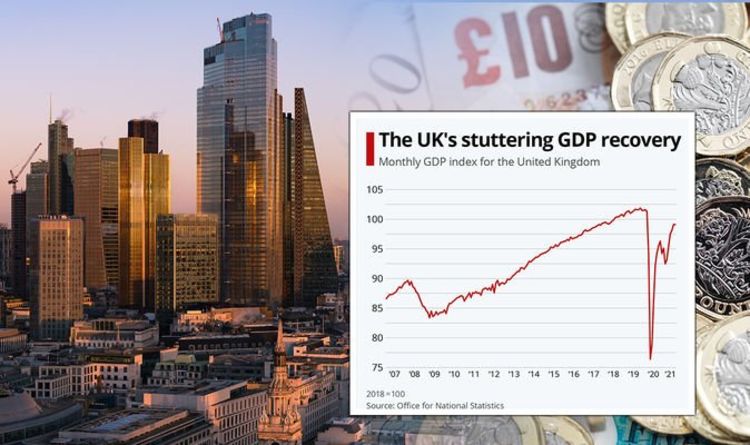
The United Kingdom is grappling with persistently high inflation, significantly exceeding targets set by the Bank of England (BoE). This cost of living crisis erodes consumer spending power and weakens the overall economy. The high inflation rate necessitates aggressive monetary policy responses, such as interest rate hikes, which, while intended to curb inflation, can also dampen economic growth and negatively impact the GBP.
Recessionary Fears
Concerns about a potential recession loom large over the UK economy. High energy prices, supply chain disruptions, and weakened global demand contribute to this pessimistic outlook. A recession would further weaken the GBP as investors typically move their capital to safer havens during periods of economic uncertainty. The prospect of lower economic output and reduced corporate earnings makes the UK a less attractive investment destination, thus impacting the GBP negatively.
Trade Deficit
The UK’s trade deficit, where imports exceed exports, puts downward pressure on the GBP. A persistent trade deficit implies that more pounds are being sold to purchase foreign goods and services than are being bought by foreigners purchasing UK goods and services. This imbalance in supply and demand contributes to the weakening of the GBP. Addressing this trade deficit is crucial for stabilizing the currency.
Government Debt Levels
High levels of government debt can also contribute to the weakening of the GBP. Investors may become concerned about the government’s ability to repay its debts, leading to a loss of confidence in the currency. Fiscal policies and debt management strategies play a vital role in maintaining investor confidence and supporting the GBP.
Political Instability and GBP Volatility
Political uncertainty has consistently been a significant driver of GBP volatility. Recent political events have amplified these concerns:
Brexit Aftermath
The long-term economic consequences of Brexit continue to weigh on the GBP. Trade barriers with the European Union, labor shortages, and regulatory divergence have all contributed to economic uncertainty. The ongoing adjustments to the post-Brexit landscape impact investor sentiment and the overall strength of the GBP. [See also: Impact of Brexit on the UK Economy]
Political Leadership Changes
Frequent changes in political leadership can create instability and undermine investor confidence. Policy uncertainty and shifts in government priorities can lead to market volatility and negatively affect the GBP. A stable and predictable political environment is essential for fostering investor confidence and supporting the currency.
Geopolitical Risks
Global geopolitical risks, such as the war in Ukraine, also impact the GBP. Increased uncertainty and risk aversion can lead investors to seek safer currencies, such as the US dollar, at the expense of the GBP. These external shocks can exacerbate existing economic vulnerabilities and further weaken the pound.
Global Market Dynamics and GBP Performance
The performance of the GBP is also influenced by global market trends and the relative strength of other currencies:
US Dollar Strength
The strength of the US dollar (USD) often has an inverse relationship with the GBP. When the USD strengthens, the GBP tends to weaken. This is because the USD is considered a safe-haven currency, and investors often flock to it during times of economic uncertainty. The US Federal Reserve’s monetary policy decisions also play a significant role in the relative strength of the USD and, consequently, the GBP.
Interest Rate Differentials
Interest rate differentials between the UK and other major economies, such as the United States and the Eurozone, can influence currency flows. If the UK offers lower interest rates compared to other countries, investors may move their capital to those countries, putting downward pressure on the GBP. Central bank policies and their impact on interest rates are crucial factors in determining currency valuations. [See also: Central Bank Interest Rate Policies]
Global Economic Growth
Slower global economic growth can negatively impact the GBP. As global demand weakens, UK exports may decline, further exacerbating the trade deficit and putting downward pressure on the currency. The interconnectedness of the global economy means that events in other countries can have significant repercussions for the GBP.
Bank of England’s Response
The Bank of England (BoE) plays a critical role in managing inflation and stabilizing the GBP. The BoE’s monetary policy decisions, such as interest rate adjustments and quantitative easing, can have a significant impact on the currency. However, the effectiveness of these policies is often debated, and their impact can be influenced by various external factors.
Interest Rate Hikes
The BoE has been raising interest rates in an attempt to combat inflation. While higher interest rates can attract foreign investment and support the GBP, they can also dampen economic growth and potentially trigger a recession. The BoE faces a delicate balancing act in trying to control inflation without causing undue harm to the economy. The impact of interest rate hikes on the GBP is complex and can vary depending on market conditions.
Quantitative Tightening
The BoE is also engaged in quantitative tightening, which involves reducing the size of its balance sheet by selling government bonds. This policy is intended to reduce liquidity in the financial system and put upward pressure on interest rates. However, quantitative tightening can also have negative consequences, such as increasing borrowing costs and potentially slowing economic growth. The effectiveness of this policy in supporting the GBP is subject to ongoing debate.
Future Outlook for the GBP
Predicting the future performance of the GBP is challenging, as it depends on a complex interplay of economic, political, and global factors. However, several key trends are likely to influence the currency’s trajectory:
Inflation Trajectory
The future path of inflation will be a crucial determinant of the GBP‘s performance. If inflation remains persistently high, the BoE may need to implement further interest rate hikes, which could support the currency but also risk triggering a recession. Conversely, if inflation begins to moderate, the BoE may be able to ease monetary policy, which could boost economic growth but potentially weaken the GBP.
Economic Growth Prospects
The UK’s economic growth prospects will also play a significant role in shaping the GBP‘s future. A strong and sustainable economic recovery would likely support the currency, while a prolonged recession would likely weigh on it. Government policies aimed at promoting economic growth, such as tax cuts and infrastructure investments, could have a positive impact on the GBP.
Political Stability
Greater political stability and policy certainty would be beneficial for the GBP. A stable political environment would help to restore investor confidence and reduce market volatility. Government efforts to address the long-term economic consequences of Brexit and to forge new trade agreements could also support the currency.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding why is GBP falling requires a comprehensive analysis of economic fundamentals, political events, and global market dynamics. High inflation, recessionary fears, Brexit-related uncertainties, and a strong US dollar are all contributing factors. The Bank of England’s monetary policy responses and the UK’s economic growth prospects will be crucial in determining the future trajectory of the GBP. Monitoring these factors closely is essential for anyone seeking to understand the pound’s recent weakness and its potential future performance. The GBP‘s value is intrinsically linked to the UK’s economic health and stability, making it a key indicator for investors and policymakers alike. Further declines in the GBP could have significant implications for the UK economy, impacting everything from import prices to investment flows. Therefore, understanding the underlying causes of the GBP‘s weakness is paramount for navigating the current economic landscape.
